Biology 340 Molecular Biology
... FGF, fibroblast growth factor EGF, epidermal growth factor Insulin ...
... FGF, fibroblast growth factor EGF, epidermal growth factor Insulin ...
Lecture 4
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
... • membrane-integrated (unlimited capacity --> transporter systems: Ca-channels, calcium pumps) • non-membranous (limited capacity --> not only buffering, but processing of signal through conformational changes that enable interaction with target proteins: Calmodulin, Troponin C ...) ...
Long distance signaling
... a series of chemical changes that cause the response. This series of chemical events that occur is called the signal-transduction path way. The new a/alpha cell has all the genes from both the different haploid yeast cells. These pathways are common to both humans and yeast cells suggesting that thi ...
... a series of chemical changes that cause the response. This series of chemical events that occur is called the signal-transduction path way. The new a/alpha cell has all the genes from both the different haploid yeast cells. These pathways are common to both humans and yeast cells suggesting that thi ...
Lymphatic System and Immunity Levels of Organization
... organizational levels will build throughout the development of modules within this unit. 1. Molecular level of organization includes 4 general categories of molecules: a. Three main types of antimicrobial substances (interferon, complement, iron-binding transferrins) b. Substances that contribute to ...
... organizational levels will build throughout the development of modules within this unit. 1. Molecular level of organization includes 4 general categories of molecules: a. Three main types of antimicrobial substances (interferon, complement, iron-binding transferrins) b. Substances that contribute to ...
inflammation 1
... • Acute: rapid onset, short duration, fluid and plasma protein exudation, predominantly neutrophils. • Chronic: insidious onset, longer duration ( days to years), lymphocytes and macrophages, vascular proliferation and fibrosis. ...
... • Acute: rapid onset, short duration, fluid and plasma protein exudation, predominantly neutrophils. • Chronic: insidious onset, longer duration ( days to years), lymphocytes and macrophages, vascular proliferation and fibrosis. ...
Cell-to-cell signaling is important to both multicellular organims and
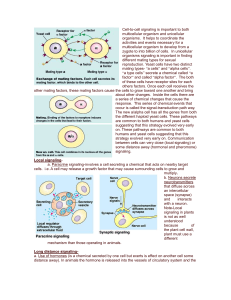
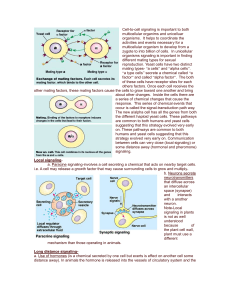
... suggesting that this strategy evolved very early on. These pathways are common to both humans and yeast cells suggesting that this strategy evolved very early on. Communication between cells can very close (local signaling) or some distance away (hormonal and pheromone) signaling. Local signalinga. ...
... suggesting that this strategy evolved very early on. These pathways are common to both humans and yeast cells suggesting that this strategy evolved very early on. Communication between cells can very close (local signaling) or some distance away (hormonal and pheromone) signaling. Local signalinga. ...
Review questions: Week 1 Nonet * cell biology Nonet * axon
... • Astrocytes – Regulate extracellular K+ – Remove excess glutamate – Regulate extracellular Na+ – Supply neurons with glutamate – Supply neurons with glutamine – Control local blood flow – Transport glucose to neurons – Transport oxygen to neurons Choose 1 or more ...
... • Astrocytes – Regulate extracellular K+ – Remove excess glutamate – Regulate extracellular Na+ – Supply neurons with glutamate – Supply neurons with glutamine – Control local blood flow – Transport glucose to neurons – Transport oxygen to neurons Choose 1 or more ...
No Slide Title
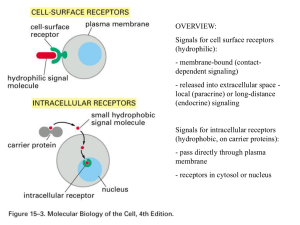
... - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
... - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
Document
... • Prominent in muscle and nerve—e.g. electrical tissues • Form of cell-cell communication ...
... • Prominent in muscle and nerve—e.g. electrical tissues • Form of cell-cell communication ...
PROTEASE SWITCHES: PATHWAYS TO INFLAMMATION AND PAIN
... CGRP in acidified early endosomes, causing disassembly of the peptide/receptor/-arrestin/Src MAP kinase signalosome. This novel mechanism allows receptors, freed of -arrestins, to recycle and resensitize, and terminates -arrestin-mediated activation of ERK1/2 and p38. Disruption of this mechanism ...
... CGRP in acidified early endosomes, causing disassembly of the peptide/receptor/-arrestin/Src MAP kinase signalosome. This novel mechanism allows receptors, freed of -arrestins, to recycle and resensitize, and terminates -arrestin-mediated activation of ERK1/2 and p38. Disruption of this mechanism ...
Student notes
... o How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligand-gated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction o How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca 2+ ions) and protein kinases. o Ho ...
... o How G protein-coupled receptors, receptor tyrosine kinases, ligand-gated ion channels, and intracellular receptors receive cell signals and start transduction o How a cell signal is amplified by a phosphorylation cascade, via second messengers (such as cAMP or Ca 2+ ions) and protein kinases. o Ho ...
Mitochondrial Mechanisms of Photobiomodulation in Context of New
... that ATP is not only an energy currency inside cells, but it is also a critical signaling molecule that allows cells and tissues throughout the body to communicate with one another.15 This new aspect of ATP as an intercellular signaling molecule allows broadening the understanding of universality ph ...
... that ATP is not only an energy currency inside cells, but it is also a critical signaling molecule that allows cells and tissues throughout the body to communicate with one another.15 This new aspect of ATP as an intercellular signaling molecule allows broadening the understanding of universality ph ...
The Molecules of Life
... They are the fuel the body uses to sustain itself. The most important one to know is Glucose – a simple sugar that the body ‘burns’ to create its energy or ATP. ...
... They are the fuel the body uses to sustain itself. The most important one to know is Glucose – a simple sugar that the body ‘burns’ to create its energy or ATP. ...
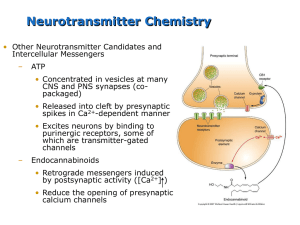
Purinergic signalling
Purinergic signalling (or signaling: see American and British English differences) is a form of extracellular signalling mediated by purine nucleotides and nucleosides such as adenosine and ATP. It involves the activation of purinergic receptors in the cell and/or in nearby cells, thereby regulating cellular functions.The purinergic signalling complex of a cell is sometimes referred to as the “purinome”.