Chapter 4 (Lecture 6-7) Schrodinger equation for some simple
... The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a heavy box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than ano ...
... The model is mainly used as a hypothetical example to illustrate the differences between classical and quantum systems. In classical systems, for example a ball trapped inside a heavy box, the particle can move at any speed within the box and it is no more likely to be found at one position than ano ...
Document
... In order to see the electron, at least one photon must bounce off it During this interaction, momentum is transferred from the photon to the electron Therefore, the light that allows you to accurately locate the electron changes the momentum of the electron ...
... In order to see the electron, at least one photon must bounce off it During this interaction, momentum is transferred from the photon to the electron Therefore, the light that allows you to accurately locate the electron changes the momentum of the electron ...
Slide 1
... http://ocw.mit.edu/NR/rdonlyres/Electrical-Engineering-and-Computer-Science/6730Physics-for-Solid-State-ApplicationsSpring2003/8A2B76D2-7D99-445BB511-EDFA06C0482B/0/lecture12c.pdf ...
... http://ocw.mit.edu/NR/rdonlyres/Electrical-Engineering-and-Computer-Science/6730Physics-for-Solid-State-ApplicationsSpring2003/8A2B76D2-7D99-445BB511-EDFA06C0482B/0/lecture12c.pdf ...
The Electronic Spectra of Coordination Compounds
... t2g set of orbitals to the eg set can involve differing changes in environment, several peaks will be seen in the spectrum. Three peaks are predicted, and often observed. One of the peaks is sometimes obscured by an intense charge transfer band. ...
... t2g set of orbitals to the eg set can involve differing changes in environment, several peaks will be seen in the spectrum. Three peaks are predicted, and often observed. One of the peaks is sometimes obscured by an intense charge transfer band. ...
AtomsFirst2e_day6_sec3.7
... Sections 3.7-3.8 quantum numbers, orbitals, Pauli exclusion principle DAY 6, Specific outcomes and skills that may be tested on exam 1: Sections 3.7-3.8 •Given a set of quantum numbers, be able to describe the energy level, subshell (s, p, d, or f), and spin state for an electron •Given information ...
... Sections 3.7-3.8 quantum numbers, orbitals, Pauli exclusion principle DAY 6, Specific outcomes and skills that may be tested on exam 1: Sections 3.7-3.8 •Given a set of quantum numbers, be able to describe the energy level, subshell (s, p, d, or f), and spin state for an electron •Given information ...
Course Syllabus Course Number and Name: CHM:160 Chemistry I
... At the end of this unit, the student will be able to: 1. Define and explain the basic concepts of thermochemistry: state properties, sign convention for heat flow, heat capacity and specific heat, and heat flow in reactions. 2. Describe the techniques and principles of calorimetry, including the sim ...
... At the end of this unit, the student will be able to: 1. Define and explain the basic concepts of thermochemistry: state properties, sign convention for heat flow, heat capacity and specific heat, and heat flow in reactions. 2. Describe the techniques and principles of calorimetry, including the sim ...
Recitation on atomic structure Solution
... act on the electron over its entire trajectory from source to detector. The combined electric and magnetic fields act as a velocity selector, only passing electrons with speed v, where v = V /Bd, while in the region where there is only a magnetic field the electron moves in a circle of radius r, with ...
... act on the electron over its entire trajectory from source to detector. The combined electric and magnetic fields act as a velocity selector, only passing electrons with speed v, where v = V /Bd, while in the region where there is only a magnetic field the electron moves in a circle of radius r, with ...
Part 2: Quantum theory of light
... Q8. What is the photoelectric effect? Shortly after J.J. Thompson's experiments led to the identification of the elementary charged particles we now know as electrons, it was discovered that the illumination of a metallic surface by light can cause electrons to be emitted from the surface. This ph ...
... Q8. What is the photoelectric effect? Shortly after J.J. Thompson's experiments led to the identification of the elementary charged particles we now know as electrons, it was discovered that the illumination of a metallic surface by light can cause electrons to be emitted from the surface. This ph ...
