Chapter 26: Earth`s Interior
... b) The density of the crust changes sharply at this depth c) The pressure changes sharply at this ...
... b) The density of the crust changes sharply at this depth c) The pressure changes sharply at this ...
geologic time scale
... that objects are moving uniformly away from our Galaxy • He used the red shift of stellar spectra to measure distances and velocities of deep space objects • Hubble concluded that the universe is expanding and that distant stars and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way. ...
... that objects are moving uniformly away from our Galaxy • He used the red shift of stellar spectra to measure distances and velocities of deep space objects • Hubble concluded that the universe is expanding and that distant stars and galaxies are moving away from the Milky Way. ...
The Theory of Continental Drift (Now Plate Tectonics)
... - It is believed that the plate movements have carried ______________ across the earth. - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tectonic forces, Pangea broke into northern _____________ and southern ____________________ ...
... - It is believed that the plate movements have carried ______________ across the earth. - It is believed that about 250 million years ago there was one large continent called _____________. - Gradually due to tectonic forces, Pangea broke into northern _____________ and southern ____________________ ...
unit 5 the planet earth
... 11. What season is it when both hemispheres receive the same amount of light? 12. What season is it in the north when the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun? 13. Make a drawing of the layers of the atmosphere. 14. Which atmospheric layer is being described? a. Meteorological phenomena happen here. ...
... 11. What season is it when both hemispheres receive the same amount of light? 12. What season is it in the north when the North Pole is tilted towards the Sun? 13. Make a drawing of the layers of the atmosphere. 14. Which atmospheric layer is being described? a. Meteorological phenomena happen here. ...
RESTLESS EARTH
... asthenosphere. These are pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. continental drift : A theory that continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past. It also explained why fossils of the same plant and animal species are found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Ancient species could not ...
... asthenosphere. These are pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. continental drift : A theory that continents can drift apart from one another and have done so in the past. It also explained why fossils of the same plant and animal species are found on both sides of the Atlantic Ocean. Ancient species could not ...
Solid Earth - SchoolNova
... • In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, geologists assumed that the Earth's major features were fixed. • In 1912, Alfred Wegener proposed that up until about 200 million years ago, all of the present continents were joined together into a single super-continent later called Pangea. ...
... • In the late 19th and early 20th centuries, geologists assumed that the Earth's major features were fixed. • In 1912, Alfred Wegener proposed that up until about 200 million years ago, all of the present continents were joined together into a single super-continent later called Pangea. ...
Plate Tectonics
... continental drift theory in 1912 • His hypothesis was that all of earth’s continents were once one giant land mass • Gradually they drifted apart • His scientist peers and friends did not agree until the middle of the 1900’s ...
... continental drift theory in 1912 • His hypothesis was that all of earth’s continents were once one giant land mass • Gradually they drifted apart • His scientist peers and friends did not agree until the middle of the 1900’s ...
The Earth - Department of Physics, USU
... – Sunlight reaches surface, converted to heat – Surface re-radiates this heat (IR) , SOME of which is absorbed by atmosphere (recall atmospheric window) – Atmosphere warmed up by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases (CO2, Methane) trapping IR light ...
... – Sunlight reaches surface, converted to heat – Surface re-radiates this heat (IR) , SOME of which is absorbed by atmosphere (recall atmospheric window) – Atmosphere warmed up by increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases (CO2, Methane) trapping IR light ...
What is geoscience? - Welcome to The College of Social
... • molecules in groundwater • individual atoms (isotope geochemistry) ...
... • molecules in groundwater • individual atoms (isotope geochemistry) ...
Earth Science - Atlanta Public Schools
... decreased, the day would get longer. 27. Draw a picture of the Earth’s orbit around the sun showing the inertial and gravitational forces. Explain how these two forces work together to keep Earth in its elliptical orbit. SEE PROMETHEAN BOARD The force of gravity and the centripetal force due to iner ...
... decreased, the day would get longer. 27. Draw a picture of the Earth’s orbit around the sun showing the inertial and gravitational forces. Explain how these two forces work together to keep Earth in its elliptical orbit. SEE PROMETHEAN BOARD The force of gravity and the centripetal force due to iner ...
L1: Continental Drift and Layers of the Earth Goals: to describe the
... Refer to BC Science Connections page 277 for the answers to the following: EARTH’S COMPOSITION The circle below represents a cross-section of Earth. Draw and label Earth’s various layers. Define them in your own words. Vocabulary: crust, mantle, outer core, inner core. outer core: ...
... Refer to BC Science Connections page 277 for the answers to the following: EARTH’S COMPOSITION The circle below represents a cross-section of Earth. Draw and label Earth’s various layers. Define them in your own words. Vocabulary: crust, mantle, outer core, inner core. outer core: ...
Slide 1
... What forces produce mountains? Why is climate so variable? How old is the earth? Why do we have ocean tides? Is there really global warming? Is there really ice ages? How do we get water out of the ground? How does earth “fit” in our universe? ...
