SUMMARY KEY TERMS APPLYING THE CONCEPTS
... as hot, molten magma cooled and crystallized to firm, hard rocks. Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments, accumulations of weathered rock materials that settle out of the atmosphere or out of water. Sediments become sedimentary rocks through a rock-forming process that involves both the compact ...
... as hot, molten magma cooled and crystallized to firm, hard rocks. Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments, accumulations of weathered rock materials that settle out of the atmosphere or out of water. Sediments become sedimentary rocks through a rock-forming process that involves both the compact ...
11.30-plate-tectonics
... • Occur along plate boundaries, but occasionally occur in the middle of a plate • Rigidity of crust builds up tension; eventually slippage occurs to release tension this is an earthquake ...
... • Occur along plate boundaries, but occasionally occur in the middle of a plate • Rigidity of crust builds up tension; eventually slippage occurs to release tension this is an earthquake ...
1. How does the water cycle show interactions of Earth systems?
... or glaciers) to new locations ...
... or glaciers) to new locations ...
2.4ab
... Indicative Content: • Described his theory that the continents were all once joined and 1 super continent: Pangaea • It was thought this happened by continental drift due to convection currents underneath the plates caused movement • Evidence, fossil evidence on matching sides of continents, seafloo ...
... Indicative Content: • Described his theory that the continents were all once joined and 1 super continent: Pangaea • It was thought this happened by continental drift due to convection currents underneath the plates caused movement • Evidence, fossil evidence on matching sides of continents, seafloo ...
11th Grade Earth Science
... What two types of weathering are there, and what are some examples of each? ...
... What two types of weathering are there, and what are some examples of each? ...
Geology Study Guide
... 2. ___________________________________ is the scientific theory explaining that the lithosphere is divided into moving slabs. It also explains Earth processes, such as volcanic activity and earthquakes. ...
... 2. ___________________________________ is the scientific theory explaining that the lithosphere is divided into moving slabs. It also explains Earth processes, such as volcanic activity and earthquakes. ...
File
... 5. Short answer: What term refers to the weak, soft layer of solidified magma underneath the lithosphere? ...
... 5. Short answer: What term refers to the weak, soft layer of solidified magma underneath the lithosphere? ...
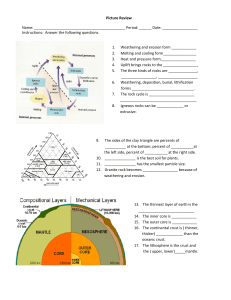
Picture Review Name
... 85. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 86. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 87. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 88. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 89. What is the relationship between o ...
... 85. Which planet has fastest orbital velocity? __________________ 86. Which planet is nearest to the Sun? ______________________ 87. Which planet has the slowest orbital velocity? ______________ 88. Which planet is farthest from the Sun? Not Pluto! ___________ 89. What is the relationship between o ...
Earth Systems & Resources
... Formation of Earth & Solar System Approx. 5 billion years ago gas & dust from an exploded star converged under the force of gravity into a spinning disc called a planetary nebula. Earth formed in a process called accretion where materials clumped together to form larger masses (increasing gravity o ...
... Formation of Earth & Solar System Approx. 5 billion years ago gas & dust from an exploded star converged under the force of gravity into a spinning disc called a planetary nebula. Earth formed in a process called accretion where materials clumped together to form larger masses (increasing gravity o ...
Introduction to Plate Tectonics California Geology 20
... scientific community but has not yet been decisively proven. Or…… ...
... scientific community but has not yet been decisively proven. Or…… ...
File
... •consist mainly of dense rock (basalt dark in color) •5-8 km thick Continental Crust •crust that forms the continents •consist mainly of less dense rock (granite ...
... •consist mainly of dense rock (basalt dark in color) •5-8 km thick Continental Crust •crust that forms the continents •consist mainly of less dense rock (granite ...
The Layered Earth - Starry Night Education
... caused by the interaction of Earth's plates. Technology is used to determine the characterisitcs and behavior of ...
... caused by the interaction of Earth's plates. Technology is used to determine the characterisitcs and behavior of ...
Ch._8__10_notes_plate_tectonics_and_earths_surface.pptx
... • There are many different types of landforms on Earth • Water shapes a lot of these landforms • Landforms can form from gradual or dramatic events ...
... • There are many different types of landforms on Earth • Water shapes a lot of these landforms • Landforms can form from gradual or dramatic events ...
Plate Tectonics - East Hanover Township School District
... Convection is like a boiling pot. Heated soup rises to the surface, spreads and begins to cool, and then sinks back to the bottom of the pot where it is reheated and rises again. ...
