msc_f_p1b2 - Bhoj University
... Here we have expressed vectors r, p and L in their components along the Cartesian axes. We have also used the orthogonal properties of vectors viz., i x i = j x j = k x k = 0 ; i x j = k, j x k = i, k x i = j and j x i= - k etc. Let us concentrate on the z-component of angular momentum (equating coe ...
... Here we have expressed vectors r, p and L in their components along the Cartesian axes. We have also used the orthogonal properties of vectors viz., i x i = j x j = k x k = 0 ; i x j = k, j x k = i, k x i = j and j x i= - k etc. Let us concentrate on the z-component of angular momentum (equating coe ...
AS Unit 1 –January 2010 –Solutions and feedback
... State, with a reason, what interaction is responsible for this decay. The weak interaction (1 mark). This can be deduced because strangeness is not conserved or there is a change/decay of quark (flavour) (1 mark) (ii) State two properties, other than energy and momentum, that are conserved in this d ...
... State, with a reason, what interaction is responsible for this decay. The weak interaction (1 mark). This can be deduced because strangeness is not conserved or there is a change/decay of quark (flavour) (1 mark) (ii) State two properties, other than energy and momentum, that are conserved in this d ...
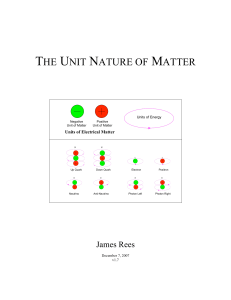
the unit nature of matter - Starlight Publishing Company
... - doublet substructures have no internal structural energy (no rest mass) - neutrinos are doublet substructures with one set of momentum energy - photons are doublet substructures with two sets of momentum energy - there must exist many doublet substructures which have no momentum energy - bosons ha ...
... - doublet substructures have no internal structural energy (no rest mass) - neutrinos are doublet substructures with one set of momentum energy - photons are doublet substructures with two sets of momentum energy - there must exist many doublet substructures which have no momentum energy - bosons ha ...
The Free Particle (PowerPoint)
... The dual nature of matter (Quick Time movie 9 MB from Wilson group, *** ) Linear polarized light ( a wave function in 1-D would propagate in a similar way) (1 MB Quick time movie from the Wilson Group, *****) Circular polarized light ( ( a wave function could propagate in a similar way) (6 MB Quick ...
... The dual nature of matter (Quick Time movie 9 MB from Wilson group, *** ) Linear polarized light ( a wave function in 1-D would propagate in a similar way) (1 MB Quick time movie from the Wilson Group, *****) Circular polarized light ( ( a wave function could propagate in a similar way) (6 MB Quick ...
the radiation belts - The Scientific Satellite Data Exchange Network
... the earth's radiation belts have now been successfully described in terms of adiabatic invariants and their perturbation. ...
... the earth's radiation belts have now been successfully described in terms of adiabatic invariants and their perturbation. ...
Neutrino Mass and Direct Measurements
... otherwise cannot be observed as the weak interaction doesn’t couple to it, or there is some other sort of mass term out there. By definition Dirac particles come in four distinct types : left- and right-handed particles, and leftand right-handed antiparticles, and are therefore represented by a 4-c ...
... otherwise cannot be observed as the weak interaction doesn’t couple to it, or there is some other sort of mass term out there. By definition Dirac particles come in four distinct types : left- and right-handed particles, and leftand right-handed antiparticles, and are therefore represented by a 4-c ...
Tasevsky_RECFA_270315
... (BIS, LUDMILA, RISK, BCDMS, UA4/2, NA57, WA94, WA97, H1, DELPHI, OPAL, D0, …) H1 and D0 finished but still a few PhD theses being completed these days A massive orientation to CERN: CMS, TOTEM, COMPASS, MOEDAL, NA62, OSQAR, AEGIS, DIRAC ...
... (BIS, LUDMILA, RISK, BCDMS, UA4/2, NA57, WA94, WA97, H1, DELPHI, OPAL, D0, …) H1 and D0 finished but still a few PhD theses being completed these days A massive orientation to CERN: CMS, TOTEM, COMPASS, MOEDAL, NA62, OSQAR, AEGIS, DIRAC ...
- Philsci
... neutron, e.g., mass and magnetic moment, cannot straightforwardly be regarded as localized at the hypothetical position of the particle in Bohm’s theory. They also argued that it is hard to understand how the Aharonov-Bohm effect is possible if that the charge of the electron which couples with the ...
... neutron, e.g., mass and magnetic moment, cannot straightforwardly be regarded as localized at the hypothetical position of the particle in Bohm’s theory. They also argued that it is hard to understand how the Aharonov-Bohm effect is possible if that the charge of the electron which couples with the ...
Quantum Mechanics- wave function
... developing "matrix mechanics". Schrödinger subsequently showed that the two approaches were equivalent.[2] In each case, the wave function was at the centre of attention in two forms, giving quantum mechanics its unity. In 1905 Planck postulated the proportionality between the frequency of a photon ...
