Potential Adverse Cardiovascular Effects From Excessive
... within 1 week. Over months to years of repetitive injury, this process, in some individuals, may lead to patchy myocardial fibrosis, particularly in the atria, interventricular septum, and right ventricle, creating a substrate for atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Additionally, long-term excessive ...
... within 1 week. Over months to years of repetitive injury, this process, in some individuals, may lead to patchy myocardial fibrosis, particularly in the atria, interventricular septum, and right ventricle, creating a substrate for atrial and ventricular arrhythmias. Additionally, long-term excessive ...
Atrial Fibrillation, Atrioventricular Nodal Ablation and Biventricular
... achieved by AV node ablation is not as great as it might be, in view of the negative results of pacing from the right ventricular apex. In recent years, in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy, sinus rhythm and disturbances of intraventricular conduction, cardiac resynchronisation through biventricu ...
... achieved by AV node ablation is not as great as it might be, in view of the negative results of pacing from the right ventricular apex. In recent years, in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy, sinus rhythm and disturbances of intraventricular conduction, cardiac resynchronisation through biventricu ...
2015 ESC Guidelines for the management of patients with
... • SC defibrillators are effective in preventing SD. ...
... • SC defibrillators are effective in preventing SD. ...
ECG tutorial
... position indicated in figure 2. Choose the size of the range as in that figure. Use the vertical handle at the right in the membrane pane to decrease the action potential amplitude. In t ...
... position indicated in figure 2. Choose the size of the range as in that figure. Use the vertical handle at the right in the membrane pane to decrease the action potential amplitude. In t ...
Myocardial Hypoxia in Dilated Cardiomyopathy: Is it Just a Matter of
... levels, and an increased BOLD signal. In the case of the stressinduced ischemia, oxygen supply does not meet demand resulting in increased myocardial oxygen extraction, increased deoxyhemoglobin levels, and decreased BOLD signal. Consistent with the known impairment in myocardial vasodilator capacit ...
... levels, and an increased BOLD signal. In the case of the stressinduced ischemia, oxygen supply does not meet demand resulting in increased myocardial oxygen extraction, increased deoxyhemoglobin levels, and decreased BOLD signal. Consistent with the known impairment in myocardial vasodilator capacit ...
A Three-Dimensional Functional Assessment of Heart and Vessel
... dimensions (http://dir.nichd.nih.gov/lmg/uvo/atlas.html). However, we have presented a technique for measuring both cardiac and vessel size in three dimensions using conventional light microscopy. Not only is this technique less costly, but, more important, it also allows the measurement of cardiova ...
... dimensions (http://dir.nichd.nih.gov/lmg/uvo/atlas.html). However, we have presented a technique for measuring both cardiac and vessel size in three dimensions using conventional light microscopy. Not only is this technique less costly, but, more important, it also allows the measurement of cardiova ...
Heart Surface Motion Estimation Framework for Robotic
... contribute to easier adaptation of the model to any patient, give flexibility in handling surgical interventions, and reduce the time for initialization of the robotic surgery system. B. Classification of meshless methods While the major difference between meshless methods comes from the techniques ...
... contribute to easier adaptation of the model to any patient, give flexibility in handling surgical interventions, and reduce the time for initialization of the robotic surgery system. B. Classification of meshless methods While the major difference between meshless methods comes from the techniques ...
Hypoplastic left heart - British Heart Foundation
... procedure is an open-heart operation where the heart is stopped and the function of the heart is taken over by a heart-lung machine. The aim of the operation is to use the right ventricle to pump blood into the aorta. To do this, the surgeon separates the main pulmonary artery from the right and lef ...
... procedure is an open-heart operation where the heart is stopped and the function of the heart is taken over by a heart-lung machine. The aim of the operation is to use the right ventricle to pump blood into the aorta. To do this, the surgeon separates the main pulmonary artery from the right and lef ...
