Sponge - A 200 kg hockey player pushes a 150 kg official after
... Gravitation - every particle in the universe exerts a force on every other particle by the following equation: F = G m1m2 /r2 G = 6.67259 x ...
... Gravitation - every particle in the universe exerts a force on every other particle by the following equation: F = G m1m2 /r2 G = 6.67259 x ...
General Physics STUDY GUIDE
... Identify a projectile’s acceleration in each direction objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (Ch. 4) Be able to draw or recognize force diagrams for an object in a consistent with these bar chart diagrams. sta ...
... Identify a projectile’s acceleration in each direction objects at different points in time. Write and solve conservation of energy problems that are Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion (Ch. 4) Be able to draw or recognize force diagrams for an object in a consistent with these bar chart diagrams. sta ...
02-5-net-force-with
... Using the Momentum Principle to Solve for Unknown Forces. Steps to applying the Momentum Principle to solve for unknown forces. 1. Apply the Momentum Principle to find the net force. 2. Sketch all forces acting on the system. 3. Apply the Principle of Superposition, by summing the forces acting on ...
... Using the Momentum Principle to Solve for Unknown Forces. Steps to applying the Momentum Principle to solve for unknown forces. 1. Apply the Momentum Principle to find the net force. 2. Sketch all forces acting on the system. 3. Apply the Principle of Superposition, by summing the forces acting on ...
Handout 1
... If two observers are in relative motion, they will not, in general, agree as to whether two events are simultaneous. If one observer finds them to be simultaneous, the other generally will not, and conversely. ...
... If two observers are in relative motion, they will not, in general, agree as to whether two events are simultaneous. If one observer finds them to be simultaneous, the other generally will not, and conversely. ...
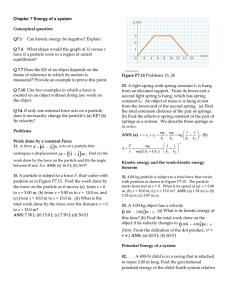
Chapter 7 Energy of a system Conceptual question Q7.1 Can kinetic
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
... particle within a system due to its intteaction with the rest of the system. The equation Fx = (2x + 4) N describes the force, where x is in meters. As the particle moves along the x axis from x = 1.00 m to x = 5.00 m, calculate (a) the work done by this force, (b) the change in the potential energy ...
Ch. 11.3
... at the same time but may not have equal effects. Example a bouncing ball never rebounds as high as tossed down. • Action/reaction is everywhere. ...
... at the same time but may not have equal effects. Example a bouncing ball never rebounds as high as tossed down. • Action/reaction is everywhere. ...
Examination Paper (Mechanics)
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
... (6) A rigid body is made of three identical thin rods, each with length L, fastened together in the form of a letter H, as shown in the diagram. The body is free to rotate about a horizontal axis that runs along the length of one of the legs of the H. The body is allowed to fall from rest from a pos ...
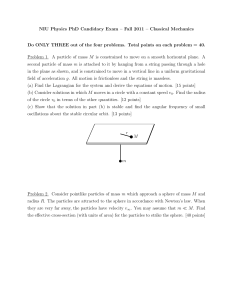
NIU Physics PhD Candidacy Exam – Fall 2011 – Classical
... gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at their natural length, a. The masses move only in the plane of the page, and with only ...
... gravitational field with acceleration g, each hanging by a massless string of length `, and coupled to each other with massless springs of spring constant K as shown. In the equilibrium position, the springs are at their natural length, a. The masses move only in the plane of the page, and with only ...
504 Advanced Placement Physics C Course Description Students
... Students are expected to complete rigorous course and lab work consistent with college level Physics and to complete 5-8 hours per week of independent practice such as homework, reading, and projects. This course will follow the curriculum prescribed for an AP Physics C – Mechanics class. Students w ...
... Students are expected to complete rigorous course and lab work consistent with college level Physics and to complete 5-8 hours per week of independent practice such as homework, reading, and projects. This course will follow the curriculum prescribed for an AP Physics C – Mechanics class. Students w ...