Geologic time
... A pebble that is part of a conglomerate rock is older than the rock. The pebble had to exist first in order to become part of the conglomerate when it formed. ...
... A pebble that is part of a conglomerate rock is older than the rock. The pebble had to exist first in order to become part of the conglomerate when it formed. ...
Rocks & The Rock Cycle
... Lumps of rock with a different composition from the main rock body Form when minerals precipitated from solutions build up around an existing rock particle Groundwater sometimes deposits dissolved quartz or calcite inside cavities of sedimentary rock where it crystallizes and forms a geode. ...
... Lumps of rock with a different composition from the main rock body Form when minerals precipitated from solutions build up around an existing rock particle Groundwater sometimes deposits dissolved quartz or calcite inside cavities of sedimentary rock where it crystallizes and forms a geode. ...
Human interaction with the rock cycle | sample answer
... To get lead and zinc they find it in sedimentary bedding planes of carboniferous limestone and dolomite rocks. These rocks that contain metal are referred to as ore, they were created 350m years ago when Ireland was under tropical sea. To extract metal from the rock, vertical and horizontal mine sha ...
... To get lead and zinc they find it in sedimentary bedding planes of carboniferous limestone and dolomite rocks. These rocks that contain metal are referred to as ore, they were created 350m years ago when Ireland was under tropical sea. To extract metal from the rock, vertical and horizontal mine sha ...
Sedimentary Rocks
... • Another useful organic sedimentary rock is coal. • Coal forms when pieces of dead plants are buried under other sediments in swamps. • These plant materials are chemically changed by microorganisms. • The resulting sediments are compacted over millions of years to form coal, an important source of ...
... • Another useful organic sedimentary rock is coal. • Coal forms when pieces of dead plants are buried under other sediments in swamps. • These plant materials are chemically changed by microorganisms. • The resulting sediments are compacted over millions of years to form coal, an important source of ...
G231 – Spring, 2012 Introductory Lecture Notes I.) Required list of
... mica intermediate and felsic Framework silicate feldspar, felsic Carbonate calcite limestone Carbonate dolomite dolomite Sulfate gypsum evaporates Sulfide pyrite hydrothermal ore bodies C) Review of common rocks: 1) Igneous rocks: crystalline rocks that cool from a magma 2) Metamorphic rocks: rocks ...
... mica intermediate and felsic Framework silicate feldspar, felsic Carbonate calcite limestone Carbonate dolomite dolomite Sulfate gypsum evaporates Sulfide pyrite hydrothermal ore bodies C) Review of common rocks: 1) Igneous rocks: crystalline rocks that cool from a magma 2) Metamorphic rocks: rocks ...
The geological time scale divides Earth`s history into units from its
... in terms of tens of millions of years to hundreds of millions of years. They are defined by the life-forms that were ...
... in terms of tens of millions of years to hundreds of millions of years. They are defined by the life-forms that were ...
LawofSuperposition
... There are three types of unconformities. 1. An unconformity in which stratified (layers) of rock rests upon unstratified rock is called a nonconformity. 2. The boundary between a set of tilted layers and a set of horizontal layers is called an angular unconformity. 3. The boundary between horizontal ...
... There are three types of unconformities. 1. An unconformity in which stratified (layers) of rock rests upon unstratified rock is called a nonconformity. 2. The boundary between a set of tilted layers and a set of horizontal layers is called an angular unconformity. 3. The boundary between horizontal ...
Unit 5: Age of the Earth - Ann Arbor Earth Science
... Law of Superposition Sedimentary rocks form when new sediments are deposited on top of old layers of sediment. As the sediments accumulate, they are compressed and harden into sedimentary rock layers. Scientists use a basic principle called the Law of Superposition to determine the relative age of ...
