Chapter 11 PPT
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... relative to the origin O is defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
Fnet = m a
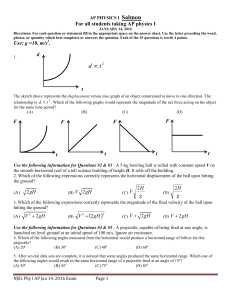
... Review of projectile motion Let’s look at the example of a cannonball fired at certain angle above the horizontal. According to Newton’s first law of motion and in the absence of gravity, the cannonball should travel in a straight line forever. However, we live on Earth and there is gravity. It act ...
... Review of projectile motion Let’s look at the example of a cannonball fired at certain angle above the horizontal. According to Newton’s first law of motion and in the absence of gravity, the cannonball should travel in a straight line forever. However, we live on Earth and there is gravity. It act ...
Patterns of Motion
... Newton had successfully used Galileo’s ideas to describe the nature of motion. Newton’s first law of motion explains that any object, once started in motion, will continue with a constant velocity in a straight line unless a force acts on the moving object. This law not only describes motion but est ...
... Newton had successfully used Galileo’s ideas to describe the nature of motion. Newton’s first law of motion explains that any object, once started in motion, will continue with a constant velocity in a straight line unless a force acts on the moving object. This law not only describes motion but est ...
UNIVERSITY OF CALICUT (Abstract)
... research phase of the project. The various steps in project works are the following:a) Wide review of a topic. b) Investigation on an area of Physics in systematic way using appropriate techniques. c) Systematic recording of the work. d) Reporting the results with interpretation in written and oral ...
... research phase of the project. The various steps in project works are the following:a) Wide review of a topic. b) Investigation on an area of Physics in systematic way using appropriate techniques. c) Systematic recording of the work. d) Reporting the results with interpretation in written and oral ...
Vectors: Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
... Newton's First Law • Newton's first law of motion: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... Newton's First Law • Newton's first law of motion: An object at rest stays at rest and an object in motion stays in motion with the same speed and in the same direction unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
soweto/diepkloof - Bancroft School
... protractor (or set square) to make an angle of 900 and you then draw the 3 km line going east (to the right) at 900 to the 4 km and make it exactly 6cm long (1 km ≙ 2 cm; 3km ≙ 6cm). At the end of this line (at 6 cm) you have found the exact position of B. You now join A to B and measure the length ...
... protractor (or set square) to make an angle of 900 and you then draw the 3 km line going east (to the right) at 900 to the 4 km and make it exactly 6cm long (1 km ≙ 2 cm; 3km ≙ 6cm). At the end of this line (at 6 cm) you have found the exact position of B. You now join A to B and measure the length ...
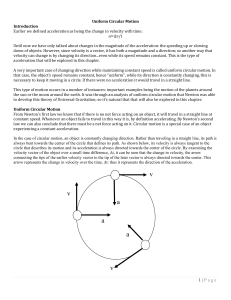
Acceleration Characteristics for Circular Motion
... matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizontal one, we have two forces acting on the object to keep its motion circular, the weight of the object will always be down, but the tension force would ...
... matters...not any one force. So for instance, if we changed the prior example by having the object moving in a vertical circle, rather than a horizontal one, we have two forces acting on the object to keep its motion circular, the weight of the object will always be down, but the tension force would ...
Momentum - Net Start Class
... High mass objects can have low momentum when they have low velocities; low mass objects can have high momentum when they have high velocities. The more momentum an object has, the harder it is to stop. Newton's second law of motion expressed in terms of momentum states that the rate of change in mom ...
... High mass objects can have low momentum when they have low velocities; low mass objects can have high momentum when they have high velocities. The more momentum an object has, the harder it is to stop. Newton's second law of motion expressed in terms of momentum states that the rate of change in mom ...
Chapter 3
... an independent mass, tend to remain at rest. You take a few steps back as you tend to maintain your position relative to the ground outside. You reach for a seat back or some part of the bus. Once you have a hold on some part of the bus it supplies the forces needed to give you the same motion as th ...
... an independent mass, tend to remain at rest. You take a few steps back as you tend to maintain your position relative to the ground outside. You reach for a seat back or some part of the bus. Once you have a hold on some part of the bus it supplies the forces needed to give you the same motion as th ...
Chapter 7 Rotational Motion 7.1 Angular Quantities Homework # 51
... 03. A truck engine slows down from 3700 rpm to 1800 rpm in 4.25 s. How many revolutions were made by the engine during this time? 04. A car, with 26-inch (66.0-cm)-diameter wheels, accelerates from rest to 72.5 km/h (45.0 mi/h) in 295 m. a.) What is the angular displacement of the wheels? b.) What i ...
... 03. A truck engine slows down from 3700 rpm to 1800 rpm in 4.25 s. How many revolutions were made by the engine during this time? 04. A car, with 26-inch (66.0-cm)-diameter wheels, accelerates from rest to 72.5 km/h (45.0 mi/h) in 295 m. a.) What is the angular displacement of the wheels? b.) What i ...
File
... The Law of Universal Gravitation (cont.) • The gravitational force becomes stronger as either or both objects increase in mass. • The gravitational force becomes weaker as the distance between the objects increases. ...
... The Law of Universal Gravitation (cont.) • The gravitational force becomes stronger as either or both objects increase in mass. • The gravitational force becomes weaker as the distance between the objects increases. ...
Introduction to Subatomic
... This article introduces the reader to the field of high-energy physics and the subatomicparticle detection techniques that it employs. We begin with an overview of the field, then briefly introduce subatomic particles and their detection before treating particle detectors in more detail. We conclude ...
... This article introduces the reader to the field of high-energy physics and the subatomicparticle detection techniques that it employs. We begin with an overview of the field, then briefly introduce subatomic particles and their detection before treating particle detectors in more detail. We conclude ...
Jason Kidd high in the air drops a 0.60-kg
... 4. Solving momentum problems in isolated systems 4.1. Summary and definitions Momentum ...
... 4. Solving momentum problems in isolated systems 4.1. Summary and definitions Momentum ...
Friction Intro - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... b) Calculate the force of friction between the book and the bench. c) Calculate the coefficient of friction between the book and the bench. d) Which coefficient of friction have you found: static or kinetic? Explain. ...
... b) Calculate the force of friction between the book and the bench. c) Calculate the coefficient of friction between the book and the bench. d) Which coefficient of friction have you found: static or kinetic? Explain. ...