File
... The graph shows that when a non-zero net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in that direction. The acceleration will be directly proportional to the net force as long as the mass remains constant. The relationship is a linear relationship, and can be written as a proportionality sta ...
... The graph shows that when a non-zero net force acts on an object, the object will accelerate in that direction. The acceleration will be directly proportional to the net force as long as the mass remains constant. The relationship is a linear relationship, and can be written as a proportionality sta ...
Relative Motion in Two Dimensions
... Centrifugal “Force” • According to Newton’s first law, you will continue moving with the same velocity unless there is a net force acting on you. • The passenger in the car would continue to move straight ahead if it were not for the force of the car acting in the direction of the acceleration. ...
... Centrifugal “Force” • According to Newton’s first law, you will continue moving with the same velocity unless there is a net force acting on you. • The passenger in the car would continue to move straight ahead if it were not for the force of the car acting in the direction of the acceleration. ...
Electrostatics - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
... Translation is motion along a straight line but rotation is the motion of wheels, gears, motors, planets, the hands of a clock, the rotor of jet engines and the blades of helicopters. First figure shows a skater gliding across the ice in a straight line with constant speed. Her motion is called tran ...
... Translation is motion along a straight line but rotation is the motion of wheels, gears, motors, planets, the hands of a clock, the rotor of jet engines and the blades of helicopters. First figure shows a skater gliding across the ice in a straight line with constant speed. Her motion is called tran ...
lecture notes on statistical mechanics - MSU Physics
... to understand why all states are equally populated from the perspective of dynamics. The Ergodic theorem is built on the symmetry of time-reversal, i.e., the rate at which one changes from state i to state j is the same as the rate at which one changes from state j to state i. Here, we can consider ...
... to understand why all states are equally populated from the perspective of dynamics. The Ergodic theorem is built on the symmetry of time-reversal, i.e., the rate at which one changes from state i to state j is the same as the rate at which one changes from state j to state i. Here, we can consider ...
The electronic Hamiltonian in an electromagnetic field
... of the system that, unlike the Newtonian formulation, is invariant to coordinate transformations and also handles constraints more naturally. Most important here, it provides the springboard to quantum mechanics. Let us consider a classical system of n degrees of freedom—that is, a system in which t ...
... of the system that, unlike the Newtonian formulation, is invariant to coordinate transformations and also handles constraints more naturally. Most important here, it provides the springboard to quantum mechanics. Let us consider a classical system of n degrees of freedom—that is, a system in which t ...
S 8.2 Unbalanced forces cause changes in velocity. As a basis for
... d. Students know how to identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single static object, including gravity, elastic forces due to tension or compression in matter, and friction. e. Students know that when the forces on an object are unbalanced, the object will change its velocit ...
... d. Students know how to identify separately the two or more forces that are acting on a single static object, including gravity, elastic forces due to tension or compression in matter, and friction. e. Students know that when the forces on an object are unbalanced, the object will change its velocit ...
Exercise 4: Force and motion
... To students, it often sounds as though Newton’s third law implies nothing could ever change its motion, since the two equal and opposite forces would always cancel. The two forces, however, are always on two different objects, so it doesn’t make sense to add them in the first place — we only add for ...
... To students, it often sounds as though Newton’s third law implies nothing could ever change its motion, since the two equal and opposite forces would always cancel. The two forces, however, are always on two different objects, so it doesn’t make sense to add them in the first place — we only add for ...
Unit 4 Packet (Labs)
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
... 1. Measure and record the mass of the ball you plan to use in this experiment. 2. Connect the Motion Detector to the DIG/SONIC 1 channel of the interface. Place the Motion Detector on the floor and protect it by placing a wire basket over it. 3. Open the file “16 Energy of a Tossed Ball” from the Ph ...
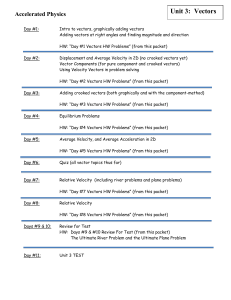
Vectors
... If you got .9827 for your answer, your calculator is in ___________ mode. Be careful of this. We will report this answer for displacement as follows: ___________________________ This has now, both magnitude and direction. It is a complete vector. The walker was displaced this much and in this direc ...
... If you got .9827 for your answer, your calculator is in ___________ mode. Be careful of this. We will report this answer for displacement as follows: ___________________________ This has now, both magnitude and direction. It is a complete vector. The walker was displaced this much and in this direc ...
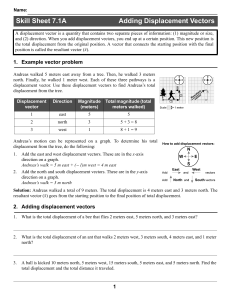
Skill Sheet 7.1A Adding Displacement Vectors
... triangle. For example, suppose you need to know the distance represented by the displacement vector (4,3)m. If you walked east 4 meters then north 3 meters, you would walk a total of 7 meters. This is a distance, but it is not the distance specified by the vector, or the shortest way to go. The vect ...
... triangle. For example, suppose you need to know the distance represented by the displacement vector (4,3)m. If you walked east 4 meters then north 3 meters, you would walk a total of 7 meters. This is a distance, but it is not the distance specified by the vector, or the shortest way to go. The vect ...







![[10] AL Kholmetskii, T. Yarman, OV Missevitch, Kündig`s Experiment](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010773015_1-b3d732fc642ab38b293e58aff252fdab-300x300.png)