GE 121 Physical and Historical Geology I Earth’s Dynamic Systems 10
... (4) sediment load, and (5) base level. 4. The variables in a stream constantly adjust toward a state of equilibrium. 5. Rivers erode by (1) removing regolith, (2) downcutting, and (3) headward erosion. 6. As a river develops a low gradient, it deposits part of its load on point bars, on natural leve ...
... (4) sediment load, and (5) base level. 4. The variables in a stream constantly adjust toward a state of equilibrium. 5. Rivers erode by (1) removing regolith, (2) downcutting, and (3) headward erosion. 6. As a river develops a low gradient, it deposits part of its load on point bars, on natural leve ...
earthquake
... – Accordion-like motion shaking – Rock material squeezes together and spreads apart repeatedly – This motion produces seismic waves that move in the same direction that the rock is shaking – They are the fastest seismic wave- the first to reach any faraway location – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2 ...
... – Accordion-like motion shaking – Rock material squeezes together and spreads apart repeatedly – This motion produces seismic waves that move in the same direction that the rock is shaking – They are the fastest seismic wave- the first to reach any faraway location – http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2 ...
Notes - Earth Science Rocks
... Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust. How Plates Move The lower part of the mantle is called the athenosphere. This layer has similar composition to the upper mantle, but it is partially melted. This makes the athenosphere like a very thick “liquid” (you can compare solid rock to very th ...
... Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust. How Plates Move The lower part of the mantle is called the athenosphere. This layer has similar composition to the upper mantle, but it is partially melted. This makes the athenosphere like a very thick “liquid” (you can compare solid rock to very th ...
Rev-sheet-English
... 35. ------------------------------layer catches the most sunlight, and exposed to the wind ,so that emergent trees have----------------------and-------------leaves that protect them the sun and wind. 36.To save the rainforest ,we have to discourage buying the products that are made from the rainfor ...
... 35. ------------------------------layer catches the most sunlight, and exposed to the wind ,so that emergent trees have----------------------and-------------leaves that protect them the sun and wind. 36.To save the rainforest ,we have to discourage buying the products that are made from the rainfor ...
Chp 12.2- Features of Plate Tectonics
... – also help us learn about the composition and distances of the Earth’s interior. ...
... – also help us learn about the composition and distances of the Earth’s interior. ...
Introduction to Earth Science
... encompassing heading of Earth science. These include geology, oceanography, meteorology, astronomy, and environmental science. It goes on to introduce the concept of scales of space and time. The nature of scientific inquiry is discussed. The chapter explains the origins and creation of the Earth an ...
... encompassing heading of Earth science. These include geology, oceanography, meteorology, astronomy, and environmental science. It goes on to introduce the concept of scales of space and time. The nature of scientific inquiry is discussed. The chapter explains the origins and creation of the Earth an ...
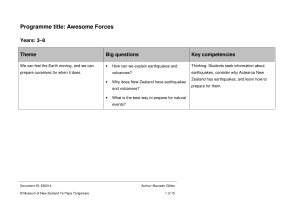
Programme title: Awesome Forces
... In this programme, students explore the inner workings of our planet. They experience what it is like at the centre of the Earth and uncover the layers of the Earth. Students piece together the puzzle of plate tectonics before investigating the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes. Finally, they disc ...
... In this programme, students explore the inner workings of our planet. They experience what it is like at the centre of the Earth and uncover the layers of the Earth. Students piece together the puzzle of plate tectonics before investigating the causes of earthquakes and volcanoes. Finally, they disc ...
How Earthquakes Happen
... stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, break and "snap" to a new position. Most earthquakes occur at the boundaries of these plates. The point where the fault first slips is the "focus" or "hypocenter" of the earthquake. A theoretical point on the earth's surface directly above the focus is the " ...
... stress exceeds the strength of the rocks, break and "snap" to a new position. Most earthquakes occur at the boundaries of these plates. The point where the fault first slips is the "focus" or "hypocenter" of the earthquake. A theoretical point on the earth's surface directly above the focus is the " ...
Geology and Nonrenewable Mineral Resources - Baxley
... How do we find and extract mineral resources from the earth’s crust, and what harmful environmental effects result from removing and using these minerals? ...
... How do we find and extract mineral resources from the earth’s crust, and what harmful environmental effects result from removing and using these minerals? ...
No Slide Title
... When S-waves hit the outer liquid core, they stop. This creates a S-wave shadow at locations greater than 103º from the focus of the earthquake. ...
... When S-waves hit the outer liquid core, they stop. This creates a S-wave shadow at locations greater than 103º from the focus of the earthquake. ...
earthquakes1
... When S-waves hit the outer liquid core, they stop. This creates a S-wave shadow at locations greater than 103º from the focus of the earthquake. ...
... When S-waves hit the outer liquid core, they stop. This creates a S-wave shadow at locations greater than 103º from the focus of the earthquake. ...
