Objectives: The student shall know the facts, understand the
... Factors that determine the ion distribution and resting membrane potential of neurons and the relative contribution of each EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS Components of neurons and their function(s) Definitions of nerves, tracts, ganglia, and nuclei Response of excitable tissue to depolarizing sti ...
... Factors that determine the ion distribution and resting membrane potential of neurons and the relative contribution of each EXCITABILITY & ACTION POTENTIALS Components of neurons and their function(s) Definitions of nerves, tracts, ganglia, and nuclei Response of excitable tissue to depolarizing sti ...
Chapter 27
... from inside is greater than Na+ gain a net loss of K+ from inside -ve charge inside ...
... from inside is greater than Na+ gain a net loss of K+ from inside -ve charge inside ...
Objectives The Synapse Associated terms Types of Synapses
... Variable in strength depending upon the amount of neurotransmitter released & time it is in the synapse. Usually occur at site of dendrites or cell bodies. Amount of response declines with distance. ...
... Variable in strength depending upon the amount of neurotransmitter released & time it is in the synapse. Usually occur at site of dendrites or cell bodies. Amount of response declines with distance. ...
The NERVOUS SYSTEM
... WHAT HAPPENS WHEN IT CHANGES? Any substance that alters permeability of ...
... WHAT HAPPENS WHEN IT CHANGES? Any substance that alters permeability of ...
document
... many as 10,000 different inputs, and may send its output (the presence or absence of a short-duration spike) to many other neurons. Neurons are wired up in a 3dimensional pattern. Real brains, however, are orders of ...
... many as 10,000 different inputs, and may send its output (the presence or absence of a short-duration spike) to many other neurons. Neurons are wired up in a 3dimensional pattern. Real brains, however, are orders of ...
Teacher Guide
... signal will continue to pass down the neuron. If the graded potential is smaller than the threshold, then an action potential will not occur and the signal will be stopped. Now, as the signal travels through the axon, it will attenuate further. At each node of Ranvier including the axon hillock, the ...
... signal will continue to pass down the neuron. If the graded potential is smaller than the threshold, then an action potential will not occur and the signal will be stopped. Now, as the signal travels through the axon, it will attenuate further. At each node of Ranvier including the axon hillock, the ...
Document
... A neuron can receive synaptic inputs from many other neurons (pyramidal neuron in cerebral cortex can have 1,000 synaptic inputs) ...
... A neuron can receive synaptic inputs from many other neurons (pyramidal neuron in cerebral cortex can have 1,000 synaptic inputs) ...
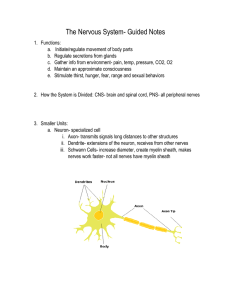
Nervous System Guided Notes
... iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal organs to muscles, brain and heart. v. Bronchi open to allow more air into the lungs vi. Pupils dilate- all in prep for physical activity such as running from a ...
... iii. Sympathetic stimulation- HR and BP increases iv. Blood shift away from the skin and abdominal organs to muscles, brain and heart. v. Bronchi open to allow more air into the lungs vi. Pupils dilate- all in prep for physical activity such as running from a ...
Plasma Membrane/Cell Transport Powerpoint
... 2) Tunnel Proteins: Open tunnels that allow passages ...
... 2) Tunnel Proteins: Open tunnels that allow passages ...
Chapter 2 - Safford Unified School
... 1. Regarding neurons, which of the following is NOT true? A) Each is a single nerve cell. B) They transmit electrical impulses. C) They contain genetic material. D) They are the only cells found in the nervous system. E) They come in three types – motor, sensory, and interneuron. ...
... 1. Regarding neurons, which of the following is NOT true? A) Each is a single nerve cell. B) They transmit electrical impulses. C) They contain genetic material. D) They are the only cells found in the nervous system. E) They come in three types – motor, sensory, and interneuron. ...
ANNB/Biology 261 Exam 1
... 15. All of the following will increase the speed with which an axon conducts action potentials EXCEPT a) Having greater distance between the nodes of Ranvier b) Increasing the diameter of the axon c) Myelinating the axon d) Increasing the number of voltage-gated Na+ channels e) There are no exceptio ...