... What forces produce mountains? Why is climate so variable? How old is the earth? Why do we have ocean tides? Is there really global warming? Is there really ice ages? How do we get water out of the ground? How does earth “fit” in our universe? ...
Earth`s Interior
... Objectives: By the end of this section you should be able to: Explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents; list the evidence used by Wegener to support his hypothesis; Explain why other scientists at the time rejected Wegener’s theory. ...
... Objectives: By the end of this section you should be able to: Explain Alfred Wegener’s hypothesis about the continents; list the evidence used by Wegener to support his hypothesis; Explain why other scientists at the time rejected Wegener’s theory. ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
... constantly changes is called theory of plate tectonic. • The theory states that the earth’s outer shell, the lithosphere is divided into eight large plates. • Because each plate moves as a single unit, the interiors of the plates are generally stable. All major activity such as ...
Document
... Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s crust is divided into ___ major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to __________, ______ _______, or __________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” featu ...
... Plate Tectonics • The Earth’s crust is divided into ___ major plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to __________, ______ _______, or __________ against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or “tectonic” featu ...
Inside the Earth
... • Outer Core – Liquid layer – Causes magnetic poles • Inner Core – Solid due to pressure, very dense ...
... • Outer Core – Liquid layer – Causes magnetic poles • Inner Core – Solid due to pressure, very dense ...
astron_ch_7c (1)
... The inner and outer core are both the same temperature and are made of the same material: nickel and iron. ...
... The inner and outer core are both the same temperature and are made of the same material: nickel and iron. ...
File
... As we go deeper into the earth we find heavier material, which means we have more density as we go deeper into the earth. ...
... As we go deeper into the earth we find heavier material, which means we have more density as we go deeper into the earth. ...
Origin of the Universe
... 35. How did we get from our initial atmosphere to our current one? 36. What role did plants have in forming our current atmosphere? 37. What is the composition of the Earth’s oceans? Where did those materials come from? 38. About how long ago did the oceans on Earth reach their current state? 39. Wh ...
... 35. How did we get from our initial atmosphere to our current one? 36. What role did plants have in forming our current atmosphere? 37. What is the composition of the Earth’s oceans? Where did those materials come from? 38. About how long ago did the oceans on Earth reach their current state? 39. Wh ...
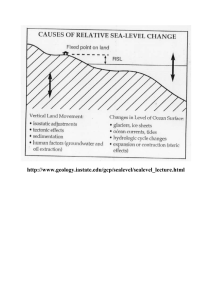
Eustatic Sea Level Change Mechanisms
... eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This includes the opening and closing of major ocean basins, the addition of new crust along mid-ocean ridges, and changes ...
... eustatic sea-level changes that are expressed worldwide. The most common tectonic mechanism to impact global sea-level change is the movement of the earth's lithospheric plates. This includes the opening and closing of major ocean basins, the addition of new crust along mid-ocean ridges, and changes ...
Earth and Space Science (Earth`s Interior)
... Content Statement ESS.1.1 The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. ESS.1.1.a The refraction and reflection of seismic waves as they move through one type of material to another is used to differentiate the layers of Earth’s interior. Earth h ...
... Content Statement ESS.1.1 The composition and properties of Earth’s interior are identified by the behavior of seismic waves. ESS.1.1.a The refraction and reflection of seismic waves as they move through one type of material to another is used to differentiate the layers of Earth’s interior. Earth h ...
Questions32
... 14. A parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates of radius 0.10 m is being discharged. A circular loop of radius 0.20 m is concentric with the capacitor and halfway between plates. The displacement current through the loop is 2.0 A. At what rate is the electric field between the plates changing? ...
... 14. A parallel-plate capacitor with circular plates of radius 0.10 m is being discharged. A circular loop of radius 0.20 m is concentric with the capacitor and halfway between plates. The displacement current through the loop is 2.0 A. At what rate is the electric field between the plates changing? ...
Spherical Earth

The concept of a spherical Earth dates back to around the 6th century BC, when it was mentioned in ancient Greek philosophy, but remained a matter of philosophical speculation until the 3rd century BC, when Hellenistic astronomy established the spherical shape of the earth as a physical given. The paradigm was gradually adopted throughout the Old World during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages. A practical demonstration of Earth's sphericity was achieved by Ferdinand Magellan and Juan Sebastián Elcano's expedition's circumnavigation (1519−1522).The concept of a spherical Earth displaced earlier beliefs in a flat Earth: In early Mesopotamian mythology, the world was portrayed as a flat disk floating in the ocean and surrounded by a spherical sky, and this forms the premise for early world maps like those of Anaximander and Hecataeus of Miletus. Other speculations on the shape of Earth include a seven-layered ziggurat or cosmic mountain, alluded to in the Avesta and ancient Persian writings (see seven climes).The realization that the figure of the Earth is more accurately described as an ellipsoid dates to the 18th century (Maupertuis).In the early 19th century, the flattening of the earth ellipsoid was determined to be of the order of 1/300 (Delambre, Everest). The modern value as determined by the US DoD World Geodetic System since the 1960s is close to 1/298.25.