Forces - School of Physics
... An interaction between two objects gives rise to a pair of forces of equal magnitude and act in opposite directions which act on separate objects (Newton’s 3rd law). ...
... An interaction between two objects gives rise to a pair of forces of equal magnitude and act in opposite directions which act on separate objects (Newton’s 3rd law). ...
Modeling of crack propagation : bridge between molecular
... Name of the supervisors: L. Chamoin (chamoin@lmt.ens-cachan.fr) P.A. Guidault (guidault@lmt.ens-cachan.fr) Context : Simulation of crack propagation is a major issue to predict the breaking of mechanical structures. Moreover, for some of these structures, it is necessary to model crack propagation a ...
... Name of the supervisors: L. Chamoin (chamoin@lmt.ens-cachan.fr) P.A. Guidault (guidault@lmt.ens-cachan.fr) Context : Simulation of crack propagation is a major issue to predict the breaking of mechanical structures. Moreover, for some of these structures, it is necessary to model crack propagation a ...
Chapter 10 - Section 3
... If an object is not moving, it will not move until a force acts on it. Clothes on the floor of your room, for example, will stay there unless you pick them up. If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. ...
... If an object is not moving, it will not move until a force acts on it. Clothes on the floor of your room, for example, will stay there unless you pick them up. If an object is already moving, it will continue to move at a constant velocity until a force acts to change either its speed or direction. ...
Power Point presentation - Physics 420 UBC Physics Demonstrations
... • Oscillatory motion occurs when a force acting on a body is proportional to the displacement of the body from equilibrium. F x • The Force acts towards the equilibrium position causing a periodic back and forth motion. ...
... • Oscillatory motion occurs when a force acting on a body is proportional to the displacement of the body from equilibrium. F x • The Force acts towards the equilibrium position causing a periodic back and forth motion. ...
1 - HCC Learning Web
... 1. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 2. Two blocks, joined by a string, have masses o ...
... 1. Two ropes are attached to a 40-kg object. The first rope applies a force of 25 N and the second, 40 N. If the two ropes are perpendicular to each other, what is the resultant acceleration of the object? a. 1.2 m/s2 b. 3.0 m/s2 c. 25 m/s2 d. 47 m/s2 2. Two blocks, joined by a string, have masses o ...
Forces, Laws of Motion & Momentum ppt
... When two or more forces act on an object at the same time, the forces combine to form the net force Forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction are called balanced forces ...
... When two or more forces act on an object at the same time, the forces combine to form the net force Forces on an object that are equal in size and opposite in direction are called balanced forces ...
Chapter 3—Forces
... Net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the force OR: acceleration = net force / mass OR: Force = mass X acceleration ...
... Net force acting on an object causes the object to accelerate in the direction of the force OR: acceleration = net force / mass OR: Force = mass X acceleration ...
Definitions
... Newton’s Second Law applies to an inertial reference frame, meaning a reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces opera ...
... Newton’s Second Law applies to an inertial reference frame, meaning a reference system for measuring position and time that is not accelerating. If we wish to use Newton’s Second Law in an accelerating reference frame, we need to add extra terms to the equation that can be considered as forces opera ...
14.2 Newton`s second law and gravity
... 14.2 Newton’s Second Law • Acceleration is the rate at which your velocity (speed with direction) changes. ...
... 14.2 Newton’s Second Law • Acceleration is the rate at which your velocity (speed with direction) changes. ...
Potential Energy - McMaster Physics and Astronomy
... what is the change of momentum ? what is the impulse ? if the collision lasts 0.1s, what was the average force ? if the force looks like below, what was the max force ? ...
... what is the change of momentum ? what is the impulse ? if the collision lasts 0.1s, what was the average force ? if the force looks like below, what was the max force ? ...
Lect-7
... Newton’s First Law describes what happens in the absence of a force Also tells us that when no net force acts on an object, the acceleration of the object is zero ...
... Newton’s First Law describes what happens in the absence of a force Also tells us that when no net force acts on an object, the acceleration of the object is zero ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Newton’s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
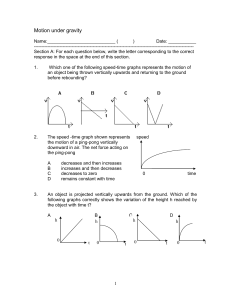
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... following graphs correctly shows the variation of the height h reached by the object with time t? A ...
... following graphs correctly shows the variation of the height h reached by the object with time t? A ...
CCC HOH FUK TONG COLLEGE
... Mary of weight W stands inside a lift. The life is moving upwards at a constant acceleration. Let the normal force exerted on Mary by the floor be R, which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) R is greater than W in magnitude. (2) R and W are in opposite directions. (3) R and W form an ac ...
... Mary of weight W stands inside a lift. The life is moving upwards at a constant acceleration. Let the normal force exerted on Mary by the floor be R, which of the following statements is/are correct? (1) R is greater than W in magnitude. (2) R and W are in opposite directions. (3) R and W form an ac ...