Hearing and Equilibrium - Liberty Hill High School
... Word Bank: cochlea, eustachian tube, external auditory meatus, inner ear, labyrinth, middle ear, ossicles, outer ear, pinna, semicircular canals, tympanic membrane, vestibule, vestibulocochlear nerve ...
... Word Bank: cochlea, eustachian tube, external auditory meatus, inner ear, labyrinth, middle ear, ossicles, outer ear, pinna, semicircular canals, tympanic membrane, vestibule, vestibulocochlear nerve ...
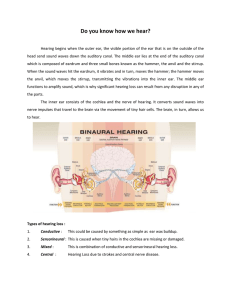
Do you know how we hear
... which is composed of eardrum and three small bones known as the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. When the sound waves hit the eardrum, it vibrates and in turn, moves the hammer; the hammer moves the anvil, which moves the stirrup, transmitting the vibrations into the inner ear. The middle ear func ...
... which is composed of eardrum and three small bones known as the hammer, the anvil and the stirrup. When the sound waves hit the eardrum, it vibrates and in turn, moves the hammer; the hammer moves the anvil, which moves the stirrup, transmitting the vibrations into the inner ear. The middle ear func ...
Your Ears - Hearing Association
... The nerve impulses are sent along the auditory nerve and the auditory processing centres in the brain. The balance part of the inner ear consists of three fluid-filled loops which act like a gyroscope and tell us which way is up, and how we are moving. Auditory brain areas The auditory brain areas i ...
... The nerve impulses are sent along the auditory nerve and the auditory processing centres in the brain. The balance part of the inner ear consists of three fluid-filled loops which act like a gyroscope and tell us which way is up, and how we are moving. Auditory brain areas The auditory brain areas i ...
Meniers disease PPT Dr Javed shah
... • Eyes, Nystagmus in Acute attack towards the unaffected ear WRONG WAY, +eye movements+Corneal reflex • Tuning fork test, And diplacusis ...
... • Eyes, Nystagmus in Acute attack towards the unaffected ear WRONG WAY, +eye movements+Corneal reflex • Tuning fork test, And diplacusis ...
Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear
... (Hearing loss in the Inner Ear) Known etiologies• Multiple Sclerosis • Leukemia • Sickle cell • syphilis • Bacterial infection( meningitis) • Mumps • ototoxic drugs (aspirin) • tumor (from cell phones?) • noise explosion • menieres disease • genetic connexin 26 • toys- noise levels • membrane ruptur ...
... (Hearing loss in the Inner Ear) Known etiologies• Multiple Sclerosis • Leukemia • Sickle cell • syphilis • Bacterial infection( meningitis) • Mumps • ototoxic drugs (aspirin) • tumor (from cell phones?) • noise explosion • menieres disease • genetic connexin 26 • toys- noise levels • membrane ruptur ...
Auditory Periphery - Center for Neural Science
... tip links from higher cilia pull up ion channel gates on adjoining cilia. ...
... tip links from higher cilia pull up ion channel gates on adjoining cilia. ...
Auditory Neuroscience - University of Sunderland
... from all lower nuclei and the contralateral IC. • The anterior portion of the laminae receive cortical inputs, while the posterior portion receives brainstem and IC inputs. • Stellate cells also present that cross the laminae. • Recently it has been found that the signal at the IC is normalized in i ...
... from all lower nuclei and the contralateral IC. • The anterior portion of the laminae receive cortical inputs, while the posterior portion receives brainstem and IC inputs. • Stellate cells also present that cross the laminae. • Recently it has been found that the signal at the IC is normalized in i ...
Children and Cochlear Implants
... A cochlear implant is an electronic device, that bypasses the damaged hair cells of the cochlea and stimulates the auditory nerve directly. It can provide the child with useful “hearing” and improved communication abilities in the ...
... A cochlear implant is an electronic device, that bypasses the damaged hair cells of the cochlea and stimulates the auditory nerve directly. It can provide the child with useful “hearing” and improved communication abilities in the ...
Biophysics of sensory receptors
... Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) They amplify eardrum resonance and transmit it to the oval window. ...
... Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) They amplify eardrum resonance and transmit it to the oval window. ...
Overview/Motivation
... Static: standing on one leg Dynamic: standing on one leg while moving arms. Which is more important? For sports? o The ends of the semicircular canals connect with the utricle, and the utricle connects with the saccule. While the semicircular canals provide information about movement of the he ...
... Static: standing on one leg Dynamic: standing on one leg while moving arms. Which is more important? For sports? o The ends of the semicircular canals connect with the utricle, and the utricle connects with the saccule. While the semicircular canals provide information about movement of the he ...
Lecture15 - hearing anatomy and physics of sound
... Sensorineural Hearing Loss Results from damage to the cochlea or the auditory nerve and upwards (CAS). The ...
... Sensorineural Hearing Loss Results from damage to the cochlea or the auditory nerve and upwards (CAS). The ...
Lecture15 - hearing anatomy and physics of sound
... Sensorineural Hearing Loss Results from damage to the cochlea or the auditory nerve and upwards (CAS). The ...
... Sensorineural Hearing Loss Results from damage to the cochlea or the auditory nerve and upwards (CAS). The ...
International Symposium on Inner Ear Research
... birds and other non-mammalian vertebrates and to find ways to coax the mammalian inner ear into this capability. I will provide an update on this work from our laboratories at the Virginia Merrill Bloedel Center and other laboratories. Studies of birds and other nonmammalian vertebrates are providin ...
... birds and other non-mammalian vertebrates and to find ways to coax the mammalian inner ear into this capability. I will provide an update on this work from our laboratories at the Virginia Merrill Bloedel Center and other laboratories. Studies of birds and other nonmammalian vertebrates are providin ...
No Slide Title
... • Pitch is perceived based on which portion of the basilar membrane is stimulated • The traveling wave peak is fairly precise because of modulation with outer hair cells (motile response) ...
... • Pitch is perceived based on which portion of the basilar membrane is stimulated • The traveling wave peak is fairly precise because of modulation with outer hair cells (motile response) ...
Ch11
... Updating Békésy’s: The Cochlear Amplifier • Békésy used basilar membranes isolated from cadavers and his results showed no difference in response for close frequencies that people can distinguish. ...
... Updating Békésy’s: The Cochlear Amplifier • Békésy used basilar membranes isolated from cadavers and his results showed no difference in response for close frequencies that people can distinguish. ...
chapter11 (new window)
... Updating Békésy’s: The Cochlear Amplifier • Békésy used basilar membranes isolated from cadavers and his results showed no difference in response for close frequencies that people can distinguish. ...
... Updating Békésy’s: The Cochlear Amplifier • Békésy used basilar membranes isolated from cadavers and his results showed no difference in response for close frequencies that people can distinguish. ...
Lesson 1 Notes
... a vacuum is a place with no matter at all (ex. outer space); sound cannot travel in a vacuum How do we hear sounds? 1. Sound waves travel from source to the ear drum 2. The ear drum transfers the vibrations to 3 tiny bones in the middle ear (hammer, anvil, and stirrup). The bones carry the vibrati ...
... a vacuum is a place with no matter at all (ex. outer space); sound cannot travel in a vacuum How do we hear sounds? 1. Sound waves travel from source to the ear drum 2. The ear drum transfers the vibrations to 3 tiny bones in the middle ear (hammer, anvil, and stirrup). The bones carry the vibrati ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.