Effects of Neuronal Activity on Glial Cells
... specific synaptic activity. Synaptic actions are confined to specialized regions on neuronal cell bodies and dendrites, and they may be excitatory or inhibitory. In contrast, signaling by potassium is not confined to structures containing receptors but occurs anywhere the glial cell is exposed to po ...
... specific synaptic activity. Synaptic actions are confined to specialized regions on neuronal cell bodies and dendrites, and they may be excitatory or inhibitory. In contrast, signaling by potassium is not confined to structures containing receptors but occurs anywhere the glial cell is exposed to po ...
Lysis of Human Monocytic Leukemia Cells by
... to ADP. Only IFN-y-treated cells showed a slight sensitivity (10.4% k 0.2% specific lysis) to ADP at 1.25 mmol/L, which was unlike human IFN-treated macrophages in which no susceptibility to ADP-mediated lysis was noted.5 Time course of IFN-y-induced efects. The timing of the addition of IFN-y to th ...
... to ADP. Only IFN-y-treated cells showed a slight sensitivity (10.4% k 0.2% specific lysis) to ADP at 1.25 mmol/L, which was unlike human IFN-treated macrophages in which no susceptibility to ADP-mediated lysis was noted.5 Time course of IFN-y-induced efects. The timing of the addition of IFN-y to th ...
Get PDF
... injected with GFP cDNA (Couve et al., 1998). This lack of functional inhibition of Ca 2⫹ currents in SCG is in agreement with the endoplasmic reticulum retention of GABABR1 after homomeric expression in neurons. In neurons injected with cDNAs for GABABR1a and GABABR2, bath application of 50 M baclo ...
... injected with GFP cDNA (Couve et al., 1998). This lack of functional inhibition of Ca 2⫹ currents in SCG is in agreement with the endoplasmic reticulum retention of GABABR1 after homomeric expression in neurons. In neurons injected with cDNAs for GABABR1a and GABABR2, bath application of 50 M baclo ...
ATP-driven Pumps
... Comparing this structure with that in Ca2+- free (E2) state…… 1. Kinase activity unleashes N domain from P domain 2. A domain associates with N & P domains, exerts downward push on M3/M4, opening luminal pathway for Ca2+ release 3. ATP binding prevents reversal, ...
... Comparing this structure with that in Ca2+- free (E2) state…… 1. Kinase activity unleashes N domain from P domain 2. A domain associates with N & P domains, exerts downward push on M3/M4, opening luminal pathway for Ca2+ release 3. ATP binding prevents reversal, ...
Regulation of glycolysis ang glycogen metabolism
... Insulin (produced in the pancreas) is released into the bloodstream. It signals cells to synthesize glycogen (glycogenesis), accelerates glycolysis and inhibits glucose synthesis. If we have enough glycogen, the extra glucose is converted to fat. ...
... Insulin (produced in the pancreas) is released into the bloodstream. It signals cells to synthesize glycogen (glycogenesis), accelerates glycolysis and inhibits glucose synthesis. If we have enough glycogen, the extra glucose is converted to fat. ...
Cannabinoid Signaling and Lipid Rafts
... Cannabinoid Signaling and Lipid Rafts More evidence is showing that CB1 receptor binding, signaling, anandamide transport, and 2-AG synthesis is influenced by lipid rafts. The plasma membrane is a highly disordered phospholipid by-layer that consists of compartmentalized microdomains. These microdom ...
... Cannabinoid Signaling and Lipid Rafts More evidence is showing that CB1 receptor binding, signaling, anandamide transport, and 2-AG synthesis is influenced by lipid rafts. The plasma membrane is a highly disordered phospholipid by-layer that consists of compartmentalized microdomains. These microdom ...
- Wiley Online Library
... The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2015/16 provides concise overviews of the key properties of over 1750 human drug targets with their pharmacology, plus links to an open access knowledgebase of drug targets and their ligands (www.guidetopharmacology.org), which provides more detailed views of target ...
... The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2015/16 provides concise overviews of the key properties of over 1750 human drug targets with their pharmacology, plus links to an open access knowledgebase of drug targets and their ligands (www.guidetopharmacology.org), which provides more detailed views of target ...
Glial Cell Inhibition of Neurons by Release of ATP
... microscopy. Responses of neurons to glial cell stimulation were monitored in whole-cell voltage- and current-clamp recordings. Ejection of agonists onto the retinal surface often evoked Ca 2⫹ increases in astrocytes and Müller cells. Glial cells displaying such Ca 2⫹ increases are referred to as be ...
... microscopy. Responses of neurons to glial cell stimulation were monitored in whole-cell voltage- and current-clamp recordings. Ejection of agonists onto the retinal surface often evoked Ca 2⫹ increases in astrocytes and Müller cells. Glial cells displaying such Ca 2⫹ increases are referred to as be ...
EMBO REPORT SUPPLEMENTARY SECTION Quantitation of
... through the inhibition of positive cell cycle regulators, such as cdks and cyclins. By midneural plate stages, cyclin A2 and cdk2 messages become detectable and are most strongly expressed in prospective dorso-anterior neural tissue (Vernon and Philpott, 2003) and Figure S2A, B), although expression ...
... through the inhibition of positive cell cycle regulators, such as cdks and cyclins. By midneural plate stages, cyclin A2 and cdk2 messages become detectable and are most strongly expressed in prospective dorso-anterior neural tissue (Vernon and Philpott, 2003) and Figure S2A, B), although expression ...
Targeting cell surface receptors for axon regeneration in the central
... After injury, axon regeneration in the adult central nervous system (CNS) is a challenging task. In addition to facing a plethora of growth inhibitory molecules such as chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG), myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and Nogo in the environment, injured neurons also la ...
... After injury, axon regeneration in the adult central nervous system (CNS) is a challenging task. In addition to facing a plethora of growth inhibitory molecules such as chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG), myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and Nogo in the environment, injured neurons also la ...
INVITED SUBMISSION FOR PERSPECTIVE (Revised)
... After injury, axon regeneration in the adult central nervous system (CNS) is a challenging task. In addition to facing a plethora of growth inhibitory molecules such as chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG), myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and Nogo in the environment, injured neurons also la ...
... After injury, axon regeneration in the adult central nervous system (CNS) is a challenging task. In addition to facing a plethora of growth inhibitory molecules such as chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPG), myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) and Nogo in the environment, injured neurons also la ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... electrical signal in the presynaptic cell is communicated to the postsynaptic cell by a chemical (the neurotransmitter) separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors ...
... electrical signal in the presynaptic cell is communicated to the postsynaptic cell by a chemical (the neurotransmitter) separation between presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes is about 20 to 30 nm a chemical transmitter is released and diffuses to bind to receptors ...
Cell communication
... 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep pathway in the transduction ...
... 1. Describe the nature of a ligand-receptor interaction and state how such interactions initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep pathway in the transduction ...
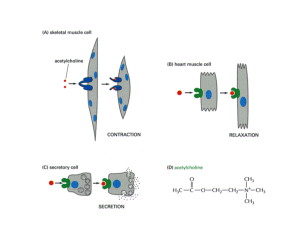
Purinergic signalling
Purinergic signalling (or signaling: see American and British English differences) is a form of extracellular signalling mediated by purine nucleotides and nucleosides such as adenosine and ATP. It involves the activation of purinergic receptors in the cell and/or in nearby cells, thereby regulating cellular functions.The purinergic signalling complex of a cell is sometimes referred to as the “purinome”.