
Lectures 6-7
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
Lectures 10-11
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
Lectures 10-11
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
... Thus, if we’re willing to accept more uncertainty about an electron’s momentum, we can have more certainty in knowing its position – and vice versa. This inverse relationship can be ...
Lectures 7-9 - U of L Class Index
... particles of matter can also behave as waves. Thus, his equation is not limited to electromagnetic radiation. In 1927, this was demonstrated by two separate experiments. Americans C.J. Davisson and L.H. Germer diffracted a beam of electrons through a nickel crystal, and Scot G.P. Thompson diffracted ...
... particles of matter can also behave as waves. Thus, his equation is not limited to electromagnetic radiation. In 1927, this was demonstrated by two separate experiments. Americans C.J. Davisson and L.H. Germer diffracted a beam of electrons through a nickel crystal, and Scot G.P. Thompson diffracted ...
Lectures 7-9
... particles of matter can also behave as waves. Thus, his equation is not limited to electromagnetic radiation. In 1927, this was demonstrated by two separate experiments. Americans C.J. Davisson and L.H. Germer diffracted a beam of electrons through a nickel crystal, and Scot G.P. Thompson diffracted ...
... particles of matter can also behave as waves. Thus, his equation is not limited to electromagnetic radiation. In 1927, this was demonstrated by two separate experiments. Americans C.J. Davisson and L.H. Germer diffracted a beam of electrons through a nickel crystal, and Scot G.P. Thompson diffracted ...
Quantum Theory 1 - Home Exercise 4
... 4. Particle on a ring - Consider a particle that is free to move on a ring of circumference L, such that ψ(x, t) = ψ(x + L, t) (a) Find the normalized stationary states of the system and explicitly show that they form an orthonormal basis. (b) Calculate the dispersion relation ωn (kn ) and show that ...
... 4. Particle on a ring - Consider a particle that is free to move on a ring of circumference L, such that ψ(x, t) = ψ(x + L, t) (a) Find the normalized stationary states of the system and explicitly show that they form an orthonormal basis. (b) Calculate the dispersion relation ωn (kn ) and show that ...
HOMEWORK ASSIGNMENT 12
... 3. [20 pts] Numerically compute the matrix elements of the z-component of the orbital electric and magnetic dipole moments for the |200i → |100i, |210i → |100i, and |211i → |100i transitions in hydrogen. Be sure to show your work. For the electric dipole moments, we need to compute ehi|Z|f i = ehi| ...
... 3. [20 pts] Numerically compute the matrix elements of the z-component of the orbital electric and magnetic dipole moments for the |200i → |100i, |210i → |100i, and |211i → |100i transitions in hydrogen. Be sure to show your work. For the electric dipole moments, we need to compute ehi|Z|f i = ehi| ...
Outline of Course Topics for Honors Chemistry
... Outline of Course Topics for Honors Chemistry Topics highlighted in red are specific to Honors Chemistry. Honors Chemistry Course Description: This course focuses on matter, its properties, and its changes. During the year, the following topics will be covered: measurement, problem solving, atomic s ...
... Outline of Course Topics for Honors Chemistry Topics highlighted in red are specific to Honors Chemistry. Honors Chemistry Course Description: This course focuses on matter, its properties, and its changes. During the year, the following topics will be covered: measurement, problem solving, atomic s ...
File
... want and don't worry whether the measurement itself has changed what they were measuring. After all, what would be the sense in determining that a table is 80 cm long if the very act of measuring it changed its length! At the atomic scale of quantum mechanics, however, measurement becomes a very del ...
... want and don't worry whether the measurement itself has changed what they were measuring. After all, what would be the sense in determining that a table is 80 cm long if the very act of measuring it changed its length! At the atomic scale of quantum mechanics, however, measurement becomes a very del ...
atomic structure sm
... from the view of the outer electrons. The outermost electrons in effect see a charge that is less that the actual charge on the nucleus, Z. ...
... from the view of the outer electrons. The outermost electrons in effect see a charge that is less that the actual charge on the nucleus, Z. ...
L 33 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics
... • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose all of its energy and collapse into the nucleus. • Classically, there could be no atoms! ...
... • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose all of its energy and collapse into the nucleus. • Classically, there could be no atoms! ...
L 34 Modern Physics [1]
... • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose all of its energy and collapse into the nucleus. • Classically, there could be no atoms! ...
... • However, the laws of mechanics and electromagnetism predict that an orbiting electron should continually radiate electromagnetic waves, and very quickly the electron would loose all of its energy and collapse into the nucleus. • Classically, there could be no atoms! ...
Exam #: Printed Name: Signature: PHYSICS DEPARTMENT
... Here ω is a parameter that describes the strength of the potential. (a) Choose a convenient scheme for labeling the energy eigenstates of this system. Using your scheme, write the energy eigenvalues as a function of the quantum numbers of the states. If you are familiar with the solutions of the Sch ...
... Here ω is a parameter that describes the strength of the potential. (a) Choose a convenient scheme for labeling the energy eigenstates of this system. Using your scheme, write the energy eigenvalues as a function of the quantum numbers of the states. If you are familiar with the solutions of the Sch ...
Problems
... (in terms of the property of the central atom or ion) do we do the calculation with fixed volume? ...
... (in terms of the property of the central atom or ion) do we do the calculation with fixed volume? ...
Some Quantum Considerations II
... n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 1, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +½. ...
... n = 1, l = 0, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 3, l = 2, ml = -2, ms = -½. n = 2, l = 1, ml = 0, ms = +½. n = 1, l = 1, ml = 1, ms = +½. ...













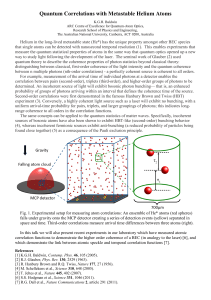


![L 33 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003217156_1-265c5a519e2bca3f33717b4abd842898-300x300.png)


![L 34 Modern Physics [1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008622077_1-047a8df5b8f51427a7d951942e25e95f-300x300.png)



