File
... hair cells are damaged, you may still hear sounds, but the sounds will be distorted. Different hair cells respond to different pitches. Typically, hair cells that respond to higher pitches are lost first. One reason is that the basilar membrane vibrates more vigorously in response to higher pitches. ...
... hair cells are damaged, you may still hear sounds, but the sounds will be distorted. Different hair cells respond to different pitches. Typically, hair cells that respond to higher pitches are lost first. One reason is that the basilar membrane vibrates more vigorously in response to higher pitches. ...
Introduction to Health Science
... specialized region in the inner ear where nerve impulses are generated by cells that detect movement (mechanoreceptors). These nerve impulses travel to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. ...
... specialized region in the inner ear where nerve impulses are generated by cells that detect movement (mechanoreceptors). These nerve impulses travel to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. ...
Information cards
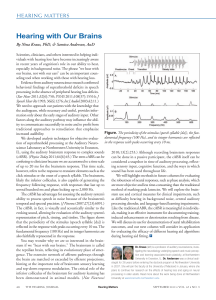
... Sound travels through the air as vibrations or small changes in air pressure. The pinna “catch” these sound waves and their shape helps the brain work out which direction the sound is coming from. The vibrations travel down the ear canal to the eardrum which moves back and forth. Having two ears hel ...
... Sound travels through the air as vibrations or small changes in air pressure. The pinna “catch” these sound waves and their shape helps the brain work out which direction the sound is coming from. The vibrations travel down the ear canal to the eardrum which moves back and forth. Having two ears hel ...
Document
... containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window ...
... containing three tiny bones (hammer, anvil, stirrup) that concentrate the vibrations of the eardrum on the cochlea’s oval window ...
understanding noise injuryes - Audiometry Nurses Association of
... middle ear bones which aid in vibrating the sound energy across to the inner ear. ...
... middle ear bones which aid in vibrating the sound energy across to the inner ear. ...
Document
... affecting the transmission of sound from the environment to the cochlea Maximum loss of 50-60 dBHL, therefore no more than mild/moderate ...
... affecting the transmission of sound from the environment to the cochlea Maximum loss of 50-60 dBHL, therefore no more than mild/moderate ...
Week 2 - Acoustics - Anderson Sound Recording
... Longitudinal waves traveling outwards from their source. These waves consist of alternating areas of high and low pressure (compression and rarefaction) Sound travels at 1130 feet per second (345 meters per second or 770 miles per hour) in dry air at room temperature. As temperature increases, s ...
... Longitudinal waves traveling outwards from their source. These waves consist of alternating areas of high and low pressure (compression and rarefaction) Sound travels at 1130 feet per second (345 meters per second or 770 miles per hour) in dry air at room temperature. As temperature increases, s ...
Signal Transmission in the Auditory System
... Together with our previous finding of neural correlates of musical pitch in interspike intervals of auditorynerve fibers, these results indicate that music perception is constrained by neural processing in the auditory periphery, brainstem and midbrain, and that percepts such as roughness may be cod ...
... Together with our previous finding of neural correlates of musical pitch in interspike intervals of auditorynerve fibers, these results indicate that music perception is constrained by neural processing in the auditory periphery, brainstem and midbrain, and that percepts such as roughness may be cod ...
2016_abstract_template_E
... Keywords: Cochlear nonlinearity, Outer hair cells, Awake preparation, Round window, Hearing sensitivity, SPL dependency ...
... Keywords: Cochlear nonlinearity, Outer hair cells, Awake preparation, Round window, Hearing sensitivity, SPL dependency ...
St. Jude study solves mystery of mammalian ears
... hearing loss, including side effects of chemotherapy for cancer. One strength of St. Jude is that researchers have the ability to ask some very basic questions about how the body works, and then use those answers to solve medical problems in the future.” The long-standing argument centers around out ...
... hearing loss, including side effects of chemotherapy for cancer. One strength of St. Jude is that researchers have the ability to ask some very basic questions about how the body works, and then use those answers to solve medical problems in the future.” The long-standing argument centers around out ...
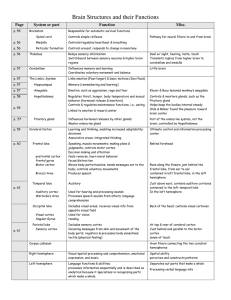
Brain Structures and their Functions
... Processes speech sounds from others; language comprehension ...
... Processes speech sounds from others; language comprehension ...
Inner-Ear Function - Cutis Laxa Research Study
... impacts middle-ear function in ADCL, and WS • There appears to be a higher incidence of hearing loss in ARCL than would be expected in the ...
... impacts middle-ear function in ADCL, and WS • There appears to be a higher incidence of hearing loss in ARCL than would be expected in the ...
hearing loss in older adults
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
... Refer to Audiology for audiometric testing for hearing aids or to ENT for treatment if any surgical intervention is warranted and feasible for patient. There are some auditory assistance devices we can suggest to patients if they can’t afford hearing aids. ...
Auditory system
The auditory system is the sensory system for the sense of hearing. It includes both the sensory organs (the ears) and the auditory parts of the sensory system.