Final heart development
... • It develops from splanchnic mesoderm (cardiogenic area), cranial to the developing mouth and nervous system. • It lies ventral to the developing pericardial sac. • The heart primordium is first evident at 18 days (as an angioplastic cords which soon canalize to form the 2 heart tubes). • After com ...
... • It develops from splanchnic mesoderm (cardiogenic area), cranial to the developing mouth and nervous system. • It lies ventral to the developing pericardial sac. • The heart primordium is first evident at 18 days (as an angioplastic cords which soon canalize to form the 2 heart tubes). • After com ...
Stabilization of the coronary sinus lead position with permanent
... vessel. Then, a stiff stylet was inserted and kept into the CS lead and end of the stylet was cut by a scissor (permanent stylet technique). Pacing and sensing properties of all leads were checked and the guiding sheath was removed. Control echocardiography did not show pericardial effusion. The mea ...
... vessel. Then, a stiff stylet was inserted and kept into the CS lead and end of the stylet was cut by a scissor (permanent stylet technique). Pacing and sensing properties of all leads were checked and the guiding sheath was removed. Control echocardiography did not show pericardial effusion. The mea ...
Controlled Trial of Physical Training in Chronic Heart
... Inclusion criteria were stable New York Heart Association class 11-III heart failure of at least 3 months' duration; ischemic etiology (as evidenced by documented myocardial infarction and/or coronary arteriography and coronary bypass surgery); stable sinus rhythm; limitation of exercise by symptoms ...
... Inclusion criteria were stable New York Heart Association class 11-III heart failure of at least 3 months' duration; ischemic etiology (as evidenced by documented myocardial infarction and/or coronary arteriography and coronary bypass surgery); stable sinus rhythm; limitation of exercise by symptoms ...
EKG Recognition: When to Worry
... • Score sinus tachycardia during sleep for a sustained sinus heart rate of greater than 90 beats per minute (bpm) for adults • Score wide complex tachycardia for a rhythm lasting a minimum of 3 consecutive beats at a rate of greater than 100 bpm with QRS duration of greater than or equal to 120 msec ...
... • Score sinus tachycardia during sleep for a sustained sinus heart rate of greater than 90 beats per minute (bpm) for adults • Score wide complex tachycardia for a rhythm lasting a minimum of 3 consecutive beats at a rate of greater than 100 bpm with QRS duration of greater than or equal to 120 msec ...
Effect of Hyperoxia on Left Ventricular Function and Filling
... consequences in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease or acute respiratory failure, as gas exchange may be worsened by denitrogenation atelectasis and increased intrapulmonary shunting.1,2 Over the last 50 years, it has also been demonstrated3,4 that hyperoxia results in hemodynamic alterat ...
... consequences in patients with chronic obstructive lung disease or acute respiratory failure, as gas exchange may be worsened by denitrogenation atelectasis and increased intrapulmonary shunting.1,2 Over the last 50 years, it has also been demonstrated3,4 that hyperoxia results in hemodynamic alterat ...
Persistent ductus arteriosus
... A coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing of the aorta at or just distal to the insertion of the ductus arteriosus (distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery. Rarely it can occur proximal to the left subclavian. It occurs twice as commonly in men as in women. It is also associated with Tur ...
... A coarctation of the aorta is a narrowing of the aorta at or just distal to the insertion of the ductus arteriosus (distal to the origin of the left subclavian artery. Rarely it can occur proximal to the left subclavian. It occurs twice as commonly in men as in women. It is also associated with Tur ...
What is a heart attack
... health problems usually do not arise until later in adulthood when the arterial narrowing becomes severe. Smoking cigarettes, high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and diabetes mellitus can accelerate atherosclerosis and lead to the earlier onset of symptoms and complications, particularly in t ...
... health problems usually do not arise until later in adulthood when the arterial narrowing becomes severe. Smoking cigarettes, high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol, and diabetes mellitus can accelerate atherosclerosis and lead to the earlier onset of symptoms and complications, particularly in t ...
slide_3
... – Signals onset of atrial contraction QRS complex: ventricular depolarization – Signals onset of ventricular contraction.. T wave: repolarization of ventricles PR interval or PQ interval: 0.16 sec – Extends from start of atrial depolarization to start of ventricular depolarization (QRS complex) cont ...
