me 231 engineering mechanics - Department of Mechanical
... Submitted by : # (050023) Albert Einstein, Jr. (your student number & name) ...
... Submitted by : # (050023) Albert Einstein, Jr. (your student number & name) ...
Chapter 12 Study Guide
... Inertia Acceleration Gravity Action and Reaction Weight Mass 1. Write out each of Newton’s three laws and explain an example of each. Newton’s First Law states: ...
... Inertia Acceleration Gravity Action and Reaction Weight Mass 1. Write out each of Newton’s three laws and explain an example of each. Newton’s First Law states: ...
Algebra - Militant Grammarian
... mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get from one point to the other. It takes a further 2.0 seconds to pass through th ...
... mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get from one point to the other. It takes a further 2.0 seconds to pass through th ...
Newton`s Law of Motion.
... • The law states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanc ...
... • The law states that if the forces acting upon an object are balanced, then the acceleration of that object will be 0 m/s/s. • Objects at equilibrium (the condition in which all forces balance) will not accelerate. • According to Newton, an object will only accelerate if there is a net or unbalanc ...
forces and the laws of motion - PAMS-Doyle
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
... that they would both hit the ground at the same time. He was right. • When the only force acting on a falling object is gravity, they are in free fall. • Acceleration of a falling object is due to the force of gravity is 9.8 m/sec/sec. • 1 meter = 9.8 m/sec/sec • 2 meters = 19.6 m/sec/sec • 3 meters ...
Test 2
... speed of the satellite to the given information (m, M, R, and h). (Hint. Assume you know the gravitational constant G.) 4. An object (“particle”) has a velocity of [3,0] m/s at one instant. Five seconds later, its velocity has changed to [8,10] m/s. Assuming that the object was subject to a constant ...
... speed of the satellite to the given information (m, M, R, and h). (Hint. Assume you know the gravitational constant G.) 4. An object (“particle”) has a velocity of [3,0] m/s at one instant. Five seconds later, its velocity has changed to [8,10] m/s. Assuming that the object was subject to a constant ...
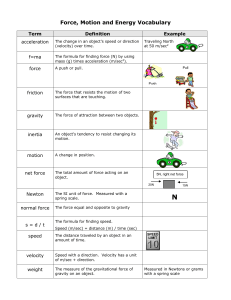
Physics Vocabulary
... • force- a push or a pull (measured in newtons) • friction- a force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact with each other • magnetism- a force that attracts or repels objects with magnetic poles • gravity- a force that pulls together objects with mass • balanced forces- forces that ar ...
... • force- a push or a pull (measured in newtons) • friction- a force that opposes motion when two surfaces are in contact with each other • magnetism- a force that attracts or repels objects with magnetic poles • gravity- a force that pulls together objects with mass • balanced forces- forces that ar ...
Twenty Questions - Kelso High School
... no forces at all) act on an object it remains at rest or continue to move at a steady speed in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
... no forces at all) act on an object it remains at rest or continue to move at a steady speed in a straight line unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. ...
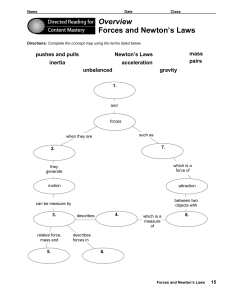
Newton`S Laws Guided Notes
... famous for his discovery of the _________ ________ of ______________. Today these laws are known as Newton’s __________of ___________ and describe _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...
... famous for his discovery of the _________ ________ of ______________. Today these laws are known as Newton’s __________of ___________ and describe _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________ ...