322. Two head lamps of a car are in parallel. They - DST
... Q 39 Two paper screens A and B are separated by a distance of 200 m. A bullet pierces A and then B. The hole in B is 40 cm below the hole in A. If the bullet is travelling horizontally at the time of hitting A, then the velocity of the bullet at A is : (a) (c) ...
... Q 39 Two paper screens A and B are separated by a distance of 200 m. A bullet pierces A and then B. The hole in B is 40 cm below the hole in A. If the bullet is travelling horizontally at the time of hitting A, then the velocity of the bullet at A is : (a) (c) ...
USING STANDARD SYSTE - The University of Iowa
... Here G ␦ Q ( ) has been assumed to have a Lorentzian shape with width Q , as discussed below in Sec. IV. Several different mechanisms can lead to charge fluctuations. One of these is the discrete nature of the charging process. Particles absorb individual electrons and ions from the plasma at ra ...
... Here G ␦ Q ( ) has been assumed to have a Lorentzian shape with width Q , as discussed below in Sec. IV. Several different mechanisms can lead to charge fluctuations. One of these is the discrete nature of the charging process. Particles absorb individual electrons and ions from the plasma at ra ...
Purdue Physics - Purdue University
... • Note the velocity of car 1 increases while the velocity of car 2 decreases. • The Th acceleration l ti and dd deceleration l ti arise i b because th the cars exert internal forces on each other. • Momentum conservation allows us to determine the change in velocity without knowing what the internal ...
... • Note the velocity of car 1 increases while the velocity of car 2 decreases. • The Th acceleration l ti and dd deceleration l ti arise i b because th the cars exert internal forces on each other. • Momentum conservation allows us to determine the change in velocity without knowing what the internal ...
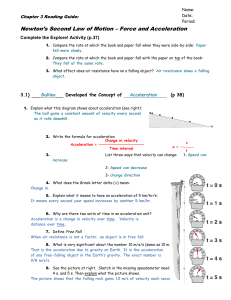
Chapter 3 Reading Guide
... also double. Similarly, it would take triple the force to get a threefold increase in acceleration. 5. Explain what the diagram at right is showing: If force is doubled, acceleration increases (doubled). Notice two hands are pushing instead of just one) If mass is doubled, acceleration decreases (by ...
... also double. Similarly, it would take triple the force to get a threefold increase in acceleration. 5. Explain what the diagram at right is showing: If force is doubled, acceleration increases (doubled). Notice two hands are pushing instead of just one) If mass is doubled, acceleration decreases (by ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Each component equation relates the forces on the object in that direction with the acceleration in that direction. A net force in the x direction will cause acceleration in the x direction. We will often just use the x and y directions in 2D. We will skip the vector notation when we are dealing wit ...
... Each component equation relates the forces on the object in that direction with the acceleration in that direction. A net force in the x direction will cause acceleration in the x direction. We will often just use the x and y directions in 2D. We will skip the vector notation when we are dealing wit ...
Chapter 7: Circular Motion and Gravitation
... body is following a straight-line path. As the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
... body is following a straight-line path. As the car enters the turn, your inertia makes to tend to move along the original straightline path. This movement is in accordance with Newton’s first law, which states that the natural tendency of a body is to continue moving in a straight line. ...
Answers
... Go to www.mrs-twedt.com on your computer. GO to the resources tab and, today, click “Newton Centers Webquest MSCredit.” Here, you will find a page that looks just like this sheet. You need to be sure you complete this sequentially. Whenever you see underlined text, it is a hyperlink to a website ful ...
... Go to www.mrs-twedt.com on your computer. GO to the resources tab and, today, click “Newton Centers Webquest MSCredit.” Here, you will find a page that looks just like this sheet. You need to be sure you complete this sequentially. Whenever you see underlined text, it is a hyperlink to a website ful ...
Lecture 06: Conservation of Angular Momentum
... dt m1 g same result followed from earlier a method using 3 FBD’s & 2nd law M m1 m2 February 24, 2011 ...
... dt m1 g same result followed from earlier a method using 3 FBD’s & 2nd law M m1 m2 February 24, 2011 ...
CYU 1: (a) (b) CYU 2:
... CYU 2: In general, the number of molecules would be different. But they could be the same, if the molecular masses of the two types of molecules happen to be the same. CYU 3: 66.4% CYU 4: The ideal gas law gives the pressure as P ⫽ nRT/V, where T and V are constant. The fan reduces n in the house an ...
... CYU 2: In general, the number of molecules would be different. But they could be the same, if the molecular masses of the two types of molecules happen to be the same. CYU 3: 66.4% CYU 4: The ideal gas law gives the pressure as P ⫽ nRT/V, where T and V are constant. The fan reduces n in the house an ...
Physics: 1 - Dominican
... 1. What is meant by the term ‘density’? 2. What is the formula used to calculate the density of an object? 3. What are the units of density? 4. Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure the density of an irregular-shaped object? 5. Describe with the aid of a diagram an experiment to measure th ...
... 1. What is meant by the term ‘density’? 2. What is the formula used to calculate the density of an object? 3. What are the units of density? 4. Draw a diagram of the apparatus used to measure the density of an irregular-shaped object? 5. Describe with the aid of a diagram an experiment to measure th ...
ExamIF04 - UMD Physics
... None of the above: a hot air ballon floats in the atmosphere with zero acceleration. ...
... None of the above: a hot air ballon floats in the atmosphere with zero acceleration. ...
Name - TeacherWeb
... Unbalanced forces cause a chance in an object’s motion. The net force acting on the object causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Changes in motion, that is, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction, are called acceleration. When an object of a certain mass is acted upon by a ...
... Unbalanced forces cause a chance in an object’s motion. The net force acting on the object causes it to speed up, slow down, or change direction. Changes in motion, that is, speeding up, slowing down, or changing direction, are called acceleration. When an object of a certain mass is acted upon by a ...
S2-3-06 - In Motion - Lesson Sequence
... if they remember what that means? Ask if they know what units force is measured in? Get them to work from the formula for force F=ma (m being mass and a being acceleration). Do they come up with kgm/s2? What does this convert to? ...
... if they remember what that means? Ask if they know what units force is measured in? Get them to work from the formula for force F=ma (m being mass and a being acceleration). Do they come up with kgm/s2? What does this convert to? ...