Chapter 2
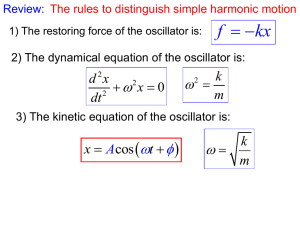
... If b>2mω0, the medium is highly viscous. x The system does not oscillate but simply returns to its equilibrium position. overdamped ...
... If b>2mω0, the medium is highly viscous. x The system does not oscillate but simply returns to its equilibrium position. overdamped ...
Introductory Physics
... Which of the following always occurs when a light ray reflects off a mirror? ...
... Which of the following always occurs when a light ray reflects off a mirror? ...
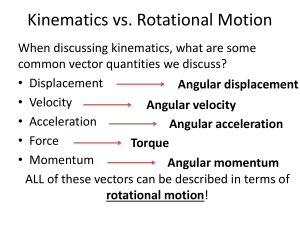
Applying Newton`s Laws
... ** Note: The value of the acceleration depends on the frame of reference. Newton’s Laws are only valid when frame is an inertial reference frame. Technically a set of axes fixed to the Earth is not an inertial reference frame due to the rotation of the Earth, but the Earth’s rotation is very slow th ...
... ** Note: The value of the acceleration depends on the frame of reference. Newton’s Laws are only valid when frame is an inertial reference frame. Technically a set of axes fixed to the Earth is not an inertial reference frame due to the rotation of the Earth, but the Earth’s rotation is very slow th ...
s - Claseshistoria.com
... A. In physics, …………… is change of location or …………….. of an object with respect to time . B. …………………. is the path that a moving object follows through space. C. ………………. is where an object is located. D. The ………………. travelled is equal to the subtraction between two …………….., the ……….. position minus t ...
... A. In physics, …………… is change of location or …………….. of an object with respect to time . B. …………………. is the path that a moving object follows through space. C. ………………. is where an object is located. D. The ………………. travelled is equal to the subtraction between two …………….., the ……….. position minus t ...
Potential Energy - McMaster University
... A periodic, external force pushes on the mass (in addition to the spring and damping): ...
... A periodic, external force pushes on the mass (in addition to the spring and damping): ...
Effects of collisions on conservation laws in gyrokinetic field theory
... how the conservation laws derived from Noether’s theorem in the collisionless system are modified in the collisional system with external sources of particles, energy, and momentum. There, we confirm the natural result that, when adding no external sources but only the collision term that conserves ...
... how the conservation laws derived from Noether’s theorem in the collisionless system are modified in the collisional system with external sources of particles, energy, and momentum. There, we confirm the natural result that, when adding no external sources but only the collision term that conserves ...
Work/Energy
... A 0.40 kg block is pushed up against a spring (with spring constant 270 N/m ) on a frictionless surface so that the spring is compressed 0.20 m. When the block is released, it slides across the surface and collides with the 0.60 kg bob of a pendulum. The bob is made of clay and the block sticks to i ...
... A 0.40 kg block is pushed up against a spring (with spring constant 270 N/m ) on a frictionless surface so that the spring is compressed 0.20 m. When the block is released, it slides across the surface and collides with the 0.60 kg bob of a pendulum. The bob is made of clay and the block sticks to i ...
Appendix B Chapter 2 Extra Practice Problems
... a. What mass will produce a 1.0-s period of oscillation if it is attached to a spring with a spring constant of 4.0 N/m? b. What length pendulum will produce a period of 1.0 s? c. How would the harmonic oscillator and the pendulum have to be modified in order to produce 1.0-s periods on the surface ...
... a. What mass will produce a 1.0-s period of oscillation if it is attached to a spring with a spring constant of 4.0 N/m? b. What length pendulum will produce a period of 1.0 s? c. How would the harmonic oscillator and the pendulum have to be modified in order to produce 1.0-s periods on the surface ...
Document
... in the absence of external forces! In the first two sample problems, we dealt with a frictionless surface. We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Frict ...
... in the absence of external forces! In the first two sample problems, we dealt with a frictionless surface. We couldn’t simply conserve momentum if friction had been present because, as the proof on the last slide shows, there would be another force (friction) in addition to the contact forces. Frict ...
Downloaded from: www.jsuniltutorial.weebly.com
... Study of motion of objects along a straight line is known as rectilinear motion. If a body does not change its position with time it is said to be at rest. If it changes its position with time it is said to be in motion. The position of the object can be specified with reference to a convenientl ...
... Study of motion of objects along a straight line is known as rectilinear motion. If a body does not change its position with time it is said to be at rest. If it changes its position with time it is said to be in motion. The position of the object can be specified with reference to a convenientl ...
Lectures in physics Part 2: Electricity, magnetism and quantum mechanics Przemysław Borys 20.05.2014
... that is stationary to the electrons, the wire in the above figure becomes... positively charged! (at a smaller velocity of the reference frame, the wire could also become neutral). But this would mean that the positive test charge in this reference frame is repulsed from the wire. This is impossible ...
... that is stationary to the electrons, the wire in the above figure becomes... positively charged! (at a smaller velocity of the reference frame, the wire could also become neutral). But this would mean that the positive test charge in this reference frame is repulsed from the wire. This is impossible ...
Honors Physics Unit 4 Notes
... • The action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, but either object may still have a net force on it. Consider driving a nail into wood with a hammer. The force that the nail exerts on the hammer is equal and opposite to the force that the hammer exerts on the nail. But there is a net force actin ...
... • The action-reaction forces are equal and opposite, but either object may still have a net force on it. Consider driving a nail into wood with a hammer. The force that the nail exerts on the hammer is equal and opposite to the force that the hammer exerts on the nail. But there is a net force actin ...
Unbalanced forces acting on an object cause the object to
... When friction is present, an object may move with a constant velocity even when an outside force is applied to it. In such a case, the friction force just balances the applied force. The net force is zero, so there is no acceleration. A diagram showing all the forces acting on an object is called a ...
... When friction is present, an object may move with a constant velocity even when an outside force is applied to it. In such a case, the friction force just balances the applied force. The net force is zero, so there is no acceleration. A diagram showing all the forces acting on an object is called a ...
LAHS Physics - LAPhysics.com
... rope may be considered massless; and the pulley may be considered frictionless. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is µs; and the coefficient of kinetic friction is k. ...
... rope may be considered massless; and the pulley may be considered frictionless. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the plane is µs; and the coefficient of kinetic friction is k. ...