File - Ms. D. Science CGPA
... ROCK SALT- made from the mineral halite which forms by evaporation. ...
... ROCK SALT- made from the mineral halite which forms by evaporation. ...
DIGGING INTO EARTH`S PAST
... This unit focuses on the formation of rocks and fossils in order to determine what conditions were present on Earth during their formation. Although many rocks look the same, different rocks can have very different compositions. All rocks begin as magma within the Earth. Geologists classify all rock ...
... This unit focuses on the formation of rocks and fossils in order to determine what conditions were present on Earth during their formation. Although many rocks look the same, different rocks can have very different compositions. All rocks begin as magma within the Earth. Geologists classify all rock ...
Igneous rocks - HEDCen Science
... • consists primarily of: • elements found in silicate minerals • gases (volatiles, water vapor) – confined within the magma by surrounding rocks • volatile = substance that occurs as gas at Earth’s surface temperature and pressure ...
... • consists primarily of: • elements found in silicate minerals • gases (volatiles, water vapor) – confined within the magma by surrounding rocks • volatile = substance that occurs as gas at Earth’s surface temperature and pressure ...
Field Guide Local Geology Review
... consistent and doesn’t have to travel through thick crust (oceanic crust is very thin ~ 5 km). Such settings include spreading centers, ocean-ocean subduction zones, and oceanic hotspots. Wherever basalt erupts, underneath the surface some of that same magma is trapped and cools slowly to form the i ...
... consistent and doesn’t have to travel through thick crust (oceanic crust is very thin ~ 5 km). Such settings include spreading centers, ocean-ocean subduction zones, and oceanic hotspots. Wherever basalt erupts, underneath the surface some of that same magma is trapped and cools slowly to form the i ...
Textures of Metamorphic Rock
... collide with each other, regional metamorphism occurs. The increased pressure and temperature causes rock to become deformed and chemically changes. Regional metamorphism occurs over thousands of cubic kilometers deep within the Earth’s crust. Rocks that have undergone regional metamorphism are foun ...
... collide with each other, regional metamorphism occurs. The increased pressure and temperature causes rock to become deformed and chemically changes. Regional metamorphism occurs over thousands of cubic kilometers deep within the Earth’s crust. Rocks that have undergone regional metamorphism are foun ...
Canada`s Landform Regions
... wall of rock • There are an obstacle to transportation • There are very few passes or gaps for roads through the mountains • Glaciers in the mountains helped to form valleys and lakes ...
... wall of rock • There are an obstacle to transportation • There are very few passes or gaps for roads through the mountains • Glaciers in the mountains helped to form valleys and lakes ...
mafic and ultmmafic rock associations in the east arc of
... belts consisting of a hlgh-pressure on the ocean side and a lowbelt pressure belt on the contlnental side. According to Mitchell and Reading (l-971-) many of the ultramafic rock assoclations ln such high-pressure belt were emplaced as cold lntrrlsions. during metamorphism. of Alpine ultramaflc withi ...
... belts consisting of a hlgh-pressure on the ocean side and a lowbelt pressure belt on the contlnental side. According to Mitchell and Reading (l-971-) many of the ultramafic rock assoclations ln such high-pressure belt were emplaced as cold lntrrlsions. during metamorphism. of Alpine ultramaflc withi ...
Quiz 6
... Ignimbrite- Rock formed when deposits of pyroclactic flows solidify. Lahar- A thick slurry formed when volcanic ash and debris mix with water, either in rivers or from rain or melting snow and ice on the flank of a volcano. lava tube- The empty space left when a lava tunnel drains; this happens when ...
... Ignimbrite- Rock formed when deposits of pyroclactic flows solidify. Lahar- A thick slurry formed when volcanic ash and debris mix with water, either in rivers or from rain or melting snow and ice on the flank of a volcano. lava tube- The empty space left when a lava tunnel drains; this happens when ...
Martian Rocks and Minerals
... Martian breccias are dominantly formed as a result of meteor impacts, although extrusive volcanic breccias also exist. Martian impact breccias form when an extraterrestrial rock impacts the surface of Mars and the rocks on the surface undergo fragmentation. These fragments, or clasts, are ejected fr ...
