Categorization of pores in sedimentary rocks II
... sedimentary rocks, “grains” include siliciclastic grains, fossils, ooids, and pellets, and they are effectively any sedimentary depositional ...
... sedimentary rocks, “grains” include siliciclastic grains, fossils, ooids, and pellets, and they are effectively any sedimentary depositional ...
KEY - Learn Earth Science
... Extrusive form on or near the Earth’s surface (small crystals) Intrusive form below the Earth’s surface (large crystals) Rocks & Minerals ©Mark Place, www.LearnEarthScience.com ...
... Extrusive form on or near the Earth’s surface (small crystals) Intrusive form below the Earth’s surface (large crystals) Rocks & Minerals ©Mark Place, www.LearnEarthScience.com ...
22Feb05_lec
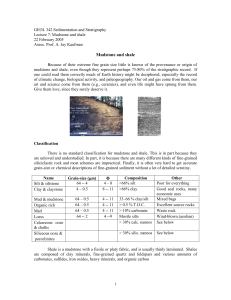
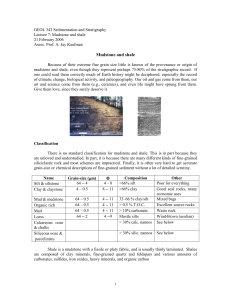
... Mudstone and shale Because of their extreme fine grain size little is known of the provenance or origin of mudstone and shale, even though they represent perhaps 75-80% of the stratigraphic record. If one could read them correctly much of Earth history might be deciphered, especially the record of c ...
... Mudstone and shale Because of their extreme fine grain size little is known of the provenance or origin of mudstone and shale, even though they represent perhaps 75-80% of the stratigraphic record. If one could read them correctly much of Earth history might be deciphered, especially the record of c ...
Mudstone and shale
... Mudstone and shale Because of their extreme fine grain size little is known of the provenance or origin of mudstone and shale, even though they represent perhaps 75-80% of the stratigraphic record. If one could read them correctly much of Earth history might be deciphered, especially the record of c ...
... Mudstone and shale Because of their extreme fine grain size little is known of the provenance or origin of mudstone and shale, even though they represent perhaps 75-80% of the stratigraphic record. If one could read them correctly much of Earth history might be deciphered, especially the record of c ...
Background
... an event is known as an extrusion. Due to exposure to air and water it cools fairly quickly and because of this the crystals which make it up are usually very small and this is described as fine grained. The best local example of this is the Antrim Plateau and the specific rock is dark or black in c ...
... an event is known as an extrusion. Due to exposure to air and water it cools fairly quickly and because of this the crystals which make it up are usually very small and this is described as fine grained. The best local example of this is the Antrim Plateau and the specific rock is dark or black in c ...
The Rock Record
... – Provides information about the geologic history of Earth – Recreating past climates – Provides clues to environmental changes that have occurred in Earth’s past. – Tracking the evolution of organisms ...
... – Provides information about the geologic history of Earth – Recreating past climates – Provides clues to environmental changes that have occurred in Earth’s past. – Tracking the evolution of organisms ...
Slide 1
... No. Although a rock is also inorganic and occurs naturally, it is not a crystalline solid. It is a consolidated material composed of grains of one or more minerals . ...
... No. Although a rock is also inorganic and occurs naturally, it is not a crystalline solid. It is a consolidated material composed of grains of one or more minerals . ...
Rock - SchoolRack
... Other compositional groups: Rocks with a composition between granitic and basaltic have an andesitic composition. They contain at least 25% dark silicate minerals. ...
... Other compositional groups: Rocks with a composition between granitic and basaltic have an andesitic composition. They contain at least 25% dark silicate minerals. ...
Geologic Time
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
Geologic Time
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
... When an adaptation (a change) makes an organism more likely to survive and reproduce, the organism may pass the new adaptation on to its offspring (babies); organisms with the new adaptation will produce more babies than organisms that don’t have the new adaptation. This process called: natural sele ...
Mineral - Weebly
... Orgin – forms from particles (sediment) deposited by water and wind due to erosion and/or deposition. Sand grains, mud, pebbles are some of the sediment that form it. 1. Compaction – over millions of years layers build up and press down on layers underneath them – squeezing together to form sedime ...
... Orgin – forms from particles (sediment) deposited by water and wind due to erosion and/or deposition. Sand grains, mud, pebbles are some of the sediment that form it. 1. Compaction – over millions of years layers build up and press down on layers underneath them – squeezing together to form sedime ...
Three Main Types of Rocks Igneous Rocks
... Rocks that form when melted rock hardens are called Igneous rocks. Lava cools and hardens before large mineral crystals have time to form. Rocks formed from lava have small mineral pieces and are called fine-grained. Melted rock that stays below Earth's surface is called magma. Magma cools and harde ...
... Rocks that form when melted rock hardens are called Igneous rocks. Lava cools and hardens before large mineral crystals have time to form. Rocks formed from lava have small mineral pieces and are called fine-grained. Melted rock that stays below Earth's surface is called magma. Magma cools and harde ...
Geology of road-forming materials as applied to Tasmania
... Ordinary weathering is going on continuously and the products of this breakdown are widely spread, although most of the material finds its way to seas and lakes where the sedimentary rock forming process starts all over again. Soft, non-coherent rocks (sandstone and siltstone) weather more easily bu ...
... Ordinary weathering is going on continuously and the products of this breakdown are widely spread, although most of the material finds its way to seas and lakes where the sedimentary rock forming process starts all over again. Soft, non-coherent rocks (sandstone and siltstone) weather more easily bu ...
