ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice * Torque
... Since a component of P balances the frictional force, P itself must be larger than f. ...
... Since a component of P balances the frictional force, P itself must be larger than f. ...
PPT
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
... A mass on a spring oscillates back & forth with simple harmonic motion of amplitude A. A plot of displacement (x) versus time (t) is shown below. At what points during its oscillation is the speed of the block biggest? 1. When x = +A or -A (i.e. maximum displacement) 2. When x = 0 (i.e. zero displac ...
Chapter 5
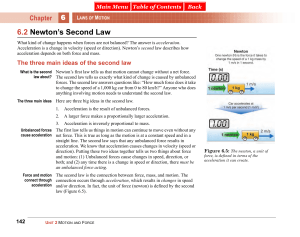
... Newton's second law of motion states that an object with mass m has an acceleration a equal to the net force ΣF acting on that object divided by its mass m: a = ΣF/m. Hint 2/Comment: The only forces acting on the shopping cart are gravitational force and the normal force (the force exerted by the g ...
... Newton's second law of motion states that an object with mass m has an acceleration a equal to the net force ΣF acting on that object divided by its mass m: a = ΣF/m. Hint 2/Comment: The only forces acting on the shopping cart are gravitational force and the normal force (the force exerted by the g ...
Rotation
... The total torque on a rotating system is the sum of the torques acting on all particles of the system about the axis of rotation – and since a is the same for all particles: ...
... The total torque on a rotating system is the sum of the torques acting on all particles of the system about the axis of rotation – and since a is the same for all particles: ...
12.3 Velocity and Acceleration
... As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) takes the form r(t) = x(t)i ...
... As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) takes the form r(t) = x(t)i ...
Preview Sample 1
... The fact that a wall or other passive object can exert a force is a new and important concept for students. In addition to the demonstrations with dynamics carts shown in Figure 2.33, you might look at the many action-reaction and thrust demonstrations in DHP, pages M-17 to M-25. Discuss challenge 4 ...
... The fact that a wall or other passive object can exert a force is a new and important concept for students. In addition to the demonstrations with dynamics carts shown in Figure 2.33, you might look at the many action-reaction and thrust demonstrations in DHP, pages M-17 to M-25. Discuss challenge 4 ...
Explaining motion - Delivery guide
... In areas where many people already have a working understanding of the main concepts, the very familiarity of the subject can be the source of confusion; our habit of confusing mass with weight in common usage should be easy enough to deal with, but the profusion of closely-related terms – work, for ...
... In areas where many people already have a working understanding of the main concepts, the very familiarity of the subject can be the source of confusion; our habit of confusing mass with weight in common usage should be easy enough to deal with, but the profusion of closely-related terms – work, for ...