student notes - science
... acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (ms-2) Since force and acceleration are both vectors they must act in t ...
... acceleration and that as an object grew in mass it would be harder to make accelerate. So mass becomes the property of a body that resists change in motion. This is summed up by the equation: Force (N) = mass (kg) x acceleration (ms-2) Since force and acceleration are both vectors they must act in t ...
Lecture 3
... light, Newtonian mechanics is replaced by Einstein’s special theory of relativity. • If the size of objects is comparable to the atomic scale, Newtonian mechanics is replaced by quantum mechanics. ...
... light, Newtonian mechanics is replaced by Einstein’s special theory of relativity. • If the size of objects is comparable to the atomic scale, Newtonian mechanics is replaced by quantum mechanics. ...
Newton`s Laws
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
... object increases with increased force and decreased with increased mass. • The acceleration of a body is parallel and directly proportional to the net force F and inverse to the mass. The two people are pushing with the same power so they don't move. ...
Newton`s Universal Law of Gravity
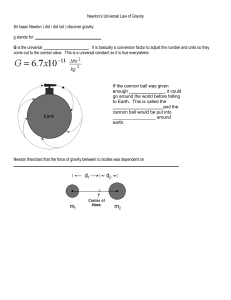
... The Law of Universal gravitation States that EVERY OBJECT IN THE UNIVERSE ________________EVERY OTHER OBJECT IN THE UNOVERSE WITH A FORCE DIRECTED ALONG THE LINE OF THE CENTERS OF THE TWO OBJECTS THAT IS PROPORTIONAL TO THE _____________________________ AND INVERSELY PROPRTIONAL TO THE SQUARE OF THE ...
... The Law of Universal gravitation States that EVERY OBJECT IN THE UNIVERSE ________________EVERY OTHER OBJECT IN THE UNOVERSE WITH A FORCE DIRECTED ALONG THE LINE OF THE CENTERS OF THE TWO OBJECTS THAT IS PROPORTIONAL TO THE _____________________________ AND INVERSELY PROPRTIONAL TO THE SQUARE OF THE ...
Physics 104 - Class Worksheet Ch 4
... frame attached to a particle on which there are no forces C) any reference frame that is at rest D) a reference frame attached to the center of the universe E) a reference frame attached to the Earth ...
... frame attached to a particle on which there are no forces C) any reference frame that is at rest D) a reference frame attached to the center of the universe E) a reference frame attached to the Earth ...
Newton`s Laws Quiz Study Guide
... This quiz will describe different scenarios involving Newton's Laws and ask you to identify which law goes with that type of motion. You should be able to justify your reasoning for your choices. Review with your notes and HW sheets from binder pages 113- Newton's Laws Notes, 114-115 Newton's Laws/ ...
... This quiz will describe different scenarios involving Newton's Laws and ask you to identify which law goes with that type of motion. You should be able to justify your reasoning for your choices. Review with your notes and HW sheets from binder pages 113- Newton's Laws Notes, 114-115 Newton's Laws/ ...
Newton`s 3 Laws
... f=force, m=mass, a=acceleration A force is a push or pull on an object. The more force applied to an object, the more it accelerates. The more massive an object is, the more force is needed to move it. Newton’s Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. m1v1 + m2v2 ...
... f=force, m=mass, a=acceleration A force is a push or pull on an object. The more force applied to an object, the more it accelerates. The more massive an object is, the more force is needed to move it. Newton’s Third Law For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. m1v1 + m2v2 ...
R07
... State the assumptions for forces in members of a perfect frame and also explain the method of sections for finding the forces in a cantilever then with help of an example. ...
... State the assumptions for forces in members of a perfect frame and also explain the method of sections for finding the forces in a cantilever then with help of an example. ...
I. Newton's Laws of Motion - x10Hosting
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) ...
... I. Newton’s Laws of Motion “If I have seen far, it is because I have stood on the shoulders of giants.” - Sir Isaac Newton (referring to Galileo) ...
45 m/s - Madison Public Schools
... at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...
... at rest and an object in motion will remain in motion at a constant velocity until acted upon by a net force. ...