Motion In Review
... continues moving in the same direction has changed it’s velocity. A moving object that changes direction but retains the same speed has changed its velocity. ...
... continues moving in the same direction has changed it’s velocity. A moving object that changes direction but retains the same speed has changed its velocity. ...
Word - IPFW
... To introduce the student to the analysis of the motion of particles and rigid bodies using the laws and principles of mechanics; to practice solving problems using techniques learned in the course; and to introduce the analysis of the motion of simple deformable bodies. ...
... To introduce the student to the analysis of the motion of particles and rigid bodies using the laws and principles of mechanics; to practice solving problems using techniques learned in the course; and to introduce the analysis of the motion of simple deformable bodies. ...
Newton`s Second Law
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
... Newton’s First Law: An object at rest remains at rest, and an object in motion remains in motion with the same speed and direction (maintains its velocity) unless it experiences an unbalanced force. Example: A soccer ball resting on the grass remains motionless until a force is applied (a kick). Th ...
Chapter 1. The Birth of Modern Physics
... Statistical Physics), was establish in the second half of the nineteenth century by Maxwell, Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906), and the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs (1839-1903). This theory bring us closer to the world of Modern Physics to come at the turn of the twentieth century in that i ...
... Statistical Physics), was establish in the second half of the nineteenth century by Maxwell, Ludwig Eduard Boltzmann (1844-1906), and the American physicist J. Willard Gibbs (1839-1903). This theory bring us closer to the world of Modern Physics to come at the turn of the twentieth century in that i ...
Relativity, Inertia, and Equivalence Principle
... Objects in motion remain moving at constant velocity (straight line and constant speed), UNLESS …a net (unbalanced) force acts ...
... Objects in motion remain moving at constant velocity (straight line and constant speed), UNLESS …a net (unbalanced) force acts ...
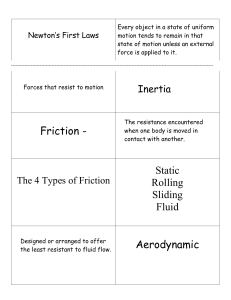
Cut squares along dotted line then fold in half to make flashcard
... The resistance encountered when one body is moved in contact with another. ...
... The resistance encountered when one body is moved in contact with another. ...
Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
Periodic Table
... Newton’s Laws, Coulomb’s Law, gravity…Quantum mechanics deals with the forces on objects of very small mass (like the electron or an atom). In QM things behave in ways that seem “odd” as they are by their nature not following the “rules” of classical mechanics. ...
... Newton’s Laws, Coulomb’s Law, gravity…Quantum mechanics deals with the forces on objects of very small mass (like the electron or an atom). In QM things behave in ways that seem “odd” as they are by their nature not following the “rules” of classical mechanics. ...
Conservation of Energy Discussion (from 16.3) Here is a brief
... Here is a brief discussion of the origin of the term conservative for a vector field, F, that is the gradient of some potential function, f . Mathematically, this relationship is F = ∇f , but let’s see where the terms come from. FIRST, let F(x, y, z) be a force vector field that moves a particle of ...
... Here is a brief discussion of the origin of the term conservative for a vector field, F, that is the gradient of some potential function, f . Mathematically, this relationship is F = ∇f , but let’s see where the terms come from. FIRST, let F(x, y, z) be a force vector field that moves a particle of ...
Force and Motion Review Questions
... The statement "for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is: the law of conservation of momentum Newton's first law of motion Newton's second law of motion Newton's third law of motion ...
... The statement "for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is: the law of conservation of momentum Newton's first law of motion Newton's second law of motion Newton's third law of motion ...
Newton Review
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...
... Speed = Distance/ Time; 20 ft/s = 200 ft/10 s 13. What is the acceleration of an object that goes from 50 m/s to 100 m/s in 10 seconds? ∆ speed/time = acceleration; 100 m/s – 50 m/s / 10 s = 50 m/s / 10 s = 5 m/s2 Fill in the blanks for the following questions below. 14. Air resistance is a kind of ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034 M.Sc. NOVEMBER 2013
... 04. What is meant by principal moment of inertia and product of inertia? 05. What are Euler's angles? 06. Show that the Hamiltonian is constant of motion if it is not an explicit function of time. 07. Show that the generating function F3 = pQ generates an identity transformation with a negative sign ...
... 04. What is meant by principal moment of inertia and product of inertia? 05. What are Euler's angles? 06. Show that the Hamiltonian is constant of motion if it is not an explicit function of time. 07. Show that the generating function F3 = pQ generates an identity transformation with a negative sign ...