Physical Science Chapter 1 & 2 Motion & Force
... Force = mass x acceleration 1. Newton’s Second Law of Motion – The net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration and its mass: 2. mass= Force / acceleration 3. acceleration = force / mass ...
... Force = mass x acceleration 1. Newton’s Second Law of Motion – The net force on an object is equal to the product of its acceleration and its mass: 2. mass= Force / acceleration 3. acceleration = force / mass ...
PHYSICS 211, Exam # 3 April 22, 2013 (Dr. Xinhua Bai`s session
... 2. Two objects interact with each other and with no other objects. Initially object A has a speed of 5 m/s and object B has a speed of 10 m/s. In the course of their motion they return to their initial positions. Then A has a speed of 4 m/s and B has a speed of 7 m/s. We can conclude: A) the potenti ...
... 2. Two objects interact with each other and with no other objects. Initially object A has a speed of 5 m/s and object B has a speed of 10 m/s. In the course of their motion they return to their initial positions. Then A has a speed of 4 m/s and B has a speed of 7 m/s. We can conclude: A) the potenti ...
the forces are exerted on different objects
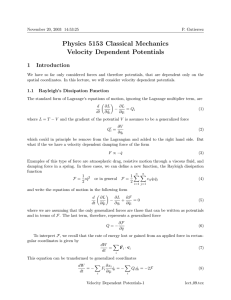
... Newton’s second law is the relation between acceleration and force. Acceleration is proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. ...
... Newton’s second law is the relation between acceleration and force. Acceleration is proportional to force and inversely proportional to mass. ...
MOTION
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
... rate at which an object is moving at a given moment in time Speedometer in a car **Average speed is computed for the entire duration of a trip, and instantaneous speed is measured at a particular ...
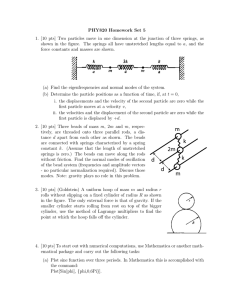
PHY820 Homework Set 5
... (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displace ...
... (b) Determine the particle positions as a function of time, if, at t = 0, i. the displacements and the velocity of the second particle are zero while the first particle moves at a velocity v, ii. the velocities and the displacement of the second particle are zero while the first particle is displace ...
Part VI
... • The curve shows the path moved by a point on the rim of the object. This path is called a cycloid • The line shows the path of the center of mass of the object • In pure rolling motion, an object rolls without slipping • In such a case, there is a simple relationship between its rotational and tra ...
... • The curve shows the path moved by a point on the rim of the object. This path is called a cycloid • The line shows the path of the center of mass of the object • In pure rolling motion, an object rolls without slipping • In such a case, there is a simple relationship between its rotational and tra ...
Newtons Laws - Cardinal Newman High School
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
... For example: When you kick a soccer ball, do you feel anything in your foot? ...
Section 1 Forces Newton`s Second Law
... The concept of force explains many occurrences in our everyday lives. From your own experience, state what will happen in the following situations. 1. A marble is placed at the top of a smooth ramp. What will happen to the marble? What force causes this? 2. A marble is rolling around in the back of ...
... The concept of force explains many occurrences in our everyday lives. From your own experience, state what will happen in the following situations. 1. A marble is placed at the top of a smooth ramp. What will happen to the marble? What force causes this? 2. A marble is rolling around in the back of ...