... Martian breccias are dominantly formed as a result of meteor impacts, although extrusive volcanic breccias also exist. Martian impact breccias form when an extraterrestrial rock impacts the surface of Mars and the rocks on the surface undergo fragmentation. These fragments, or clasts, are ejected fr ...
Distribution of velocities of longitudinal body waves (P waves) in an
... Chemically and mineralogically gabbro is equivalent to basalt. It is only in grain size that it differs from it. Basalt is aphanitic, whereas gabbro is phaneritic. Basalt occurs as lava; gabbro occurs as plutonic rock. So we call gabbros the deepseated equialents of basat. The intermediate grain-siz ...
... Chemically and mineralogically gabbro is equivalent to basalt. It is only in grain size that it differs from it. Basalt is aphanitic, whereas gabbro is phaneritic. Basalt occurs as lava; gabbro occurs as plutonic rock. So we call gabbros the deepseated equialents of basat. The intermediate grain-siz ...
Unit Design
... investigations form a basis for concepts about soil, rocks, water, and air. young learners’ understanding of properties of Earth materials. ...
... investigations form a basis for concepts about soil, rocks, water, and air. young learners’ understanding of properties of Earth materials. ...
Rocks Chapter 4
... resistant to nature’s forces. It can be slowly worn down until bits of granite flake off and fall in streams and are eventually reduced to sand. The sand from granite, along with other sediments is carried to the sea and is deposited on the floor. The weight of layers piling on puts pressure on lowe ...
... resistant to nature’s forces. It can be slowly worn down until bits of granite flake off and fall in streams and are eventually reduced to sand. The sand from granite, along with other sediments is carried to the sea and is deposited on the floor. The weight of layers piling on puts pressure on lowe ...
The Boggulakonda Gabbros, Prakasam District, Andhra Pradesh
... Earthy building material can be defined as ‘any hard or soft material formed by natural processes of magmatism, sedimentation, metamorphism and weathering of rocks over geological time and space’. The products of these processes include igneous rocks (formed from magma and lava including plutonic, h ...
... Earthy building material can be defined as ‘any hard or soft material formed by natural processes of magmatism, sedimentation, metamorphism and weathering of rocks over geological time and space’. The products of these processes include igneous rocks (formed from magma and lava including plutonic, h ...
metamorphic rock - Mr. Meyer`s Science Page
... the shearing effect of the plates sliding past each other causes the rocks coming in contact with the descending rocks to change. Some of the descending rock will melt because of this friction. When rock melts it is then considered igneous not metamorphic, but the rock next to the melted rock ca ...
... the shearing effect of the plates sliding past each other causes the rocks coming in contact with the descending rocks to change. Some of the descending rock will melt because of this friction. When rock melts it is then considered igneous not metamorphic, but the rock next to the melted rock ca ...
Name
... over millions of years; trace fossils are imprints that plants or animals left that changed to solid rock over millions of years. Fossils give information about the once-living things that made them. (Lesson Eight) ...
... over millions of years; trace fossils are imprints that plants or animals left that changed to solid rock over millions of years. Fossils give information about the once-living things that made them. (Lesson Eight) ...
1.Beginning of the Earth
... As the outer skin that covers the world. Is divided into two areas. 1.continental crust Means that the whole earth. Both continents and the continental shelf. The average thickness of 35-40 km, some of the more than 70 kilometers, most of the elements silicon and aluminum. Sometimes called the SIAl ...
... As the outer skin that covers the world. Is divided into two areas. 1.continental crust Means that the whole earth. Both continents and the continental shelf. The average thickness of 35-40 km, some of the more than 70 kilometers, most of the elements silicon and aluminum. Sometimes called the SIAl ...
BUILDING STONES OF THE BROOKLYN COLLEGE CAMPUS
... (e.g., sandstone), and chemical sedimentary rock that form from the precipitation of minerals from solution (e.g., limestone). When grains settle they may form layers, or beds, that may be defined by differences in color or grain size (see Examples of Rock Fabrics plate). This layering is called bed ...