Topic 11
... [70% of all sedimentary rocks are shale; almost all rocks in your backyard are shale] 2. cementation -- larger clastic sediments are cemented together as they are compressed on the seafloor or lake bed (natural cements come from minerals in seawater or groundwater) EX/ sand sandstone; mixed sizes ...
... [70% of all sedimentary rocks are shale; almost all rocks in your backyard are shale] 2. cementation -- larger clastic sediments are cemented together as they are compressed on the seafloor or lake bed (natural cements come from minerals in seawater or groundwater) EX/ sand sandstone; mixed sizes ...
Physical Attributes of Rocks and Minerals
... Minerals are non-living solid, non-living objects formed in nature. Rocks are naturally formed solid made of one or more minerals. Streak tests are used to help determine what minerals are in a rock. The test shows what color is left behind. Types of Rocks 1. Sedimentary Rocks are formed when sand, ...
... Minerals are non-living solid, non-living objects formed in nature. Rocks are naturally formed solid made of one or more minerals. Streak tests are used to help determine what minerals are in a rock. The test shows what color is left behind. Types of Rocks 1. Sedimentary Rocks are formed when sand, ...
Rocks, Minerals, Soil, and Erosion Study Guide
... Minerals are non-living solid, non-living objects formed in nature. Rocks are naturally formed solid made of one or more minerals. Streak tests are used to help determine what minerals are in a rock. The test shows what color is left behind. Types of Rocks 1. Sedimentary Rocks are formed when sand, ...
... Minerals are non-living solid, non-living objects formed in nature. Rocks are naturally formed solid made of one or more minerals. Streak tests are used to help determine what minerals are in a rock. The test shows what color is left behind. Types of Rocks 1. Sedimentary Rocks are formed when sand, ...
Rocks: Earth`s Crust
... origin. An igneous rock, such as granite or obsidian, originates as hot liquid magma that cools and hardens, such as when the magma reaches cold seawater. A sedimentary rock, such as sandstone or limestone, originates as particles of sand, silt, mud, and other materials on Earth’s surface are moved ...
... origin. An igneous rock, such as granite or obsidian, originates as hot liquid magma that cools and hardens, such as when the magma reaches cold seawater. A sedimentary rock, such as sandstone or limestone, originates as particles of sand, silt, mud, and other materials on Earth’s surface are moved ...
Ocenography Marine rocks
... darker colored, finer grained material. This dark material represents an additional bleb of magma that entered the magma chamber as the lighter colored material cooled. 3a. Igneous Volcanic --Siliceous. Siliceous volcanic rocks typify continental regions. Remember SiO2 content is one of the things t ...
... darker colored, finer grained material. This dark material represents an additional bleb of magma that entered the magma chamber as the lighter colored material cooled. 3a. Igneous Volcanic --Siliceous. Siliceous volcanic rocks typify continental regions. Remember SiO2 content is one of the things t ...
MarineSediments
... darker colored, finer grained material. This dark material represents an additional bleb of magma that entered the magma chamber as the lighter colored material cooled. 3a. Igneous Volcanic --Siliceous. Siliceous volcanic rocks typify continental regions. Remember SiO2 content is one of the things t ...
... darker colored, finer grained material. This dark material represents an additional bleb of magma that entered the magma chamber as the lighter colored material cooled. 3a. Igneous Volcanic --Siliceous. Siliceous volcanic rocks typify continental regions. Remember SiO2 content is one of the things t ...
Rock Cycle Power Point
... • Sediments are loose rock fragments, mineral grains, and shell that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity. • Sedimentary rocks form when sediments are pressed and cemented together. • They often form layers. The oldest layer of rock is on the bottom. ...
... • Sediments are loose rock fragments, mineral grains, and shell that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity. • Sedimentary rocks form when sediments are pressed and cemented together. • They often form layers. The oldest layer of rock is on the bottom. ...
Rocks Power Point
... • Sediments are loose rock fragments, mineral grains, and shell that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity. • Sedimentary rocks form when sediments are pressed and cemented together. • They often form layers. The oldest layer of rock is on the bottom. ...
... • Sediments are loose rock fragments, mineral grains, and shell that have been moved by wind, water, ice, or gravity. • Sedimentary rocks form when sediments are pressed and cemented together. • They often form layers. The oldest layer of rock is on the bottom. ...
Name
... made of fragments (pieces) of weathered Earth materials that may be many different sizes. Chemical Rocks are sedimentary rocks that form when minerals precipitate (fall) out of a solution (mixture of liquid and solids). Biochemical Rocks are sedimentary rocks that form due to organic processes (invo ...
... made of fragments (pieces) of weathered Earth materials that may be many different sizes. Chemical Rocks are sedimentary rocks that form when minerals precipitate (fall) out of a solution (mixture of liquid and solids). Biochemical Rocks are sedimentary rocks that form due to organic processes (invo ...
Lab1B rock classification 2010
... understanding of the information they provide about sediment sources and depositional environments. Sediments to Rocks Sediments, such as those in Lab 1A, become consolidated into rocks through the processes of compaction and cementation. Cements are crystals that grow between grains and bind them t ...
... understanding of the information they provide about sediment sources and depositional environments. Sediments to Rocks Sediments, such as those in Lab 1A, become consolidated into rocks through the processes of compaction and cementation. Cements are crystals that grow between grains and bind them t ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.