Solutions for class #7 from Yosumism website Problem 44:
... One can derive the frequency of small oscillation for a rigid body in general by using the torque form of Newton's Laws: . (I is moment of inertia, r is moment arm) In this case, one has a constant downwards force , which acts at a moment arm angle . Thus, , where the approximation works if ...
... One can derive the frequency of small oscillation for a rigid body in general by using the torque form of Newton's Laws: . (I is moment of inertia, r is moment arm) In this case, one has a constant downwards force , which acts at a moment arm angle . Thus, , where the approximation works if ...
Chp+12+Quest REVISED 2012
... 13. What other force is involved that determines terminal velocity? ...
... 13. What other force is involved that determines terminal velocity? ...
Midterms: Place, Rules, How to study
... vy (t) = -gt vx (t) = vx0 Answer: xf = 89.3 m, yf = -62.5 m d = 109 m, t = 3.57 s Mechanics Unit 2, Slide 4 ...
... vy (t) = -gt vx (t) = vx0 Answer: xf = 89.3 m, yf = -62.5 m d = 109 m, t = 3.57 s Mechanics Unit 2, Slide 4 ...
forces_and_energy_review
... Friction: A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. Weight: The mass of an object with respect to gravitational pull. Speed: The distance traveled divided by the time interval during which the motion occurred. Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. Fo ...
... Friction: A force that opposes motion between two surfaces that are in contact. Weight: The mass of an object with respect to gravitational pull. Speed: The distance traveled divided by the time interval during which the motion occurred. Velocity: The speed of an object in a particular direction. Fo ...
R - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... HO = constant We conclude that the angular momentum of a particle moving under a central force is constant, both in magnitude and direction, and that the particle moves in a plane perpendicular to HO . ...
... HO = constant We conclude that the angular momentum of a particle moving under a central force is constant, both in magnitude and direction, and that the particle moves in a plane perpendicular to HO . ...
PHYS4330 Theoretical Mechanics HW #8 Due 25 Oct 2011
... (3) (See Taylor 7.49.) A mass m with charge q moves in a uniform constant magnetic field B = Bẑ. Prove that B = ∇ × A where A = 12 B × r. (You can do this in a coordinateindependent way, only assuming that B is a constant field, and using some vector identities.) Show that A = 12 Bρφ̂ in cylindrica ...
... (3) (See Taylor 7.49.) A mass m with charge q moves in a uniform constant magnetic field B = Bẑ. Prove that B = ∇ × A where A = 12 B × r. (You can do this in a coordinateindependent way, only assuming that B is a constant field, and using some vector identities.) Show that A = 12 Bρφ̂ in cylindrica ...
Newton`s second law File
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION states: ...
... BACKGROUND: The relationship between forces and the way objects move was described clearly for the first time by Sir Isaac Newton in his three Laws of Motion. NEWTON’S SECOND LAW OF MOTION states: ...
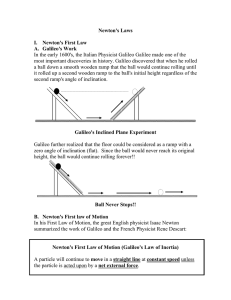
Newton`s Laws - Uplands blogs
... car going 80 km/h is stopped by the brick wall, your body keeps moving at 80 km/h. ...
... car going 80 km/h is stopped by the brick wall, your body keeps moving at 80 km/h. ...
PH2011 - Physics 2A - University of St Andrews
... them to the thermodynamic identity. - Solve problems involving thermal expansion, heat capacity and the transport of energy by heating in terms of the thermal properties of materials. - Appreciate the differences between reversible and irreversible processes. - State the ideal gas law and equipartit ...
... them to the thermodynamic identity. - Solve problems involving thermal expansion, heat capacity and the transport of energy by heating in terms of the thermal properties of materials. - Appreciate the differences between reversible and irreversible processes. - State the ideal gas law and equipartit ...
Math 2250-4 Mon Jan 30
... actually an approximation to the universal inverse square law of gravitational attraction, which says the attractive force between two objects of mass m, M has magnitude GMm F = r2 where r is the distance between their centers of mass and G is a universal constant. Write R for the radius of the eart ...
... actually an approximation to the universal inverse square law of gravitational attraction, which says the attractive force between two objects of mass m, M has magnitude GMm F = r2 where r is the distance between their centers of mass and G is a universal constant. Write R for the radius of the eart ...