AngularPhysics
... So this equation says the angular momentum of point B looking from A is the dot product of the perpendicularized radius vector and the linear momentum of the point (pB) Operation is called the perp-dot product ...
... So this equation says the angular momentum of point B looking from A is the dot product of the perpendicularized radius vector and the linear momentum of the point (pB) Operation is called the perp-dot product ...
(a) from to and (b) - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Consider the street pattern shown in Fig. 2–42. Each intersection has a traffic signal, and the speed limit is 50 km h. Suppose you are driving from the west at the speed limit. When you are 10 m from the first intersection, all the lights turn green. The lights are green for 13 s each. (a) Calculat ...
... Consider the street pattern shown in Fig. 2–42. Each intersection has a traffic signal, and the speed limit is 50 km h. Suppose you are driving from the west at the speed limit. When you are 10 m from the first intersection, all the lights turn green. The lights are green for 13 s each. (a) Calculat ...
Physics review
... First Law Redux Newton's first law is also called the law of inertia. It states that if the vector sum of all forces (that is, the net force) acting on an object is zero, then the acceleration of the object is zero and its velocity is constant. The first point needs no comment, but the second seems ...
... First Law Redux Newton's first law is also called the law of inertia. It states that if the vector sum of all forces (that is, the net force) acting on an object is zero, then the acceleration of the object is zero and its velocity is constant. The first point needs no comment, but the second seems ...
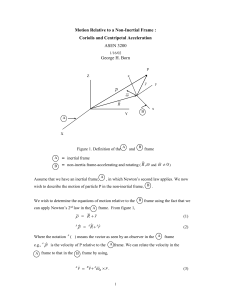
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... Using the right hand rule, we see that if an observer imagines him/herself aligned with the spin axis and facing in the direction of B r , the Coriolis force will always be to the right of the observer in the northern hemisphere and to the left of the observer in the southern hemisphere. Note that ...
... Using the right hand rule, we see that if an observer imagines him/herself aligned with the spin axis and facing in the direction of B r , the Coriolis force will always be to the right of the observer in the northern hemisphere and to the left of the observer in the southern hemisphere. Note that ...
Types of Variation
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
Types of Variation
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
... A vector is a quantity that is expressed using both a magnitude and a direction. Directions can be communicated algebraically (+/-), common references (left, right, up, down), using compass notation (N, S, E, W), or using trigonometry (angle in standard position). Vectors are adding using the “head- ...
AP Physics B:
... Projectile Motion occurs if an object is moving vertically under free-fall but also moving horizontally at a uniform rate. The vertical and horizontal components of the projectile’s velocity and displacement can be analyzed independently. Position-time and Velocity time Graphs The position-time grap ...
... Projectile Motion occurs if an object is moving vertically under free-fall but also moving horizontally at a uniform rate. The vertical and horizontal components of the projectile’s velocity and displacement can be analyzed independently. Position-time and Velocity time Graphs The position-time grap ...
laws of motion
... • We know that objects with different masses accelerate to the ground at the same rate. • However, because of the 2nd Law we know that they don’t hit the ground with the same force. F = ma 98 N = 10 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
... • We know that objects with different masses accelerate to the ground at the same rate. • However, because of the 2nd Law we know that they don’t hit the ground with the same force. F = ma 98 N = 10 kg x 9.8 m/s/s ...
Day 2: What does it take to make an object Move?
... Velocity: The speed of a moving object taken with it's direction of travel. So in order to determine an objects velocity you need to know 2 things. 1. The speed of the object 2. The direction in which the object is traveling Objects can have the same speed but have different velocities. Objects can ...
... Velocity: The speed of a moving object taken with it's direction of travel. So in order to determine an objects velocity you need to know 2 things. 1. The speed of the object 2. The direction in which the object is traveling Objects can have the same speed but have different velocities. Objects can ...