Exam Review with Answers
... independent variable, the answer should be one. If there was more than one than you do not know which of the variables caused the results to turn out the way that they did. 4. Why is accurate record keeping necessary during a scientific investigation? So that someone else can replicate your experime ...
... independent variable, the answer should be one. If there was more than one than you do not know which of the variables caused the results to turn out the way that they did. 4. Why is accurate record keeping necessary during a scientific investigation? So that someone else can replicate your experime ...
Inner Structure of the Earth - Relevance to Earthquakes
... and sima (Suess,1831–1914). It is estimated that sima starts about 11 km below the Conrad discontinuity (a second order discontinuity). The uppermost mantle together with the crust constitutes the lithosphere. The crust-mantle boundary occurs as two physically different events. First, there is a dis ...
... and sima (Suess,1831–1914). It is estimated that sima starts about 11 km below the Conrad discontinuity (a second order discontinuity). The uppermost mantle together with the crust constitutes the lithosphere. The crust-mantle boundary occurs as two physically different events. First, there is a dis ...
Chapter 10: Section 1 Continental Drift
... • Convection is the movement of heated material due to differences in density that are caused by differences in temperatures. • The convection process can be modeled by boiling water in a pot on the stove. As the water at the bottom of the pot is heated, the water at the bottom expands and becomes l ...
... • Convection is the movement of heated material due to differences in density that are caused by differences in temperatures. • The convection process can be modeled by boiling water in a pot on the stove. As the water at the bottom of the pot is heated, the water at the bottom expands and becomes l ...
Chapter 3 section 1 2015
... largest magnitude ever recorded is 9.5. Magnitudes greater than 7.0 cause widespread damage. • Each increase of magnitude by one whole number indicates the release of 31.7 times more energy than the whole number below it. ...
... largest magnitude ever recorded is 9.5. Magnitudes greater than 7.0 cause widespread damage. • Each increase of magnitude by one whole number indicates the release of 31.7 times more energy than the whole number below it. ...
msword - rgs.org
... was caused by a giant earthquake where one of the earth’s major tectonic plates – the Indo-Australian plate (A) – collides with the smaller Burma microplate (B) at a rate of about 6 cm/year. At this destructive plate boundary, the denser Indo-Australian plate is subducted beneath the overriding Burm ...
... was caused by a giant earthquake where one of the earth’s major tectonic plates – the Indo-Australian plate (A) – collides with the smaller Burma microplate (B) at a rate of about 6 cm/year. At this destructive plate boundary, the denser Indo-Australian plate is subducted beneath the overriding Burm ...
Chapter 18
... Theory of Plate Tectonics • Continental shapes suggest that the continents were at one time together, breaking apart and moving to their present position sometime in the past. For example, the Americas and Europe and Africa. • A geologist named Wegener in the early 1900’s believed that at one time ...
... Theory of Plate Tectonics • Continental shapes suggest that the continents were at one time together, breaking apart and moving to their present position sometime in the past. For example, the Americas and Europe and Africa. • A geologist named Wegener in the early 1900’s believed that at one time ...
File
... Pangaea From Greek Means all land Wegener revived the early idea of continental drift, contending that all of the present-day continents were connected. He called the super continental mass Pangaea ...
... Pangaea From Greek Means all land Wegener revived the early idea of continental drift, contending that all of the present-day continents were connected. He called the super continental mass Pangaea ...
Plate Tectonics Edible Model
... Core Standards: www.state.nj.us/njded/cccs/ Objective: To build a model using edible materials to model the Theory of Continental drift or Plate Tectonics: Background: “The Earth’s crust is broken up into a series of plates that move to form mountains, spreading centers and earthquakes. There are th ...
... Core Standards: www.state.nj.us/njded/cccs/ Objective: To build a model using edible materials to model the Theory of Continental drift or Plate Tectonics: Background: “The Earth’s crust is broken up into a series of plates that move to form mountains, spreading centers and earthquakes. There are th ...
Chapter 6 lesson 1-4
... Isotopes- are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but have different number of neutrons. Radioactive Decay- radioactive isotopes breaking down into stable isotopes of other elements. Radiometric Dating- determining the absolute age of a sample based on the ratio of parent ...
... Isotopes- are atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but have different number of neutrons. Radioactive Decay- radioactive isotopes breaking down into stable isotopes of other elements. Radiometric Dating- determining the absolute age of a sample based on the ratio of parent ...
Volcanoes, Earthquakes, Plates after
... *Lava flows not only from the top but also from the cracks in the ground. *Slow to erupt so usually animals and people have enough time to escape. *Some of the largest volcanoes in the world ...
... *Lava flows not only from the top but also from the cracks in the ground. *Slow to erupt so usually animals and people have enough time to escape. *Some of the largest volcanoes in the world ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.