... Law of Superposition Sedimentary rocks form when new sediments are deposited on top of old layers of sediment. As the sediments accumulate, they are compressed and harden into sedimentary rock layers. Scientists use a basic principle called the Law of Superposition to determine the relative age of ...
dating_rock_layers
... What is a Fault? • A BREAK in the Earth’s crust. • A fault is always YOUNGER than the rock it cuts through. ...
... What is a Fault? • A BREAK in the Earth’s crust. • A fault is always YOUNGER than the rock it cuts through. ...
Earth Science – Chapter 3 Study Guide 1. Know that contact
... 3. Know an example of plutonic rock is granite. 4. Know that silty shale was most likely formed farthest from the shoreline. 5. Know the features of sedimentary rocks. 6. Know that mafic magma is best described as low silica content, dark color, think and fluid. 7. What kinds of rocks are formed whe ...
... 3. Know an example of plutonic rock is granite. 4. Know that silty shale was most likely formed farthest from the shoreline. 5. Know the features of sedimentary rocks. 6. Know that mafic magma is best described as low silica content, dark color, think and fluid. 7. What kinds of rocks are formed whe ...
Chemical Sedimentary Rocks
... to chemid wmthering, it tends to conccnuate residually in sand as less resistant minerals such as feldspar are weathered away, probably in a low-lying humid region that dows chemical weathering to continue for a long time. The quartz grains in a quartz sandstone ax usually well-sorted and well-round ...
... to chemid wmthering, it tends to conccnuate residually in sand as less resistant minerals such as feldspar are weathered away, probably in a low-lying humid region that dows chemical weathering to continue for a long time. The quartz grains in a quartz sandstone ax usually well-sorted and well-round ...
GY 112 Lecture Notes - University of South Alabama
... humid area will preserve a record of wet conditions. They may contain abundant organic material (coals), or they may record constant water current activity (cross-bedded sandstone). In contrast, arid regions tend to produce red bed type rocks (red shales, hematite stained sandstone), or in some case ...
... humid area will preserve a record of wet conditions. They may contain abundant organic material (coals), or they may record constant water current activity (cross-bedded sandstone). In contrast, arid regions tend to produce red bed type rocks (red shales, hematite stained sandstone), or in some case ...
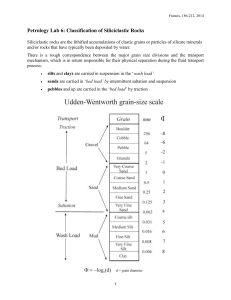
Petrology Lab 6: Siliciclastic Rocks
... This station contains a number of different types of mud rock. Siltstones can be distinguish from shales and mudstones by biting a piece between your teeth. If it feels "gritty" then it is a siltstone, if it feels smooth or slick, then it is a shale or claystone. One of the most important features o ...
... This station contains a number of different types of mud rock. Siltstones can be distinguish from shales and mudstones by biting a piece between your teeth. If it feels "gritty" then it is a siltstone, if it feels smooth or slick, then it is a shale or claystone. One of the most important features o ...
Metamorphic Rocks - The Science Queen
... Foliated Metamorphic Rocks FOLIATED metamorphic rocks are those in which the minerals have been flattened and pushed down into parallel layers. The bands in foliated metamorphic rock look like pages in a book. Examples of foliated rocks are slate, shale, and gneiss. ...
... Foliated Metamorphic Rocks FOLIATED metamorphic rocks are those in which the minerals have been flattened and pushed down into parallel layers. The bands in foliated metamorphic rock look like pages in a book. Examples of foliated rocks are slate, shale, and gneiss. ...
Science 8-Chapter 13HD Les 2 Notes Ans
... ways that rocks form. Write the type of rock that forms in each box on the right. Parent rocks are squeezed, heated, or exposed to hot fluids. ...
... ways that rocks form. Write the type of rock that forms in each box on the right. Parent rocks are squeezed, heated, or exposed to hot fluids. ...
