Topic 4: Dynamics – Force, Newton’s Three Laws, and Friction
... Purpose: To determine how acceleration is related to different masses when the force is the same. Assume the force is always greater than friction. Theory: Labs C-1 and C-2 have shown that a constant force produces constant acceleration on a given mass and the acceleration of a body is directly rela ...
... Purpose: To determine how acceleration is related to different masses when the force is the same. Assume the force is always greater than friction. Theory: Labs C-1 and C-2 have shown that a constant force produces constant acceleration on a given mass and the acceleration of a body is directly rela ...
Physics 231 Topic 7: Oscillations Wade Fisher October 5-10 2012
... Newton’s second law: F=ma -kx=ma a=-kx/m acceleration(a) kA/m ...
... Newton’s second law: F=ma -kx=ma a=-kx/m acceleration(a) kA/m ...
Chapter #11 (Read Please)
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
Problem Set 9 Angular Momentum Solution
... What is the direction and magnitude of the rotational velocity of the ring when the bug is (a) halfway around and (b) back at the pivot. Solution: We begin by choosing our system to consist of the bug and the ring. Choose the positive z -direction to point into the figure above. Because there are no ...
... What is the direction and magnitude of the rotational velocity of the ring when the bug is (a) halfway around and (b) back at the pivot. Solution: We begin by choosing our system to consist of the bug and the ring. Choose the positive z -direction to point into the figure above. Because there are no ...
Ph211_CH5_worksheet-f06
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
... Since the masses are attached their accelerations are equal: a1y = a2x = asystem Solving for asystem: m2gsin – m1asystem - m1g = m2asystem asystem = (m2gsin – m1g)/(m1 + m2) = -1.03 m/s2 (i.e. up the incline!) e. What are the tension forces acting on each mass? Express the tension vectors in compo ...
ELECTRONS: THE HIGH ENERGY DISTRIBUTION S.
... The time rate of change of the density of tail electrons is obtained by integrating the time dependent Fokker-Planck equation over all p1 annihilates the collision operator when p ...
... The time rate of change of the density of tail electrons is obtained by integrating the time dependent Fokker-Planck equation over all p1 annihilates the collision operator when p ...
Feynman Says: “Newton implies Kepler, No Calculus Needed!”
... planet’s speed is also constant at every point. The distance the planet travels in one orbit is the circumference 2 . Let the period – the time it takes to orbit – be . So, the average speed is 2 / , which is also the speed at every point in the orbit. The star’s tugs on the planet don’t change its ...
... planet’s speed is also constant at every point. The distance the planet travels in one orbit is the circumference 2 . Let the period – the time it takes to orbit – be . So, the average speed is 2 / , which is also the speed at every point in the orbit. The star’s tugs on the planet don’t change its ...
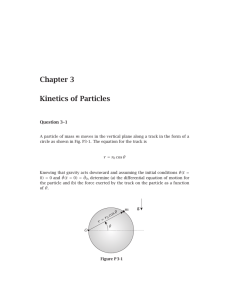
Chapter 3 Kinetics of Particles
... Observing that θ̇ ≠ 0 as a function of time, the differential equation of motion is obtained as p mgα mR 2 (1 + α2 )θ̈ + √ ...
... Observing that θ̇ ≠ 0 as a function of time, the differential equation of motion is obtained as p mgα mR 2 (1 + α2 )θ̈ + √ ...
lectur~4-1 - Dr. Khairul Salleh Basaruddin
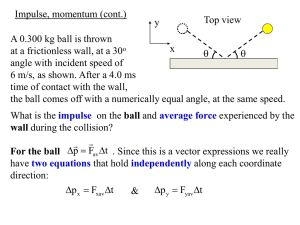
... • Establish the x, y, z coordinate system. • Draw the particle’s free-body diagram and establish the direction of the particle’s initial and final velocities, drawing the impulse and momentum diagrams for the particle. Show the linear momentum and force impulse vectors. • Resolve the force and veloc ...
... • Establish the x, y, z coordinate system. • Draw the particle’s free-body diagram and establish the direction of the particle’s initial and final velocities, drawing the impulse and momentum diagrams for the particle. Show the linear momentum and force impulse vectors. • Resolve the force and veloc ...