... (e.g., sandstone), and chemical sedimentary rock that form from the precipitation of minerals from solution (e.g., limestone). When grains settle they may form layers, or beds, that may be defined by differences in color or grain size (see Examples of Rock Fabrics plate). This layering is called bed ...
Sedimentary Rocks - East Hanover Township School District
... ocean water. It is an example of a chemical sedimentary rock. • When calcium carbonate (CaCO3) comes out of solution as calcite and itmany crystals grow together, limestone forms. • Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. • Limestone usual ...
... ocean water. It is an example of a chemical sedimentary rock. • When calcium carbonate (CaCO3) comes out of solution as calcite and itmany crystals grow together, limestone forms. • Limestone also can contain other minerals and sediments, but it must be at least 50 percent calcite. • Limestone usual ...
Present chemical weathering of basalt in Iceland
... Cl, and Sr/C1 ratios in the precipitation are close to oceanic ratios, indicating a sole marine source for these elements in the precipitation. The concentration of Ca, SO4, NO3 and N H 3 is higher than predicted by an unfractionated marine contribution. The pH of spring fed rivers in Iceland is hig ...
... Cl, and Sr/C1 ratios in the precipitation are close to oceanic ratios, indicating a sole marine source for these elements in the precipitation. The concentration of Ca, SO4, NO3 and N H 3 is higher than predicted by an unfractionated marine contribution. The pH of spring fed rivers in Iceland is hig ...
building stones of the brooklyn college campus
... (e.g., sandstone), and chemical sedimentary rock that form from the precipitation of minerals from solution (e.g., limestone). When grains settle they may form layers, or beds, that may be defined by differences in color or grain size (see Examples of Rock Fabrics plate). This layering is called bed ...
... (e.g., sandstone), and chemical sedimentary rock that form from the precipitation of minerals from solution (e.g., limestone). When grains settle they may form layers, or beds, that may be defined by differences in color or grain size (see Examples of Rock Fabrics plate). This layering is called bed ...
The rock cycle shows how rocks change.
... cementing it together. Some sedimentary rocks form in other ways, as when water evaporates, leaving behind minerals that were dissolved in it. Metamorphic rock (MEHT-uh-MAWR-fihk) forms when heat or pressure causes older rocks to change into new types of rocks. For example, a rock can get buried dee ...
... cementing it together. Some sedimentary rocks form in other ways, as when water evaporates, leaving behind minerals that were dissolved in it. Metamorphic rock (MEHT-uh-MAWR-fihk) forms when heat or pressure causes older rocks to change into new types of rocks. For example, a rock can get buried dee ...
This is another Regents Review Packet to help you.
... 3. Does POROSITY change if only the size of the particles changes? (Hint: see p. 135 in the ESRTs for help.) ...
... 3. Does POROSITY change if only the size of the particles changes? (Hint: see p. 135 in the ESRTs for help.) ...
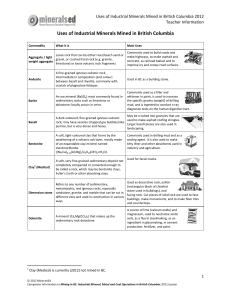
Uses of Industrial Minerals Mined in British Columbia
... Used in pencil lead, in automobile gaskets and brake linings, in high technology electrical A mineral composed of carbon (C) which most circuitry, in fuel cells, in sports equipment, as commonly occurs in metamorphic rocks. It can be a flame retardant in paint and carpet, as a found as large c ...
... Used in pencil lead, in automobile gaskets and brake linings, in high technology electrical A mineral composed of carbon (C) which most circuitry, in fuel cells, in sports equipment, as commonly occurs in metamorphic rocks. It can be a flame retardant in paint and carpet, as a found as large c ...
Igneous rock

Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ignis meaning fire) is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. Igneous rock may form with or without crystallization, either below the surface as intrusive (plutonic) rocks or on the surface as extrusive (volcanic) rocks. This magma can be derived from partial melts of pre-existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Over 700 types of igneous rocks have been described, most of them having formed beneath the surface of Earth's crust.