Why do volcanoes erupt?
... Magma is a mixture of molten or semi-molten rock, solid rock and gases formed from the partial melting of the crust and/or mantle. Most of the world’s 550 active volcanoes on Earth are located along the margins of adjacent plates. When two plates collide at a destructive plate boundary, subduction w ...
... Magma is a mixture of molten or semi-molten rock, solid rock and gases formed from the partial melting of the crust and/or mantle. Most of the world’s 550 active volcanoes on Earth are located along the margins of adjacent plates. When two plates collide at a destructive plate boundary, subduction w ...
Location of Atlantic Canada PowerPoint
... Latitude and Longitude • Globes, maps, and charts have a system of North-South and EastWest lines which make up the Earth’s Grid • This grid is the basis for locating points on Earth • Imagine a piece of graph paper covering the planet • A coordinate is the intersection of two lines (latitude and l ...
... Latitude and Longitude • Globes, maps, and charts have a system of North-South and EastWest lines which make up the Earth’s Grid • This grid is the basis for locating points on Earth • Imagine a piece of graph paper covering the planet • A coordinate is the intersection of two lines (latitude and l ...
The Layer`s Of The Earth!
... is very thin compared to the other three layers. *The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. * The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called plates. ...
... is very thin compared to the other three layers. *The crust makes up 1% of the Earth. * The crust of the Earth is broken into many pieces called plates. ...
Document
... Review and Pre-Assess Objective: I will prepare to reach mastery on the unit test and assess what I know about the new unit. HW: complete review practice, prepare for test, project due Warm Up: Am I ready for the test? How much do I remember? * Answer the questions on the sheet ...
... Review and Pre-Assess Objective: I will prepare to reach mastery on the unit test and assess what I know about the new unit. HW: complete review practice, prepare for test, project due Warm Up: Am I ready for the test? How much do I remember? * Answer the questions on the sheet ...
Plate Tectonics Vocabulary PPP- Sidney
... A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area The mantle is made of much denser, thicker material, because of this the plates "float" on it like oil floats on water. Many geologists believe that the mantle "flows" because of conve ...
... A circulation pattern in which material is heated and rises in one area, then cools and sinks in another area The mantle is made of much denser, thicker material, because of this the plates "float" on it like oil floats on water. Many geologists believe that the mantle "flows" because of conve ...
Earth,Notes,RevQs,Ch1
... a. e.g., Weather system b. e.g., Solar system B. Parts of the Earth system are linked so that a change in one part can produce changes in any or all other parts C. Characterized by processes that 1. Vary on spatial scales from fractions of a millimeter to thousands of kilometers 2. Have time scales ...
... a. e.g., Weather system b. e.g., Solar system B. Parts of the Earth system are linked so that a change in one part can produce changes in any or all other parts C. Characterized by processes that 1. Vary on spatial scales from fractions of a millimeter to thousands of kilometers 2. Have time scales ...
Mid Term I - earthjay science
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the m ...
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the m ...
GEOL 106 Earthquake Country Mid Term I Study
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the magn ...
... first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the magn ...
GEOL 106 Earthquake Country Mid Term I Study
... is first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the m ...
... is first, second, third, to arrive and why? What is refraction? What does the plot of the seismic wave velocity vs. depth into the earth tell us? What is the difference between earthquakes in California and Virginia? How can one locate an earthquake with seismologic data? How can one determine the m ...
ch03_sec1 revised
... scoured by running water, which moves rocks around and changes their appearance. • Erosion is the process in which the materials of the Earth’s surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. • Erosion w ...
... scoured by running water, which moves rocks around and changes their appearance. • Erosion is the process in which the materials of the Earth’s surface are loosened, dissolved, or worn away and transported form one place to another by a natural agent, such as wind, water, ice or gravity. • Erosion w ...
Unit 4-Dynamic Crust PowerPoint
... S-waves are given off In many places on Earth, both waves are received; however, in other places, only P-Waves are received _________________________. -Since S waves cannot pass through a liquid, the conclusion is some parts of the Earth’s that _______________________ interior are liquid. __________ ...
... S-waves are given off In many places on Earth, both waves are received; however, in other places, only P-Waves are received _________________________. -Since S waves cannot pass through a liquid, the conclusion is some parts of the Earth’s that _______________________ interior are liquid. __________ ...
course outline - UTSC - University of Toronto
... Lithospheric plates are created at mid-ocean ridges (called spreading centres) where new magma rises to the surface and cools before being pushed apart by new magma arriving from depth. The movement of plates leads to collisions between adjoining plates (called orogeny) and destruction of some plate ...
... Lithospheric plates are created at mid-ocean ridges (called spreading centres) where new magma rises to the surface and cools before being pushed apart by new magma arriving from depth. The movement of plates leads to collisions between adjoining plates (called orogeny) and destruction of some plate ...
ES 3209 Unit 1 Aug 22 2011.indd
... pressure, density, and temperature all increase with increasing depth below the Earth’s surface. Students should know that the inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid, and that both layers are comprised of nickel and iron due to the process of segregation. Segregation caused high density el ...