... – Signals onset of atrial contraction QRS complex: ventricular depolarization – Signals onset of ventricular contraction.. T wave: repolarization of ventricles PR interval or PQ interval: 0.16 sec – Extends from start of atrial depolarization to start of ventricular depolarization (QRS complex) cont ...
right → left shunt
... Valve of sinus venosus (L): part of atrial septum Common atrium: rough part of right and left atria and the auricles Embryonic pulmonary vein: large part of the left atrial wall Septum primum: left side of the atrial septum Septum secundum: right side of the atrial septum Foramen secundum: dimple in ...
... Valve of sinus venosus (L): part of atrial septum Common atrium: rough part of right and left atria and the auricles Embryonic pulmonary vein: large part of the left atrial wall Septum primum: left side of the atrial septum Septum secundum: right side of the atrial septum Foramen secundum: dimple in ...
transient severe left ventricular diastolic dysfunction during
... outcome for a wide range of cardiovascular diseases including ischemic heart disease. Echocardiography provides both a quantitative and qualitative measure of systolic and diastolic function1. Intraoperative TEE is a useful monitoring tool for assessing systolic and diastolic function and regional w ...
... outcome for a wide range of cardiovascular diseases including ischemic heart disease. Echocardiography provides both a quantitative and qualitative measure of systolic and diastolic function1. Intraoperative TEE is a useful monitoring tool for assessing systolic and diastolic function and regional w ...
Characterizing the M..
... At a fixed time, after contrast administration, T1 may be reduced in cardiac disease suggesting increased myocardial interstitial space (Table 1, technique 2).[39–41] However, care is needed as the disease may have altered body composition (a higher percentage of body fat and, thus, a greater contra ...
... At a fixed time, after contrast administration, T1 may be reduced in cardiac disease suggesting increased myocardial interstitial space (Table 1, technique 2).[39–41] However, care is needed as the disease may have altered body composition (a higher percentage of body fat and, thus, a greater contra ...
Reverse takotsubo cardiomyopathy with use of
... receptors located in the central nervous system, where it acts to increase blood pressure and heart rate. It has been well acknowledged that with relatively low doses it can produce side effects such as tachycardia, chest pain, hypertension, lacrimation, ...
... receptors located in the central nervous system, where it acts to increase blood pressure and heart rate. It has been well acknowledged that with relatively low doses it can produce side effects such as tachycardia, chest pain, hypertension, lacrimation, ...
Chapter 9 – Enhancing Your Cardiovascular Health
... coronary bypass surgery, in which the coronary obstruction is bypassed by grafting an artery to the aorta to a location just beyond the coronary obstruction. percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty), a procedure in which a coronary catheter is inserted into the narrowed coronary artery and i ...
... coronary bypass surgery, in which the coronary obstruction is bypassed by grafting an artery to the aorta to a location just beyond the coronary obstruction. percutaneous coronary intervention (angioplasty), a procedure in which a coronary catheter is inserted into the narrowed coronary artery and i ...
Exploring Inside a Snowman by Magnetic Resonance Imaging
... he snowman sign is a sign on a chest x-ray image that indicates a supra-cardiac type total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR).1 TAPVR is a serious congenital heart disease which occurs due to an abnormal development of the fetal heart. This leads to an inappropriate connection of all four pul ...
... he snowman sign is a sign on a chest x-ray image that indicates a supra-cardiac type total anomalous pulmonary venous return (TAPVR).1 TAPVR is a serious congenital heart disease which occurs due to an abnormal development of the fetal heart. This leads to an inappropriate connection of all four pul ...
