Manuscript Instruction
... Keywords: Cochlear nonlinearity, Outer hair cells, Awake preparation, Round window, Hearing sensitivity, SPL dependency ...
... Keywords: Cochlear nonlinearity, Outer hair cells, Awake preparation, Round window, Hearing sensitivity, SPL dependency ...
Hearing Aids & Cochlear Implants
... Not very pretty, bulky, impractical. Range of sound frequencies that are amplified depends on resonance of device and is usually not well matched to the patient's needs. Amplification provided by ear trumpet is strictly linear, yet non-linear (“compressive”) amplification would provide better compen ...
... Not very pretty, bulky, impractical. Range of sound frequencies that are amplified depends on resonance of device and is usually not well matched to the patient's needs. Amplification provided by ear trumpet is strictly linear, yet non-linear (“compressive”) amplification would provide better compen ...
Anatomy of the Ear
... full length of Scala Media resides on basilar membrane lined with nerve endings come together to make 8th nerve ...
... full length of Scala Media resides on basilar membrane lined with nerve endings come together to make 8th nerve ...
Why do loud noises cause your ears to ring
... When you hear exceptionally loud noises, your stereocilia become damaged and mistakenly keep sending sound information to the auditory nerve cells. In the case of rock concerts and fireworks displays, the ringing happens because the tips of some of your stereocilia actually have broken off. You hear ...
... When you hear exceptionally loud noises, your stereocilia become damaged and mistakenly keep sending sound information to the auditory nerve cells. In the case of rock concerts and fireworks displays, the ringing happens because the tips of some of your stereocilia actually have broken off. You hear ...
The Inner Ear: The Basilar Membrane as a Harmonic Oscillator
... Each point of the basilar membrane is modeled as a simple damped harmonic oscillator with mass m(x), damping coefficient r (x), and stiffness (Hooke’s constant) k (x) that vary along the length of the membrane. Let η(x, t) denote the displacement of the membrane at the distance x along the membrane. ...
... Each point of the basilar membrane is modeled as a simple damped harmonic oscillator with mass m(x), damping coefficient r (x), and stiffness (Hooke’s constant) k (x) that vary along the length of the membrane. Let η(x, t) denote the displacement of the membrane at the distance x along the membrane. ...
Unit V Practice Exam – Sensation and Perception
... c. An equal number of rods and cones d. More bipolar cells than an animal active only during the day 13. The brain breaks vision into separate dimensions such as color, depth, movement and form, and works on each aspect simultaneously. This is known as: a. Feature detection c. Accommodation b. Paral ...
... c. An equal number of rods and cones d. More bipolar cells than an animal active only during the day 13. The brain breaks vision into separate dimensions such as color, depth, movement and form, and works on each aspect simultaneously. This is known as: a. Feature detection c. Accommodation b. Paral ...
Interaural Time Difference
... • Differing effect of short distance (i.e., within arms length) v. longer distances • Short distances are dramatically influenced by interaural level differences (ILD) ...
... • Differing effect of short distance (i.e., within arms length) v. longer distances • Short distances are dramatically influenced by interaural level differences (ILD) ...
Somatic and Special Senses
... receptors are hair cells inside the cochlea • The hair cells are attached to membranes. When the membranes vibrate, the hair cells are bent. • This triggers the attached neuron to depolarize, sending the impulse to the temporal lobe of the brain ...
... receptors are hair cells inside the cochlea • The hair cells are attached to membranes. When the membranes vibrate, the hair cells are bent. • This triggers the attached neuron to depolarize, sending the impulse to the temporal lobe of the brain ...
File - Learnin` with burton
... continue to pass along the sound vibrations. • The sound vibrations eventually reach a specialized structure of the inner ear called the Organ of Corti where nerve impulses are generated. The impulses are transmitted to the brain where they are interpreted. ...
... continue to pass along the sound vibrations. • The sound vibrations eventually reach a specialized structure of the inner ear called the Organ of Corti where nerve impulses are generated. The impulses are transmitted to the brain where they are interpreted. ...
The Human Eye - Burroughs Middle School
... A snail-shaped organ of the inner ear filled with fluid Inside the cochlea there are hundreds of special hair-like cells attached to nerve fibers, which can transmit information to the brain by changing sound waves to nerve impulses The brain processes the sounds we hear and lets us distinguish betw ...
... A snail-shaped organ of the inner ear filled with fluid Inside the cochlea there are hundreds of special hair-like cells attached to nerve fibers, which can transmit information to the brain by changing sound waves to nerve impulses The brain processes the sounds we hear and lets us distinguish betw ...
Sensation and Perception - Weebly
... • A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside and allows the bones of the middle ear to vibrate properly. ...
... • A tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose; it equalizes the pressure between the middle ear and the air outside and allows the bones of the middle ear to vibrate properly. ...
Sound and Hearing Study Guide Answer Key What does pitch
... 3. What does an object have to do in order to hear a sound? An object would have to vibrate. 4. Name 3 materials that can absorb sound best: pillows, curtains, and carpets 5. When a sound bounces back to you or is “reflected”, what is that called? It is called an echo. 6. In order for sound messages ...
... 3. What does an object have to do in order to hear a sound? An object would have to vibrate. 4. Name 3 materials that can absorb sound best: pillows, curtains, and carpets 5. When a sound bounces back to you or is “reflected”, what is that called? It is called an echo. 6. In order for sound messages ...
Ch. 5 - Quia
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
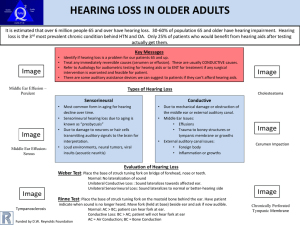
HEARING LOSS in Older Adults
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
File
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
Chapter 05 - Mrs.Meyer`s Class
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
... • A) can be caused by exposure to amplitude over 80 decibels. • B) can be corrected by a hearing aid. • C) is more likely the result of heavy traffic than by a rock concert. • D) all of the above. ...
10b Central Auditory Pathways
... localization -- recent studies show multimodal neurons in the colliculus which share visual and auditory information for orientation movements • Medial Geniculate Nucleus (MGN) Relays information from the SO to A1 Anthony J Greene ...
... localization -- recent studies show multimodal neurons in the colliculus which share visual and auditory information for orientation movements • Medial Geniculate Nucleus (MGN) Relays information from the SO to A1 Anthony J Greene ...
Sound Notes
... • Outer Ear- collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal • Middle Ear- the three bones act as levers to increase the size of vibration • Inner Ear- converts vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to ...
... • Outer Ear- collects sound waves and directs them into the ear canal • Middle Ear- the three bones act as levers to increase the size of vibration • Inner Ear- converts vibrations into electrical signals for the brain to ...
ch_15_lecture_outline_d
... Inferior colliculus Lateral lemniscus Superior olivary nucleus (pons-medulla junction) ...
... Inferior colliculus Lateral lemniscus Superior olivary nucleus (pons-medulla junction) ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.