... pressure, density, and temperature all increase with increasing depth below the Earth’s surface. Students should know that the inner core is solid and the outer core is liquid, and that both layers are comprised of nickel and iron due to the process of segregation. Segregation caused high density el ...
Plate Tectonic Booklet (test make up)
... It is important that you LEARN the content objectives, you will be tested on this again!!! Construct a booklet to cover the following: Please use complete sentences in your booklet. Page # Required Information Cover ...
... It is important that you LEARN the content objectives, you will be tested on this again!!! Construct a booklet to cover the following: Please use complete sentences in your booklet. Page # Required Information Cover ...
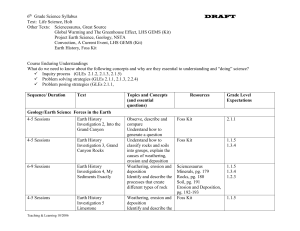
6th Grade Science Syllabus
... Other Texts: Sciencesaurus, Great Source Global Warming and The Greenhouse Effect, LHS GEMS (Kit) Project Earth Science, Geology, NSTA Convection, A Current Event, LHS GEMS (Kit) Earth History, Foss Kit Sequence/ Duration Text Topics and Concepts (and essential questions) processes that create diffe ...
... Other Texts: Sciencesaurus, Great Source Global Warming and The Greenhouse Effect, LHS GEMS (Kit) Project Earth Science, Geology, NSTA Convection, A Current Event, LHS GEMS (Kit) Earth History, Foss Kit Sequence/ Duration Text Topics and Concepts (and essential questions) processes that create diffe ...
Flash Cards - tclauset.org
... Q3-2: Draw a simplified diagram of Earth’s interior: a.) Indicate where on the diagram you would find aluminum & silicon & iron. b.) Using the following density values (Al-2.7, Si2.3, Fe-7.9, H2O-1.0) to explain why water floats on the earth’s surface. c.) How does the density of the mantle compare ...
... Q3-2: Draw a simplified diagram of Earth’s interior: a.) Indicate where on the diagram you would find aluminum & silicon & iron. b.) Using the following density values (Al-2.7, Si2.3, Fe-7.9, H2O-1.0) to explain why water floats on the earth’s surface. c.) How does the density of the mantle compare ...
The Dynamic Earth
... volcano at speeds of up to 200 km/hr and sear everything in their path. During an eruption, volcanic ash can mix with water and produce a mudflow. In 1985, Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia erupted, melting ice at the volcano’s summit. A mudflow raced downhill and engulfed the town of Armero. In addition, ...
... volcano at speeds of up to 200 km/hr and sear everything in their path. During an eruption, volcanic ash can mix with water and produce a mudflow. In 1985, Nevado del Ruiz in Colombia erupted, melting ice at the volcano’s summit. A mudflow raced downhill and engulfed the town of Armero. In addition, ...
Plate Tectonics
... They travel through any material but are slowed by less dense materials such as liquids & gases. They are push/pull waves. – Secondary waves (S waves). These are slower waves that will not travel through liquids. They are upward waves that cause the land they travel through to move at right angles. ...
... They travel through any material but are slowed by less dense materials such as liquids & gases. They are push/pull waves. – Secondary waves (S waves). These are slower waves that will not travel through liquids. They are upward waves that cause the land they travel through to move at right angles. ...
THIRD QUARTER II. UNIT 4: Landforms and Constructive and
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Word - New Haven Science
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
... 1. Earth’s surface features, such as mountains, volcanoes and continents, are the constantlychanging result of dynamic processes and forces at work inside the Earth. 2. Earth is formed of three basic layers, with the densest being the iron and nickel core. The middle layer, the mantle, of the Earth ...
Name - Quia
... Inside Earth – CRT # 1 Review Chapter 1 Section 1 – Earth’s Interior The Science of Geology (page 17-18) Who are the scientists who study the forces that make and shape planet Earth? ...
... Inside Earth – CRT # 1 Review Chapter 1 Section 1 – Earth’s Interior The Science of Geology (page 17-18) Who are the scientists who study the forces that make and shape planet Earth? ...
Lecture 2 Notes: Origin and Age of the Earth
... 1. The big bang produced elements through fusion, but only up to the mass of 7Be. Heavier elements like C have to be produced through triple collisions of 4He, which take a lot longer to happen. 2. The remaining heavy elements, many of which are so important for the aforementioned reasons, were pro ...
... 1. The big bang produced elements through fusion, but only up to the mass of 7Be. Heavier elements like C have to be produced through triple collisions of 4He, which take a lot longer to happen. 2. The remaining heavy elements, many of which are so important for the aforementioned reasons, were pro ...
Earth/Environmental Science Review Packet
... C. change in direction of the axis, but without any change in tilt—this changes the stars near (or not near) the Pole D. wobbling around the axis (This occurs over an 18 year period) E. the center of mass where two or more celestial bodies orbit each other(This is the point about which the Earth and ...
... C. change in direction of the axis, but without any change in tilt—this changes the stars near (or not near) the Pole D. wobbling around the axis (This occurs over an 18 year period) E. the center of mass where two or more celestial bodies orbit each other(This is the point about which the Earth and ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.