Thermodynamics
... The picture above can be used for both a refrigerator and a heat pump. The idea is to get heat inside a house and to put the cold reservoir outside the house. Some heat pumps work with the reservoir as the air around us, while others use ground source heat, which has about the same temperature the w ...
... The picture above can be used for both a refrigerator and a heat pump. The idea is to get heat inside a house and to put the cold reservoir outside the house. Some heat pumps work with the reservoir as the air around us, while others use ground source heat, which has about the same temperature the w ...
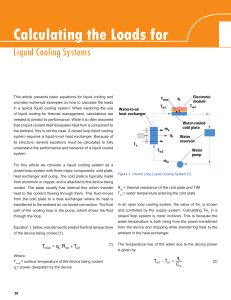
Calculating the Loads for Liquid cooling Systems
... and controlled by the supply system. Calculating Tw1 in a closed loop system is more involved. This is because the water temperature is both rising from the power transferred from the device and dropping while transferring heat to the ambient in the heat exchanger. The temperature rise of the water ...
... and controlled by the supply system. Calculating Tw1 in a closed loop system is more involved. This is because the water temperature is both rising from the power transferred from the device and dropping while transferring heat to the ambient in the heat exchanger. The temperature rise of the water ...
Static and dynamic thermal characterisation of a hollow brick wall
... r (kg/m ) k (W/m K) c (J/kg K) ...
... r (kg/m ) k (W/m K) c (J/kg K) ...
Lesson
... The major cost comes from the digital thermometers and portable stove. The other items can be bought at supermarkets or borrowed from a chemistry classroom. Learning Goals: After this lesson, students should be able to: Understand heat flows from a hot source to a cold source Recall the equation ...
... The major cost comes from the digital thermometers and portable stove. The other items can be bought at supermarkets or borrowed from a chemistry classroom. Learning Goals: After this lesson, students should be able to: Understand heat flows from a hot source to a cold source Recall the equation ...
specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g•°C heat of vaporization of water
... 6) An underwater explosion caused the temperature of a pond to change from 76.0oC to 78.5oC. If the pond has a volume of 10,500 L, how many kilojoules of heat was released by the explosion? What law allows one to assume all heat lost from the explosion was absorbed by the water? Hint: D water = 1.0 ...
... 6) An underwater explosion caused the temperature of a pond to change from 76.0oC to 78.5oC. If the pond has a volume of 10,500 L, how many kilojoules of heat was released by the explosion? What law allows one to assume all heat lost from the explosion was absorbed by the water? Hint: D water = 1.0 ...
U3g L4 4-24 Test Review
... natural eyes. Therefore, infrared photography allows us to “see” the heat given off by objects even if the material is not hot enough for there to be a color change. Test Review ...
... natural eyes. Therefore, infrared photography allows us to “see” the heat given off by objects even if the material is not hot enough for there to be a color change. Test Review ...
16.2 Heat and Thermodynamics
... • Rising hot air cools as it moves away _________ from the heat source. • The cool air contracts, become sinks more dense, and _________ ...
... • Rising hot air cools as it moves away _________ from the heat source. • The cool air contracts, become sinks more dense, and _________ ...
Experiment 5
... phase change (boiling, melting, etc.). The relation is Q = mL (eq. 2) where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the obj ...
... phase change (boiling, melting, etc.). The relation is Q = mL (eq. 2) where L is the latent heat of transformation appropriate for the type of phase change taking place. In using eq. 2, the sign must be chosen appropriately according to the sign convention discussed above. As an example, if the obj ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide - School District of La Crosse
... energy needed to ______one________of a substance is called the heat of fusion of the substance. For an object at its melting point, adding this energy changes the object's, _____________. but not its __________.If the substance is heated after melting is complete, the temperature_____________ When t ...
... energy needed to ______one________of a substance is called the heat of fusion of the substance. For an object at its melting point, adding this energy changes the object's, _____________. but not its __________.If the substance is heated after melting is complete, the temperature_____________ When t ...
Unit 4: Themodynamics
... The overall heat of a reaction (ΔH ) is the sum of the ΔHs of each step in the process Can obtain “heat of formation” (ΔH) data for compounds from tables Formation of 1 mole of compounds from their elements ...
... The overall heat of a reaction (ΔH ) is the sum of the ΔHs of each step in the process Can obtain “heat of formation” (ΔH) data for compounds from tables Formation of 1 mole of compounds from their elements ...
First Law of Thermodynamics - Erwin Sitompul
... thermodynamic process, where: Heat Q can be added to the gas (positive heat) or withdrawn from it (negative heat), by regulating the temperature of the adjustable ...
... thermodynamic process, where: Heat Q can be added to the gas (positive heat) or withdrawn from it (negative heat), by regulating the temperature of the adjustable ...
Advantages of Plate-Type Heat Exchanger over Tube-Type
... Vol. 9, No. 2, June 1999 (ISSN 1053-5381) Copyright © by The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers ...
... Vol. 9, No. 2, June 1999 (ISSN 1053-5381) Copyright © by The International Society of Offshore and Polar Engineers ...
Phase Changes
... temperature from -15 to 0C? 6. How much heat energy must be absorbed to raise the temperature of a 200 gram block of ice from -10 to 0C and then completely melt it to a liquid at the same temperature? 7. How much energy would be required to heat the same 200g of liquid water in #6 (at 0C) to the nor ...
... temperature from -15 to 0C? 6. How much heat energy must be absorbed to raise the temperature of a 200 gram block of ice from -10 to 0C and then completely melt it to a liquid at the same temperature? 7. How much energy would be required to heat the same 200g of liquid water in #6 (at 0C) to the nor ...
Review of 17.1, 17.2 and 17.3 Name: 1.) When 2 moles of NO burn
... by knowing the specific heat of the reactants b. by mixing the reactants in a calorimeter and measuring the temperature change c. by knowing the mass of the reactants d. The enthalpy change for this type of reaction cannot be determined. 11.) During a phase change, the temperature of a substance ___ ...
... by knowing the specific heat of the reactants b. by mixing the reactants in a calorimeter and measuring the temperature change c. by knowing the mass of the reactants d. The enthalpy change for this type of reaction cannot be determined. 11.) During a phase change, the temperature of a substance ___ ...
Sec. 15.1 - Midland Park School District
... the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by one degree Celsius. Energy released from food is measured in Calories. ...
... the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of pure water by one degree Celsius. Energy released from food is measured in Calories. ...