Geology of the Hawaiian Islands
... Most common minerals in the earth's crust Divided into light and darkdark-colored minerals Light colored minerals, such as quartz and feldspar contain K, Na, Al Dark minerals, such as pyroxene contain either Mg, Fe, or both ...
... Most common minerals in the earth's crust Divided into light and darkdark-colored minerals Light colored minerals, such as quartz and feldspar contain K, Na, Al Dark minerals, such as pyroxene contain either Mg, Fe, or both ...
Rocks, Part III
... and cementation of sediments that are deposited onto the solid Earth surface from water, wind, and ice. These form from Siliciclastic sediments, which form via the mechanical breakdown of pre-existing rocks, largely silicate-bearing igneous and metamorphic rocks, to yield particles ranging in size f ...
... and cementation of sediments that are deposited onto the solid Earth surface from water, wind, and ice. These form from Siliciclastic sediments, which form via the mechanical breakdown of pre-existing rocks, largely silicate-bearing igneous and metamorphic rocks, to yield particles ranging in size f ...
Perth GeoHistory Booklet
... Sandstones are clastic rocks composed of a framework of mineral and rock particles of sand size. Some of these particles may be surrounded by what is called a “matrix” of even finer grains. They are compacted by “intergranular cement,” which is typically quartz or calcite, or as a result of the fram ...
... Sandstones are clastic rocks composed of a framework of mineral and rock particles of sand size. Some of these particles may be surrounded by what is called a “matrix” of even finer grains. They are compacted by “intergranular cement,” which is typically quartz or calcite, or as a result of the fram ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... rocks form at or very close to the earth’s surface, and their rapid cooling and solidification usually result in fine-grained textures. (b) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments at low temperatures. Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from fragments of preexisting rocks; examples include sand ...
... rocks form at or very close to the earth’s surface, and their rapid cooling and solidification usually result in fine-grained textures. (b) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments at low temperatures. Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from fragments of preexisting rocks; examples include sand ...
CHAPTER 2CROCKS AND MINERALS C A FIRST LOOK
... rocks form at or very close to the earth’s surface, and their rapid cooling and solidification usually result in fine-grained textures. (b) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments at low temperatures. Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from fragments of preexisting rocks; examples include sand ...
... rocks form at or very close to the earth’s surface, and their rapid cooling and solidification usually result in fine-grained textures. (b) Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments at low temperatures. Clastic sedimentary rocks are formed from fragments of preexisting rocks; examples include sand ...
16-Rocks and the Rock Cycle in pdf
... materials are formed in the process. Warm, tropical climates are ideal environments for chemical weathering to take place as the chemical reactions are quickened by the bountiful rain and warm temperatures. ...
... materials are formed in the process. Warm, tropical climates are ideal environments for chemical weathering to take place as the chemical reactions are quickened by the bountiful rain and warm temperatures. ...
Rocks and Minerals Test April 28, 2016
... Be able to answer questions similar to the following: 1. Why are qualitative tests both good and bad? 2. Why would the Mohs hardness test be considered both qualitative quantitative? 3. Why does a fossil have to be present in the original sedimentary rock so that a fossil can be found in a metamorp ...
... Be able to answer questions similar to the following: 1. Why are qualitative tests both good and bad? 2. Why would the Mohs hardness test be considered both qualitative quantitative? 3. Why does a fossil have to be present in the original sedimentary rock so that a fossil can be found in a metamorp ...
SEDIMENTARY ROCK - Taylor County Schools
... classified by the way in which they formed! IGNEOUS ROCK CHEMICAL Sedimentary Rocks form when minerals crystallize directly from water. These rocks have an MAGMA cooling interlocking crystalline structure, are composed of one type of mineral, and are uniform in color. weathering & erosion ...
... classified by the way in which they formed! IGNEOUS ROCK CHEMICAL Sedimentary Rocks form when minerals crystallize directly from water. These rocks have an MAGMA cooling interlocking crystalline structure, are composed of one type of mineral, and are uniform in color. weathering & erosion ...
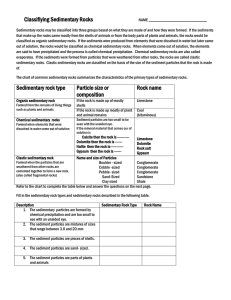
Classifiying Sedimentary Rocks
... rocks have crystal sizes, or grain sizes, that are larger than sand- sized and, under rare circumstances, may be larger than a penny. If the melted rock materials cooled near or even on the earth’s surface, the resulting rocks are called extrusive igneous rocks. However, some extrusive igneous rocks ...
... rocks have crystal sizes, or grain sizes, that are larger than sand- sized and, under rare circumstances, may be larger than a penny. If the melted rock materials cooled near or even on the earth’s surface, the resulting rocks are called extrusive igneous rocks. However, some extrusive igneous rocks ...
Classifying Rocks
... natural setting might be found in various states of decomposition due to weathering. Depending on the degree of weathering, it may be challenging even to tell if a particular rock is igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic! In any case, when learning to classify rocks there is no substitute for looking ...
... natural setting might be found in various states of decomposition due to weathering. Depending on the degree of weathering, it may be challenging even to tell if a particular rock is igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic! In any case, when learning to classify rocks there is no substitute for looking ...