... Convection is like a boiling pot. Heated soup rises to the surface, spreads and begins to cool, and then sinks back to the bottom of the pot where it is reheated and rises again. ...
Development of the oceans as a manifestation of the expansion of
... of a gigantic process of the spreading of the oceanic lithosphere which occurs at midoceanic ridges. The process can be treated as a manifestation of the expansion of the whole globe, as it was seen by the authors of the theory of spreading – Carey (1958) and Heezen (1960)1, or it can be combined w ...
... of a gigantic process of the spreading of the oceanic lithosphere which occurs at midoceanic ridges. The process can be treated as a manifestation of the expansion of the whole globe, as it was seen by the authors of the theory of spreading – Carey (1958) and Heezen (1960)1, or it can be combined w ...
Modifying Text Complexity Tools
... fjords, kettle lakes, moraines, cirques, horns, etc. were left behind. The heavy weight of the ice deformed the Earth’s crust and mantle. Global sea levels dropped over 330 feet (100 meters) to expose continental shelves in some areas. This caused land bridges to be formed between land masses and al ...
... fjords, kettle lakes, moraines, cirques, horns, etc. were left behind. The heavy weight of the ice deformed the Earth’s crust and mantle. Global sea levels dropped over 330 feet (100 meters) to expose continental shelves in some areas. This caused land bridges to be formed between land masses and al ...
Earth`s Magnetic Field, Atmosphere and Geology
... “bow shock”, just like a boat pushes some water out of the way at its bow as it sails forward. ...
... “bow shock”, just like a boat pushes some water out of the way at its bow as it sails forward. ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10th ed.
... • Composed of both crust and uppermost mantle • Makes up Earth’s tectonic “plates” ...
... • Composed of both crust and uppermost mantle • Makes up Earth’s tectonic “plates” ...
pdf 4.5Mb
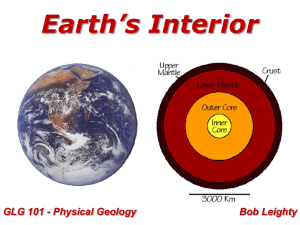
... How do we know that the Earth comprises: – crust – mantle – metallic core (solid and liquid portions) ? How deep have we drilled? ...
... How do we know that the Earth comprises: – crust – mantle – metallic core (solid and liquid portions) ? How deep have we drilled? ...
Study guide: exam #1
... Energy sources of the Earth Origin of the Sun and Planets Fusion: definition Sun formation Formation of the Earth Formation of atmosphere and water on Earth The layered Earth: figure 2.10: order of layers and compositions Figure 2.11: two types of crust (composition and characteristics); lithosphere ...
... Energy sources of the Earth Origin of the Sun and Planets Fusion: definition Sun formation Formation of the Earth Formation of atmosphere and water on Earth The layered Earth: figure 2.10: order of layers and compositions Figure 2.11: two types of crust (composition and characteristics); lithosphere ...
Inside Earth
... • Over millions of year, stresses can turn flat land surfaces into towering mountains ...
... • Over millions of year, stresses can turn flat land surfaces into towering mountains ...
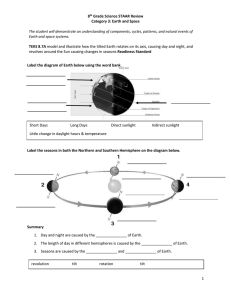
8th Grade Science STAAR Review Category 3: Earth and Space
... 9. Convection not only happens in the air, but in the __________________ & _________________. 10. Convection causes _______________ in the ocean and the _______________ to move in the ...
... 9. Convection not only happens in the air, but in the __________________ & _________________. 10. Convection causes _______________ in the ocean and the _______________ to move in the ...
The Origin of Continents and Oceans
... where one tectonic plate rides up over another and causes it to be pushed down and recycled (melted) ...
... where one tectonic plate rides up over another and causes it to be pushed down and recycled (melted) ...
Earth`s Internal Structure Earth`s Layered Structure In the preceding
... and oceanic crust. Both share the word “crust,” but the similarity ends there. Theoceanic crust is roughly 7 kilometers (5 miles) thick and composed of the dark igneousrock basalt. By contrast, the continental crust averages about 35 kilometers (22 miles) thickbut may exceed 70 kilometers (40 miles) ...
... and oceanic crust. Both share the word “crust,” but the similarity ends there. Theoceanic crust is roughly 7 kilometers (5 miles) thick and composed of the dark igneousrock basalt. By contrast, the continental crust averages about 35 kilometers (22 miles) thickbut may exceed 70 kilometers (40 miles) ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.