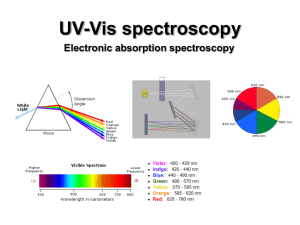
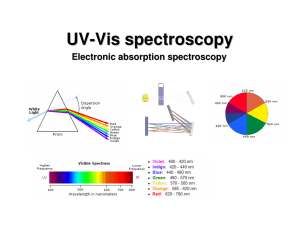
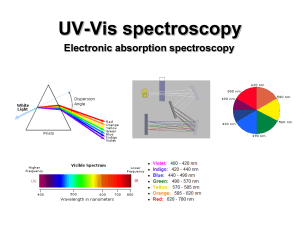
PHYSICAL MEANING OF IMAGINARY UNIT i
... Fig. 1. Distribution of domains of maxima of the wave function modulus ̂ at l =1 and m=0 in a spherical space-field of the hydrogen atom; a) Yˆl ,m (, ) is the surface of the modulus of the polar-azimuth factor of the wave function, describes a surface shaped like a dumbbell; s1 and s2 (b) are do ...
... Fig. 1. Distribution of domains of maxima of the wave function modulus ̂ at l =1 and m=0 in a spherical space-field of the hydrogen atom; a) Yˆl ,m (, ) is the surface of the modulus of the polar-azimuth factor of the wave function, describes a surface shaped like a dumbbell; s1 and s2 (b) are do ...
Relativity Problem Set 9 - Solutions Prof. J. Gerton October 23, 2011
... In quantum mechanics instead, the wave function extends in the classically forbidden region as well, so there is a certain probability to find the particle in this region. This phenomenon is peculiar of quantum mechanics, and gives rise to cute effects like the quantum tunneling, which explains the ...
... In quantum mechanics instead, the wave function extends in the classically forbidden region as well, so there is a certain probability to find the particle in this region. This phenomenon is peculiar of quantum mechanics, and gives rise to cute effects like the quantum tunneling, which explains the ...
Spin-Orbit Interaction - diss.fu
... functions . In a free atom without SOC, there are three degenerate p functions, so three p bands will appear in the model . These bands will all be degenerate at the Γ point (k = 0, see Fig. 8.1(a)), transforming one into the other through cubic symmetry transformations at this point. Each of the th ...
... functions . In a free atom without SOC, there are three degenerate p functions, so three p bands will appear in the model . These bands will all be degenerate at the Γ point (k = 0, see Fig. 8.1(a)), transforming one into the other through cubic symmetry transformations at this point. Each of the th ...
Some Success Applications for Local
... This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY). http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ...
... This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution International License (CC BY). http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ...
Chemistry Quarter 1 Module
... Students often ask, “Why did Rutherford use gold foil?” The most common response is that gold is soft and malleable and can be made into very thin sheets of foil. There is another reason, which you can discover for yourself. 1. Turn off the phosphor detection screen. Double-click the base of the met ...
... Students often ask, “Why did Rutherford use gold foil?” The most common response is that gold is soft and malleable and can be made into very thin sheets of foil. There is another reason, which you can discover for yourself. 1. Turn off the phosphor detection screen. Double-click the base of the met ...
Hydrogen Atom
... The functions have names that are based on there shape. The shape comes predominately from the angular part and mostly from l. Thus the names depend on l. l=0 is S, l=1 is P, l=2 is D, l=3 if F, l=4 is G, …. What do the radial functions look like? Mostly they are an exponential decay multiplied by ...
... The functions have names that are based on there shape. The shape comes predominately from the angular part and mostly from l. Thus the names depend on l. l=0 is S, l=1 is P, l=2 is D, l=3 if F, l=4 is G, …. What do the radial functions look like? Mostly they are an exponential decay multiplied by ...
Quantum and Photo-electric effects - Delivery guide
... particle is influenced in some way, but does not have to actually have physical contact. ...
... particle is influenced in some way, but does not have to actually have physical contact. ...
Chapter 40
... produced. These wavelengths are labeled K and K. What does the letter “K” indicate in this notation? a) The characteristic lines involve the n = 1 shell of the molybdenum atoms. b) The K stands for “klystron,” which is the radiation generator. c) The characteristic lines involve the electrons at t ...
... produced. These wavelengths are labeled K and K. What does the letter “K” indicate in this notation? a) The characteristic lines involve the n = 1 shell of the molybdenum atoms. b) The K stands for “klystron,” which is the radiation generator. c) The characteristic lines involve the electrons at t ...
Parametric evolution of eigenstates: Beyond perturbation theory and
... electric field, magnetic flux, gate voltage兲 or a change of an effective interaction 共as in molecular dynamics兲. Thus, these studies are relevant for diverse areas of physics ranging from nuclear 关1,2兴 and atomic physics 关3,4兴 to quantum chaos 关5–8兴 and mesoscopics 关9,10兴. Up to now the majority of ...
... electric field, magnetic flux, gate voltage兲 or a change of an effective interaction 共as in molecular dynamics兲. Thus, these studies are relevant for diverse areas of physics ranging from nuclear 关1,2兴 and atomic physics 关3,4兴 to quantum chaos 关5–8兴 and mesoscopics 关9,10兴. Up to now the majority of ...