Answers Rocks
... 2 The Port Campbell Limestone is estimated to be about 15-20 million years old. This limestone belongs to the cenozoic era. 3 According to the above map, the oldest rocks in Australia are found in southern Western Australia, in South Australia, and a smaller amount in the Northern Australia. 4 Ac ...
... 2 The Port Campbell Limestone is estimated to be about 15-20 million years old. This limestone belongs to the cenozoic era. 3 According to the above map, the oldest rocks in Australia are found in southern Western Australia, in South Australia, and a smaller amount in the Northern Australia. 4 Ac ...
Chapter 9
... flood, wind, etc… It is then “glued” together by pressure This sediment is called clastic sedimentary rock ...
... flood, wind, etc… It is then “glued” together by pressure This sediment is called clastic sedimentary rock ...
Save 0 - Science Lec | Home
... What are Sedimentary Rocks? • Sedimentary rocks are secondary rocks (i.e. they are formed from pre-existing rocks) • They are formed via the deposition and lithification (diagenesis) of loose sediments, which are the product of f chemical h i l and d physical h i l weathering th i of f All rocks ...
... What are Sedimentary Rocks? • Sedimentary rocks are secondary rocks (i.e. they are formed from pre-existing rocks) • They are formed via the deposition and lithification (diagenesis) of loose sediments, which are the product of f chemical h i l and d physical h i l weathering th i of f All rocks ...
Rock Cycle - rms
... collect. The sediment pushes down forcing the sediment to form layers. This is called _______________. Fossils are often found in sedimentary rocks. There is enough pressure and heat to preserve the bones but not enough to destroy them. Shale, sandstone, and conglomerates are common sedimentary roc ...
... collect. The sediment pushes down forcing the sediment to form layers. This is called _______________. Fossils are often found in sedimentary rocks. There is enough pressure and heat to preserve the bones but not enough to destroy them. Shale, sandstone, and conglomerates are common sedimentary roc ...
Are you Ready to Rock
... The name Metamorphic comes from the Greek to "change form” •Metamorphic rock is formed by applying great pressure and temperature to existing rock converting it into a new distinct type of rock. •Igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and even other metamorphic rocks and be modified into metamorphic rock ...
... The name Metamorphic comes from the Greek to "change form” •Metamorphic rock is formed by applying great pressure and temperature to existing rock converting it into a new distinct type of rock. •Igneous rocks, sedimentary rocks, and even other metamorphic rocks and be modified into metamorphic rock ...
Introduction to stratigraphy
... marker beds that represent a “geologic instant” in time, like a volcanic ash layer. ...
... marker beds that represent a “geologic instant” in time, like a volcanic ash layer. ...
Sedimentary rock
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition of material at the Earth's surface and within bodies of water. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause mineral and/or organic particles (detritus) to settle and accumulate or minerals to precipitate from a solution. Particles that form a sedimentary rock by accumulating are called sediment. Before being deposited, sediment was formed by weathering and erosion in a source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers which are called agents of denudation.The sedimentary rock cover of the continents of the Earth's crust is extensive, but the total contribution of sedimentary rocks is estimated to be only 8% of the total volume of the crust. Sedimentary rocks are only a thin veneer over a crust consisting mainly of igneous and metamorphic rocks. Sedimentary rocks are deposited in layers as strata, forming a structure called bedding. The study of sedimentary rocks and rock strata provides information about the subsurface that is useful for civil engineering, for example in the construction of roads, houses, tunnels, canals or other structures. Sedimentary rocks are also important sources of natural resources like coal, fossil fuels, drinking water or ores.The study of the sequence of sedimentary rock strata is the main source for scientific knowledge about the Earth's history, including palaeogeography, paleoclimatology and the history of life. The scientific discipline that studies the properties and origin of sedimentary rocks is called sedimentology. Sedimentology is part of both geology and physical geography and overlaps partly with other disciplines in the Earth sciences, such as pedology, geomorphology, geochemistry and structural geology.