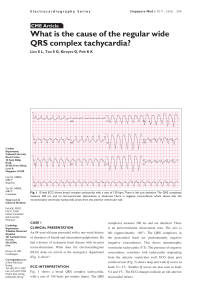
What is the cause of the regular wide QRS
... 9. Mallidi J, Nadkarni GN, Berger RD, Calkins H, Nazarian S. Metaanalysis of catheter ablation as an adjunct to medical therapy for treatment of ventricular tachycardia in patients with structural ...
... 9. Mallidi J, Nadkarni GN, Berger RD, Calkins H, Nazarian S. Metaanalysis of catheter ablation as an adjunct to medical therapy for treatment of ventricular tachycardia in patients with structural ...
LV Dssynchrony and Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy in Heart
... Echocardiographic parameters assessing dyssynchrony do not have enough predictive value to be recommended as selection criteria for CRT beyond current indications ...
... Echocardiographic parameters assessing dyssynchrony do not have enough predictive value to be recommended as selection criteria for CRT beyond current indications ...
Cardiovascular System - Comed.uobaghdad.edu.iq
... The atrioventricular valves (AV valves) are composed of thin membranous cusps (fibrous flaps of tissue covered with endothelium), which hangdown in the ventricular cavities during diastole. After atrial contraction and just before ventricular contraction, the AV valves begin to close and the leaflet ...
... The atrioventricular valves (AV valves) are composed of thin membranous cusps (fibrous flaps of tissue covered with endothelium), which hangdown in the ventricular cavities during diastole. After atrial contraction and just before ventricular contraction, the AV valves begin to close and the leaflet ...
Heart failure

Heart failure (HF), often referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), occurs when the heart is unable to pump sufficiently to maintain blood flow to meet the body's needs. The terms chronic heart failure (CHF) or congestive cardiac failure (CCF) are often used interchangeably with congestive heart failure. Signs and symptoms commonly include shortness of breath, excessive tiredness, and leg swelling. The shortness of breath is usually worse with exercise, while lying down, and may wake the person at night. A limited ability to exercise is also a common feature.Common causes of heart failure include coronary artery disease including a previous myocardial infarction (heart attack), high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, excess alcohol use, infection, and cardiomyopathy of an unknown cause. These cause heart failure by changing either the structure or the functioning of the heart. There are two main types of heart failure: heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction and heart failure with normal ejection fraction depending on if the ability of the left ventricle to contract is affected, or the heart's ability to relax. The severity of disease is usually graded by the degree of problems with exercise. Heart failure is not the same as myocardial infarction (in which part of the heart muscle dies) or cardiac arrest (in which blood flow stops altogether). Other diseases that may have symptoms similar to heart failure include obesity, kidney failure, liver problems, anemia and thyroid disease.The condition is diagnosed based on the history of the symptoms and a physical examination with confirmation by echocardiography. Blood tests, electrocardiography, and chest radiography may be useful to determine the underlying cause. Treatment depends on the severity and cause of the disease. In people with chronic stable mild heart failure, treatment commonly consists of lifestyle modifications such as stopping smoking, physical exercise, and dietary changes, as well as medications. In those with heart failure due to left ventricular dysfunction, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors or angiotensin receptor blockers along with beta blockers are recommended. For those with severe disease, aldosterone antagonists, or hydralazine plus a nitrate may be used. Diuretics are useful for preventing fluid retention. Sometimes, depending on the cause, an implanted device such as a pacemaker or an implantable cardiac defibrillator may be recommended. In some moderate or severe cases cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) may be suggested or cardiac contractility modulation may be of benefit. A ventricular assist device or occasionally a heart transplant may be recommended in those with severe disease despite all other measures.Heart failure is a common, costly, and potentially fatal condition. In developed countries, around 2% of adults have heart failure and in those over the age of 65, this increases to 6–10%. In the year after diagnosis the risk of death is about 35% after which it decreases to below 10% each year. This is similar to the risks with a number of types of cancer. In the United Kingdom the disease is the reason for 5% of emergency hospital admissions. Heart failure has been known since ancient times with the Ebers papyrus commenting on it around 1550 BCE.