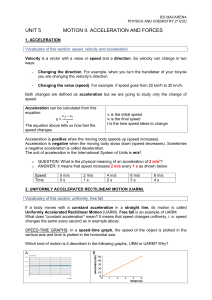
UNIT 5 MOTION II. ACCELERATION AND FORCES
... Changing the direction. For example, when you turn the handlebar of your bicycle you are changing the velocity’s direction. ...
... Changing the direction. For example, when you turn the handlebar of your bicycle you are changing the velocity’s direction. ...
GRADE 10F: Physics 2
... Use light gates or ticker-timers to measure the average speed of a dynamics trolley over a complete ‘journey’ along a straight line and to find its speed during successive small time intervals. Allow each pair or small group of students to experience using the apparatus and ...
... Use light gates or ticker-timers to measure the average speed of a dynamics trolley over a complete ‘journey’ along a straight line and to find its speed during successive small time intervals. Allow each pair or small group of students to experience using the apparatus and ...
Testing
... Many forces are of form F ( r1 r2 ) Remove dependence of result on choice of origin ...
... Many forces are of form F ( r1 r2 ) Remove dependence of result on choice of origin ...
The Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when
... and long periods of time, such as large-scale movements of air in the atmosphere or water in the ocean. Such motions are constrained by the surface of the earth, so generally only the horizontalcomponent of the Coriolis force is important. This force causes moving objects on the surface of the Earth ...
... and long periods of time, such as large-scale movements of air in the atmosphere or water in the ocean. Such motions are constrained by the surface of the earth, so generally only the horizontalcomponent of the Coriolis force is important. This force causes moving objects on the surface of the Earth ...
I. Newton`s Laws of Motion
... tree on the side of the road begin to move forward. You have mistakenly set yourself as the reference point. ...
... tree on the side of the road begin to move forward. You have mistakenly set yourself as the reference point. ...
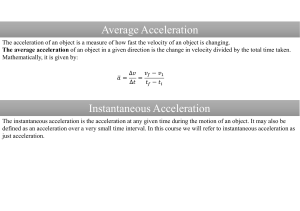
Average Acceleration Instantaneous Acceleration
... 3. Write down the available values for the kinematic variables (s, u, v, a and t). Be careful to assign the appropriate sign depending on the choice of coordinate axes made in 2. 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be imp ...
... 3. Write down the available values for the kinematic variables (s, u, v, a and t). Be careful to assign the appropriate sign depending on the choice of coordinate axes made in 2. 4. At least three of the kinematic variables should have values. Be sure to read the question carefully. There may be imp ...
A - Eastchester High School
... Kittinger reports in a 1960 article for National Geographic: “Sitting in my gondola, which gently twisted with the balloon's slow turnings, I had begun to sweat lightly, though the temperature read 36 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Sunlight burned in on me under the edge of an aluminized antiglare c ...
... Kittinger reports in a 1960 article for National Geographic: “Sitting in my gondola, which gently twisted with the balloon's slow turnings, I had begun to sweat lightly, though the temperature read 36 degrees below zero Fahrenheit. Sunlight burned in on me under the edge of an aluminized antiglare c ...
mi11sol
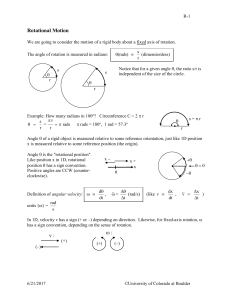
... A. Review of Basic Ideas: Spinning around When we want to describe the movement of an object we can talk about its velocity and its acceleration. But what about something like a CD which stays in the same place but spins around? Different points on the CD are moving at different velocities, but they ...
... A. Review of Basic Ideas: Spinning around When we want to describe the movement of an object we can talk about its velocity and its acceleration. But what about something like a CD which stays in the same place but spins around? Different points on the CD are moving at different velocities, but they ...
RotationalMotion - University of Colorado Boulder
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
... Aside: Torque, like force, is a vector quantity. Torque has a direction. Definition of vector torque : r F = cross product of r and F: "r cross F" Vector Math interlude: The cross-product of two vectors is a third vector A B C defined like this: The magnitude of A B is A B sin . The dir ...
Influence of the block-hierarchical structure of rocks on the
... The outcome has the following physical sense. The velocity С* is a movement velocity of a quasifront x = С*t with a cluster of low-frequency oscillations in its vicinity. Behind the front, with a decreasing velocity, higher-frequency modes move. Wave propagating from the area of influence are oscill ...
... The outcome has the following physical sense. The velocity С* is a movement velocity of a quasifront x = С*t with a cluster of low-frequency oscillations in its vicinity. Behind the front, with a decreasing velocity, higher-frequency modes move. Wave propagating from the area of influence are oscill ...
AP PHYSICS C: MECHANICS
... Describe the effect of mass and distance on gravitational force. Determine the gravitational field strength at a given point outside of a spherical mass. Describe the gravitational force inside and outside of a spherical mass, and how the field at the surface depends on the radius and density of the ...
... Describe the effect of mass and distance on gravitational force. Determine the gravitational field strength at a given point outside of a spherical mass. Describe the gravitational force inside and outside of a spherical mass, and how the field at the surface depends on the radius and density of the ...
Rotational and Projectile Motion
... When the vfinal - vinitial vector is moved to the circle, you can see the direction of the vector points toward the center of the circle. Regardless of where on the circle the vectors are chosen, the ∆v difference vector will always point toward the center of the circle. The conclusion is that the a ...
... When the vfinal - vinitial vector is moved to the circle, you can see the direction of the vector points toward the center of the circle. Regardless of where on the circle the vectors are chosen, the ∆v difference vector will always point toward the center of the circle. The conclusion is that the a ...