... developing "matrix mechanics". Schrödinger subsequently showed that the two approaches were equivalent.[2] In each case, the wave function was at the centre of attention in two forms, giving quantum mechanics its unity. In 1905 Planck postulated the proportionality between the frequency of a photon ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... implies that the particle moves on a curve: the position of the particle is determined by a single parameter, corresponding to a single degree of freedom. In general, each geometric bilateral constraint applied to a system reduces its number of degrees of freedom by one. Note that the coordinates of ...
... implies that the particle moves on a curve: the position of the particle is determined by a single parameter, corresponding to a single degree of freedom. In general, each geometric bilateral constraint applied to a system reduces its number of degrees of freedom by one. Note that the coordinates of ...
Chapter 20 - Solutions
... charges creates an electric field that can be found by taking the vector sum of the fields created by individual point charges. Note that if a charge q is placed in an electric field created by q’ , q will not significantly affect the electric field if it is small compared to q’. Imagine an isolated ...
... charges creates an electric field that can be found by taking the vector sum of the fields created by individual point charges. Note that if a charge q is placed in an electric field created by q’ , q will not significantly affect the electric field if it is small compared to q’. Imagine an isolated ...
Honors Physics Electric Potential Energy and Potential Difference
... 6. An electric field is created by a Van de Graaf generator. A test charge of (q) is placed in the field at a distance r. a) If the test charge has a magnitude of +1q write an expression for i) the potential energy between the charges ii) the potential of the system b) if the test charge has a magni ...
... 6. An electric field is created by a Van de Graaf generator. A test charge of (q) is placed in the field at a distance r. a) If the test charge has a magnitude of +1q write an expression for i) the potential energy between the charges ii) the potential of the system b) if the test charge has a magni ...
Derivation of the Equation E=mc2-v3
... remark that I derived Einstein's equation without using the above law. So I have also proved that this law, along with the other above mentioned laws, are sufficient but not necessary to derive the famous formula of equivalence of mass and energy. One point that could be criticized is that this rese ...
... remark that I derived Einstein's equation without using the above law. So I have also proved that this law, along with the other above mentioned laws, are sufficient but not necessary to derive the famous formula of equivalence of mass and energy. One point that could be criticized is that this rese ...
The Solar Flare: A Strongly Turbulent Particle Accelerator
... the microscopic plasma physics of particle acceleration. The global environment for particle acceleration is created by MHD, but there is a feedback, with the MHD affected by the nature of the turbulent transport coefficients”. We draw attention in particular to the word “feedback”: the fundamental ...
... the microscopic plasma physics of particle acceleration. The global environment for particle acceleration is created by MHD, but there is a feedback, with the MHD affected by the nature of the turbulent transport coefficients”. We draw attention in particular to the word “feedback”: the fundamental ...
EE 5340©
... • The symm. of the crystal struct. gives “allowed” and “forbidden” energies (sim to pass- and stop-band) • The curvature at band-edge (where k = (n+1)p) gives an “effective” mass. ©L02 Aug 28 ...
... • The symm. of the crystal struct. gives “allowed” and “forbidden” energies (sim to pass- and stop-band) • The curvature at band-edge (where k = (n+1)p) gives an “effective” mass. ©L02 Aug 28 ...
Elementary particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a particle whose substructure is unknown, thus it is unknown whether it is composed of other particles. Known elementary particles include the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons), which generally are ""matter particles"" and ""antimatter particles"", as well as the fundamental bosons (gauge bosons and Higgs boson), which generally are ""force particles"" that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle.Everyday matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be matter's elementary particles—atom meaning ""indivisible"" in Greek—although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1910, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Soon, subatomic constituents of the atom were identified. As the 1930s opened, the electron and the proton had been observed, along with the photon, the particle of electromagnetic radiation. At that time, the recent advent of quantum mechanics was radically altering the conception of particles, as a single particle could seemingly span a field as would a wave, a paradox still eluding satisfactory explanation.Via quantum theory, protons and neutrons were found to contain quarks—up quarks and down quarks—now considered elementary particles. And within a molecule, the electron's three degrees of freedom (charge, spin, orbital) can separate via wavefunction into three quasiparticles (holon, spinon, orbiton). Yet a free electron—which, not orbiting an atomic nucleus, lacks orbital motion—appears unsplittable and remains regarded as an elementary particle.Around 1980, an elementary particle's status as indeed elementary—an ultimate constituent of substance—was mostly discarded for a more practical outlook, embodied in particle physics' Standard Model, science's most experimentally successful theory. Many elaborations upon and theories beyond the Standard Model, including the extremely popular supersymmetry, double the number of elementary particles by hypothesizing that each known particle associates with a ""shadow"" partner far more massive, although all such superpartners remain undiscovered. Meanwhile, an elementary boson mediating gravitation—the graviton—remains hypothetical.