force and acceleration
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. As already mentioned, mass depends on the number and kinds of atoms in the object. Weight, however, depends on gravity. You would weigh less on the Moon, for example, than you do on Earth. Why? The Moon's gravity is weaker than Earth's, so you ...
... Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. As already mentioned, mass depends on the number and kinds of atoms in the object. Weight, however, depends on gravity. You would weigh less on the Moon, for example, than you do on Earth. Why? The Moon's gravity is weaker than Earth's, so you ...
3 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
Momentum
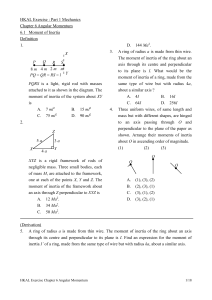
... A 1.2 kg green puck travelling at 2.0 m/s due east collides with a 2.4 kg red puck travelling at 4.5 m/s due west. After the collision the red puck travels due west at 2.5 m/s. What is the velocity of the green puck after the collision? m = 1.2 kg v = 4.5 m/s v = 2.0 m/s ...
... A 1.2 kg green puck travelling at 2.0 m/s due east collides with a 2.4 kg red puck travelling at 4.5 m/s due west. After the collision the red puck travels due west at 2.5 m/s. What is the velocity of the green puck after the collision? m = 1.2 kg v = 4.5 m/s v = 2.0 m/s ...
here.
... state of the atom is ∆E . There is only one way in which this quantum of energy can be possessed by the atom: by being in the first excited state. On the other hand, this energy can be kept in the radiation field in very many ways, essentially, since the electromagnetic field has very many degrees o ...
... state of the atom is ∆E . There is only one way in which this quantum of energy can be possessed by the atom: by being in the first excited state. On the other hand, this energy can be kept in the radiation field in very many ways, essentially, since the electromagnetic field has very many degrees o ...
Wells Problem Workbook Pack
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
... Just look at the y axis and read off the axis what the velocity is, include a direction with the answer. - Displacement at a certain time (implies from when you started until that time), Find the areas between the motion line and the x axis for each section from start to the point in question. If yo ...
Nuts and Bolts of the Ion Band State Theory
... fluxes involving) different particles within the bulk region. B) The GS is defined in a preferred reference frame, in which the balance between outside forces defines the zero of energy and momentum, which, together, establish the energies and overlap of possible many-body states. An important point ...
... fluxes involving) different particles within the bulk region. B) The GS is defined in a preferred reference frame, in which the balance between outside forces defines the zero of energy and momentum, which, together, establish the energies and overlap of possible many-body states. An important point ...
Chapter 6 Impulse and Momentum Continued
... Chapter 6 is about the COLLISION of TWO masses. To understand the interaction, both masses must be considered. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) mass ...
... Chapter 6 is about the COLLISION of TWO masses. To understand the interaction, both masses must be considered. Newton's 3rd Law plays a very important part. Collisions involve two new concepts: Impulse and Momentum. Impulse concept leads to the Momentum definition. Also applied to two (or more) mass ...
Sample
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...
... the same place it would if the bus were at rest? Answer: In accord with Newton's first law, in both cases there is no horizontal force on the dropped pencil, so no change occurs horizontally. The dropped pencil in the moving bus simply keeps up with you as you move, not changing its velocity in the ...