Version A of Chapter 11 Quiz
... ____ 15. What is the speed of a bobsled whose distance-time graph indicates that it traveled 250 m in 25 s? a. 4 m/s c. 0.25 mph b. 250 m/s d. 10 m/s ____ 16. A distance-time graph indicates that an object moves 100 m in 4 s , remains at rest for 1 s, and then moves 150 m in 5 s. What is the average ...
... ____ 15. What is the speed of a bobsled whose distance-time graph indicates that it traveled 250 m in 25 s? a. 4 m/s c. 0.25 mph b. 250 m/s d. 10 m/s ____ 16. A distance-time graph indicates that an object moves 100 m in 4 s , remains at rest for 1 s, and then moves 150 m in 5 s. What is the average ...
Document
... Senior Class trip to Disney world. You find yourself hanging on for dear life due to a technical error with the ride. Your distance from the center of the ride is 3 meters and you make 10 rotations in 18.25 seconds. You have a mass of 50 kilograms. ...
... Senior Class trip to Disney world. You find yourself hanging on for dear life due to a technical error with the ride. Your distance from the center of the ride is 3 meters and you make 10 rotations in 18.25 seconds. You have a mass of 50 kilograms. ...
Integrated Physical Science: Semester 2 Exam Review
... 20. If a 2 kg mass is pushed with a force of 8 N to the right against a 4N force of friction, what is the acceleration of the mass (hint: figure out the net force first)? ...
... 20. If a 2 kg mass is pushed with a force of 8 N to the right against a 4N force of friction, what is the acceleration of the mass (hint: figure out the net force first)? ...
Learning Goals
... connected objects, simple pulleys and uniform circular motion. Solve a variety of problems in mechanics (as described above) using Newton’s second law in component form following the recommended strategy of: 1. Identify the givens, 2. Draw the situation and identify the object of interest and then a ...
... connected objects, simple pulleys and uniform circular motion. Solve a variety of problems in mechanics (as described above) using Newton’s second law in component form following the recommended strategy of: 1. Identify the givens, 2. Draw the situation and identify the object of interest and then a ...
Sects. 4.9 & 4.10
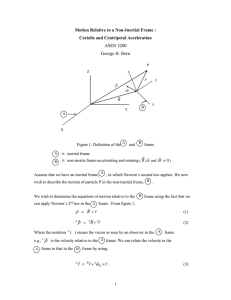
... • (3): Basic kinematical law for discussing dynamics of rigid body motion (Ch. 5). Not restricted to rigid bodies! Valid whenever we want to discuss the motion of a particle or particles relative to a rotating coordinate system. • Important application: Motion relative to coordinates of the rotating ...
... • (3): Basic kinematical law for discussing dynamics of rigid body motion (Ch. 5). Not restricted to rigid bodies! Valid whenever we want to discuss the motion of a particle or particles relative to a rotating coordinate system. • Important application: Motion relative to coordinates of the rotating ...
UNIT 3 Lab
... 2 kg mass Bathroom scale Balance Standard masses 1.1 In Unit 1 you observed that falling objects accelerate at the same rate near the surface of the Earth when there is very little friction. a. Consider a super ball dropped from 2.5 meters above the floor and allowed to bounce three or four times. D ...
... 2 kg mass Bathroom scale Balance Standard masses 1.1 In Unit 1 you observed that falling objects accelerate at the same rate near the surface of the Earth when there is very little friction. a. Consider a super ball dropped from 2.5 meters above the floor and allowed to bounce three or four times. D ...
Relativistic Dynamics
... our two clocks in the time dilation experiment). This string corresponds to the chalk line on the pool table. Suppose now we have two identical spaceships approaching each other with equal and opposite velocities parallel to the string from the two ends of the string, aimed so that they suffer a sli ...
... our two clocks in the time dilation experiment). This string corresponds to the chalk line on the pool table. Suppose now we have two identical spaceships approaching each other with equal and opposite velocities parallel to the string from the two ends of the string, aimed so that they suffer a sli ...