Force & Motion Buckle Down Review
... often with greatly different masses. Look at the illustration of a hammer pounding a nail into a board. The hammer supplies an action force, one that pushes on the nail downward. The nail supplies a reaction force, one that is equal to the action force and pushes on the hammer upward. Because the ha ...
... often with greatly different masses. Look at the illustration of a hammer pounding a nail into a board. The hammer supplies an action force, one that pushes on the nail downward. The nail supplies a reaction force, one that is equal to the action force and pushes on the hammer upward. Because the ha ...
Lecture 8
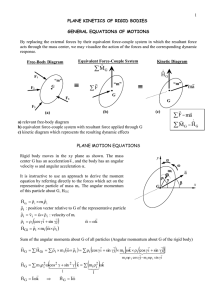
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy ...
... Another equation for working kinetics problems involving particles can be derived by integrating the equation of motion (F = ma) with respect to displacement By substituting at = v (dv/ds) into Ft = mat, the result is integrated to yield an equation known as the principle of work and energy ...
Final 2
... You may use both sides of two 8.5 x 11 sheets for formulas and reference information. Choose 30 of the 40 questions on the test. Each is worth 3 1/3 points. If you answer more than 30 questions, only the FIRST 30 will be counted. Answer all questions on the Scantron sheet. Be sure your name ...
... You may use both sides of two 8.5 x 11 sheets for formulas and reference information. Choose 30 of the 40 questions on the test. Each is worth 3 1/3 points. If you answer more than 30 questions, only the FIRST 30 will be counted. Answer all questions on the Scantron sheet. Be sure your name ...
5. Universal Laws of Motion
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
Force
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
... How did Newton change our view of the universe? • He realized the same physical laws that operate on Earth also operate in the heavens: one universe • He discovered laws of motion and gravity. • Much more: Experiments with light; first reflecting telescope, calculus… Sir Isaac Newton ...
Document
... which interval the velocity was not constant. Explain. Since velocity is the slope of the curve in a x vs t graph we can look for the interval where the slope is not constant. That interval is BC. ...
... which interval the velocity was not constant. Explain. Since velocity is the slope of the curve in a x vs t graph we can look for the interval where the slope is not constant. That interval is BC. ...
Newton`s First Law of Motion
... Net Forces the net force is the sum of all the forces acting on an object as long as the forces acting on an object are balanced (offset), then the motion of the object will not change ...
... Net Forces the net force is the sum of all the forces acting on an object as long as the forces acting on an object are balanced (offset), then the motion of the object will not change ...
Ch 6 Work, Power, Energy
... there is a displacement (the tray is moved horizontally across the room).Yet the force does not cause the displacement. ...
... there is a displacement (the tray is moved horizontally across the room).Yet the force does not cause the displacement. ...
Newton`s Laws powerpoint
... skating rink, two skaters push off from each other over a time period of 1.2 s. What is the force of the push by the smaller skater? F 16 N Newton’s 3rd law states that forces are G 32 N equal & opposite in H 88 N direction J 100 N ...
... skating rink, two skaters push off from each other over a time period of 1.2 s. What is the force of the push by the smaller skater? F 16 N Newton’s 3rd law states that forces are G 32 N equal & opposite in H 88 N direction J 100 N ...