2. Practice Test Answer Key
... C) compaction and cementation of shells and skeletal remains D) chemical precipitation of minerals from seawater 4. Of the Earth's more than 2,000 identified minerals, only a small number are commonly found in rocks. This fact indicates that most A) minerals weather before they can be identified B) ...
... C) compaction and cementation of shells and skeletal remains D) chemical precipitation of minerals from seawater 4. Of the Earth's more than 2,000 identified minerals, only a small number are commonly found in rocks. This fact indicates that most A) minerals weather before they can be identified B) ...
Back
... • Temperature and pressure increase on Earth as this increases • Answer • Depth…the greater the distance into Earth’s interior, the greater the heat and pressure ...
... • Temperature and pressure increase on Earth as this increases • Answer • Depth…the greater the distance into Earth’s interior, the greater the heat and pressure ...
The Process of Erosion and Deposition of Sediments Power Point
... rasping, or scraping. • Most often done by some mollusks, sponges, chiton, urchins, algae, bacteria, and fish ...
... rasping, or scraping. • Most often done by some mollusks, sponges, chiton, urchins, algae, bacteria, and fish ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... Does it have a matrix (usually micrite = fine-grained calcite crystals)? Does it how a cement (usually sparite = clear, glassylooking calcite crystals)? Does it contain skeletal grains (bioclasts)? Does it contain non-skeletal grains* (e.g. ooids, peloids, intraclasts)? (*Name the grains you ...
... Does it have a matrix (usually micrite = fine-grained calcite crystals)? Does it how a cement (usually sparite = clear, glassylooking calcite crystals)? Does it contain skeletal grains (bioclasts)? Does it contain non-skeletal grains* (e.g. ooids, peloids, intraclasts)? (*Name the grains you ...
G6 U9 Erosion and Deposition Cscope ppt
... rasping, or scraping. • Most often done by some mollusks, sponges, chiton, urchins, algae, bacteria, and fish ...
... rasping, or scraping. • Most often done by some mollusks, sponges, chiton, urchins, algae, bacteria, and fish ...
Rock Identification and stories lab
... to about 2mm in diameter. Story: Sandstones formed in moderate-energy environments where working of wind or water swept away smaller particles and deposited sand-sized particles. particularly well-sorted sandstones may represent beaches where wave action washed the sand particularly clean before it ...
... to about 2mm in diameter. Story: Sandstones formed in moderate-energy environments where working of wind or water swept away smaller particles and deposited sand-sized particles. particularly well-sorted sandstones may represent beaches where wave action washed the sand particularly clean before it ...
Geology – EXAM-1 Fall-2009
... B) low temperatures; very moist C) high temperatures; very dry D) warm temperatures; very moist 40. In which area are pedocal soils most likely to be found? A) a tropical rainforest in the Amazon Basin of Brazil B) a bitterly cold, permafrost area in north-central Siberia C) a forested area of the s ...
... B) low temperatures; very moist C) high temperatures; very dry D) warm temperatures; very moist 40. In which area are pedocal soils most likely to be found? A) a tropical rainforest in the Amazon Basin of Brazil B) a bitterly cold, permafrost area in north-central Siberia C) a forested area of the s ...
CHAPTER 10_Deep Time..
... approximate temporal equivalence of two bodies of rock (which may be of disparate lithologies). Because a single locality does not provide strata that span in age throughout Earth’s history, fossil correlation was required to provide time equivalence for units that are geographically isolated. With ...
... approximate temporal equivalence of two bodies of rock (which may be of disparate lithologies). Because a single locality does not provide strata that span in age throughout Earth’s history, fossil correlation was required to provide time equivalence for units that are geographically isolated. With ...
rock_id_lab
... (from physical or chemical alteration of other rocks by heating or intense pressure beneath Earth's surface) Some Possible Textures: 1. Foliated (folds such that minerals lie parallel to one another) 2. Banded (separate bands of light and dark minerals make wavy folds in the rock -- not like the fla ...
... (from physical or chemical alteration of other rocks by heating or intense pressure beneath Earth's surface) Some Possible Textures: 1. Foliated (folds such that minerals lie parallel to one another) 2. Banded (separate bands of light and dark minerals make wavy folds in the rock -- not like the fla ...
Lecture 7 Geologic Time
... assemblages can be determined using the other principles of relative time. Here are some things to remember about correlations (correlating rock units) of rocks units in different regions. ...
... assemblages can be determined using the other principles of relative time. Here are some things to remember about correlations (correlating rock units) of rocks units in different regions. ...
The Agents of Erosion - teachearthscience.org
... Mass wasting (commonly referred to as landslides) involves the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence of gravity. Gravity is the key factor in mass wasting and the movement of material does not require a mobile agent. ...
... Mass wasting (commonly referred to as landslides) involves the transfer of rock and soil downslope under the influence of gravity. Gravity is the key factor in mass wasting and the movement of material does not require a mobile agent. ...
Rocks and Their Origins
... • Igneous rocks are classified based on their texture. • Coarse texture- igneous rocks with large crystals. • Fine Grain texture- rocks that have small crystals. • Glassy- rocks that cool so fast they have no specific ...
... • Igneous rocks are classified based on their texture. • Coarse texture- igneous rocks with large crystals. • Fine Grain texture- rocks that have small crystals. • Glassy- rocks that cool so fast they have no specific ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.