... 15. All of the following will increase the speed with which an axon conducts action potentials EXCEPT a) Having greater distance between the nodes of Ranvier b) Increasing the diameter of the axon c) Myelinating the axon d) Increasing the number of voltage-gated Na+ channels e) There are no exceptio ...
ppt
... After an action potential occurs, the membrane cannot be stimulated to undergo another action potential. This brief period of time (usually a few milliseconds) is called the refractory period of the membrane. The events that occur in an action potential continue down the length of the axon unt ...
... After an action potential occurs, the membrane cannot be stimulated to undergo another action potential. This brief period of time (usually a few milliseconds) is called the refractory period of the membrane. The events that occur in an action potential continue down the length of the axon unt ...
in the central nervous system
... meters/sec b) Large myelinated neuron’s speed ~ 100 meters/sec Myelinated neurons are faster because the impulse “jumps” from one node of Ranvier to the next node of Ranvier This is called SALTATORY CONDUCTION ...
... meters/sec b) Large myelinated neuron’s speed ~ 100 meters/sec Myelinated neurons are faster because the impulse “jumps” from one node of Ranvier to the next node of Ranvier This is called SALTATORY CONDUCTION ...
The Nervous System
... – Long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrite of the next neuron – Can be short or several feet long ...
... – Long fiber that carries the impulses away from the cell body toward the dendrite of the next neuron – Can be short or several feet long ...
Biology 30 NERVOUS SYSTEM
... Dorsal Root Ganglion – entry of sensory neurons to spinal cord and CNS, ganglion is the collection of cell bodies Ventral Root – exit of motor neurons from the spinal cord White Matter – contains myelinated nerve cells Grey Matter – contains un-myelinated nerve cells Meninges – 3 protective ...
... Dorsal Root Ganglion – entry of sensory neurons to spinal cord and CNS, ganglion is the collection of cell bodies Ventral Root – exit of motor neurons from the spinal cord White Matter – contains myelinated nerve cells Grey Matter – contains un-myelinated nerve cells Meninges – 3 protective ...
chapter 2 - Angelfire
... Sometimes axons have many branches at their ends and each branch forms a synapse on dendrites or cell bodies in the same region. These branches are called terminal arbor. Some axons have synapses at swollen regions along their length. These swellings are called boutons en passant. When a neuro ...
... Sometimes axons have many branches at their ends and each branch forms a synapse on dendrites or cell bodies in the same region. These branches are called terminal arbor. Some axons have synapses at swollen regions along their length. These swellings are called boutons en passant. When a neuro ...
some of Chapter 25 - Concordia College
... opens and closes more slowly lets potassium flow out of cell repolarizes membrane ...
... opens and closes more slowly lets potassium flow out of cell repolarizes membrane ...
File
... • The movement of an action potential down a neuron is caused by the moving exchange of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions moving in and out of the cell. • The movement of an action potential through a neuron consists of 2 main stages : depolarization and repolarization. ...
... • The movement of an action potential down a neuron is caused by the moving exchange of sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) ions moving in and out of the cell. • The movement of an action potential through a neuron consists of 2 main stages : depolarization and repolarization. ...
Ramon y Cajal deduced basic functioning of neuron
... suppresses expression of NCAM and NGF receptors. ...
... suppresses expression of NCAM and NGF receptors. ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... 14C in the atmosphere reacts with oxygen and forms CO2, which enters the biotope through photosynthesis. Our consumption of plants, and of animals that live off plants, results in 14C levels in the human body paralleling those in the atmosphere. Most molecules in a cell are in constant flux, with th ...
... 14C in the atmosphere reacts with oxygen and forms CO2, which enters the biotope through photosynthesis. Our consumption of plants, and of animals that live off plants, results in 14C levels in the human body paralleling those in the atmosphere. Most molecules in a cell are in constant flux, with th ...
Node of Ranvier

The nodes of Ranvier also known as myelin sheath gaps, are the gaps (approximately 1 micrometer in length) formed between the myelin sheaths generated by different cells. A myelin sheath is a many-layered coating, largely composed of a fatty substance called myelin, that wraps around the axon of a neuron and very efficiently insulates it. At nodes of Ranvier, the axonal membrane is uninsulated and, therefore, capable of generating electrical activity.