Quantum Fusion Hypothesis Abstract
... Part of the problem for established physics is that their information is based on big science accelerator experiments. This led to a policy at the National Nuclear Data Center (NNDC) that defines the “ground state” of a nucleus as the “lowest energy at which it has been observed”. The first three l ...
... Part of the problem for established physics is that their information is based on big science accelerator experiments. This led to a policy at the National Nuclear Data Center (NNDC) that defines the “ground state” of a nucleus as the “lowest energy at which it has been observed”. The first three l ...
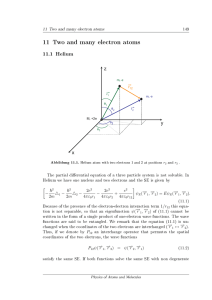
11 Two and many electron atoms - FU Berlin
... If one of the two electrons in helium is not in its ground state but in a higher orbital, we nd the energy of the excited state in zero order perturbation to be µ ...
... If one of the two electrons in helium is not in its ground state but in a higher orbital, we nd the energy of the excited state in zero order perturbation to be µ ...
1. (a) state Law of multiple proportion (2) (b) A compound contains
... In an examination one student wrote that ‘Real gases be have ideally at low temperature and high pressure. (i) Is the above statement correct or not? (ii) Why do real gases deviate from ideality? (iii) Write Vander waal’s equation for ‘n’ moles of an ideal gas. ...
... In an examination one student wrote that ‘Real gases be have ideally at low temperature and high pressure. (i) Is the above statement correct or not? (ii) Why do real gases deviate from ideality? (iii) Write Vander waal’s equation for ‘n’ moles of an ideal gas. ...
Your Paper`s Title Starts Here:
... d 2 ( z ) 1,8 108 me kT ln exp F Een 1 en z 2 ...
... d 2 ( z ) 1,8 108 me kT ln exp F Een 1 en z 2 ...
Document
... Surprise: In the early 20th century, it was discovered that light has particle-like properties (e.g., localized lumps of energy) in some situations! Furthermore, matter exhibits wave-like properties (e.g., electrons, protons, etc.) under certain circumstances. It may seem surprising that an entity m ...
... Surprise: In the early 20th century, it was discovered that light has particle-like properties (e.g., localized lumps of energy) in some situations! Furthermore, matter exhibits wave-like properties (e.g., electrons, protons, etc.) under certain circumstances. It may seem surprising that an entity m ...
CH 27 – Quantum Physics
... One of the important applications of x-rays is in analyzing the structure of materials. In crystal diffraction, monochromatic x-rays are diffracted from a crystal lattice. The diffracted intensity is a maximum at angles that depend on the wavelength, the types of atoms in the crystal, and their atom ...
... One of the important applications of x-rays is in analyzing the structure of materials. In crystal diffraction, monochromatic x-rays are diffracted from a crystal lattice. The diffracted intensity is a maximum at angles that depend on the wavelength, the types of atoms in the crystal, and their atom ...
Lecture XV
... • Quantum mechanics acknowledges the waveparticle duality of matter by supposing that, rather than traveling along a definite path, a particle is distributed through space like a wave. The wave that in quantum mechanics replaces the classical concept of particle trajectory is called a wavefunction, ...
... • Quantum mechanics acknowledges the waveparticle duality of matter by supposing that, rather than traveling along a definite path, a particle is distributed through space like a wave. The wave that in quantum mechanics replaces the classical concept of particle trajectory is called a wavefunction, ...
2 is
... = 3 : ml = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3 ms = ½ , -½ 2 states l = 4 : ml = -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4 ms = ½ , -½ 2 states ...
... = 3 : ml = -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3 ms = ½ , -½ 2 states l = 4 : ml = -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, +1, +2, +3, +4 ms = ½ , -½ 2 states ...
The multiscale modeling techniques I will discuss below are
... Modelers of nanoscale solids need to use these multiscale methods—the coupling together of different levels of description—because each individual theoretical framework is inadequate on its own at the scale in question. The traditional theoretical framework for studying the mechanical behavior of so ...
... Modelers of nanoscale solids need to use these multiscale methods—the coupling together of different levels of description—because each individual theoretical framework is inadequate on its own at the scale in question. The traditional theoretical framework for studying the mechanical behavior of so ...