2565 Bio 1
... 9 - NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION 10 - NEWTON’s FIRST LAW 11 - NEWTON’s FIRST LAW - EXAMPLES / THE EFFECT OF FORCES 12 - NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION - FORMULA 13 - NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION - THE SPRINTER 14 - NEWTON’s THIRD LAW OF MOTION 15 - NEWTON’s THIRD LAW OF MOTION - APPLICATIONS ...
... 9 - NEWTON’S LAWS OF MOTION 10 - NEWTON’s FIRST LAW 11 - NEWTON’s FIRST LAW - EXAMPLES / THE EFFECT OF FORCES 12 - NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION - FORMULA 13 - NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION - THE SPRINTER 14 - NEWTON’s THIRD LAW OF MOTION 15 - NEWTON’s THIRD LAW OF MOTION - APPLICATIONS ...
Midterm Exam 3
... 6. A 500 g rubber ball is dropped from a height of 10 m and undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with the earth. (a) For an elastic collision, what quantities are conserved? (b) Write out the conservation of momentum equation for this problem. (c) Write out the conservation of energy equation for ...
... 6. A 500 g rubber ball is dropped from a height of 10 m and undergoes a perfectly elastic collision with the earth. (a) For an elastic collision, what quantities are conserved? (b) Write out the conservation of momentum equation for this problem. (c) Write out the conservation of energy equation for ...
Introduction to Particle Physics for Teachers
... There are three color charges and three corresponding anticolor (complementary color) charges. Each quark has one of the three color charges and each antiquark has one of the three anticolor charges. Just as a mix of red, green, and blue light yields white light, in a baryon a combination of "red," ...
... There are three color charges and three corresponding anticolor (complementary color) charges. Each quark has one of the three color charges and each antiquark has one of the three anticolor charges. Just as a mix of red, green, and blue light yields white light, in a baryon a combination of "red," ...
Lesson 1: Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if ...
... Newton's Second Law of Motion Newton's Second Law Newton's first law of motion predicts the behavior of objects for which all existing forces are balanced. Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if ...
forces christina danielle ali
... There are several examples of Newton’s 3 Laws in your everyday life. 1st Law: Imagine you are playing in a soccer game, and you kick the ball at the goal, and think it is going to go in. However, the goalie blocks it and keeps it from continuing in its original path of motion, so you don’t score a g ...
... There are several examples of Newton’s 3 Laws in your everyday life. 1st Law: Imagine you are playing in a soccer game, and you kick the ball at the goal, and think it is going to go in. However, the goalie blocks it and keeps it from continuing in its original path of motion, so you don’t score a g ...
Kinetic Energy and Work
... glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 to the right of its unstretched length and spring 2 is stretched by xi2 to the left. Now a horizontal force Fapp is applied to the glider to move it a distance xa to the ...
... glider attached to both springs is located between them. When the glider is in equilibrium, spring 1 is stretched by extension xi1 to the right of its unstretched length and spring 2 is stretched by xi2 to the left. Now a horizontal force Fapp is applied to the glider to move it a distance xa to the ...
Newton`s Second Law of Motion
... Solving Equations 4-5 algebraically for the acceleration we get Equation 6 This is the theoretical value of acceleration. Note that the acceleration scales linearly with the hanging mass m2. In the experiment, the hanging mass m2 provides the force, while the cart and any additional mass (m1) on it ...
... Solving Equations 4-5 algebraically for the acceleration we get Equation 6 This is the theoretical value of acceleration. Note that the acceleration scales linearly with the hanging mass m2. In the experiment, the hanging mass m2 provides the force, while the cart and any additional mass (m1) on it ...
Alignment to Michigan Educational Standards- Physical Science Design and
... Analyze why seat belts may be more important in autos than in buses. Forces and Acceleration The change of speed and/or direction (acceleration) of an object is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The acceleration and net force are always in the same ...
... Analyze why seat belts may be more important in autos than in buses. Forces and Acceleration The change of speed and/or direction (acceleration) of an object is proportional to the net force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The acceleration and net force are always in the same ...
Date: Thu, 4 Aug 2005 - ASU Modeling Instruction
... center, which works as long as you have string or gravity but falls apart when you have more then one force as in banked curves or roller coasters. So we only use mass and net force for these two archaic terms. -----------------------------Date: Thu, 4 Aug 2005 From: JosephVanderway I agree with Don ...
... center, which works as long as you have string or gravity but falls apart when you have more then one force as in banked curves or roller coasters. So we only use mass and net force for these two archaic terms. -----------------------------Date: Thu, 4 Aug 2005 From: JosephVanderway I agree with Don ...
Newton`s Laws PPT
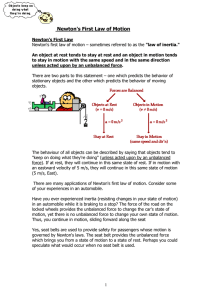
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
... a constant speed along a straight line (constant velocity). Inertia is the resistance of any physical object to any change in its state of motion, including changes to its speed and direction. ...
Document
... • Solve problems involving banking angles, the conical pendulum, and the vertical circle. ...
... • Solve problems involving banking angles, the conical pendulum, and the vertical circle. ...