Exploring Motion Introduction
... Newton’s three laws of motion describe the interaction of forces that control movement. The first law states that a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. The same is true for a body at rest. The second law predicts that when an unbalanced force is applied to ...
... Newton’s three laws of motion describe the interaction of forces that control movement. The first law states that a body in motion will remain in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. The same is true for a body at rest. The second law predicts that when an unbalanced force is applied to ...
Physical Science (Forces)
... field, the two objects experience electric forces that can attract or repel them, depending on the charges involved. Electric force weakens rapidly with increasing distance. Magnetic fields exist around magnetic objects. If a second magnetic object is placed in the field, the two objects experience ...
... field, the two objects experience electric forces that can attract or repel them, depending on the charges involved. Electric force weakens rapidly with increasing distance. Magnetic fields exist around magnetic objects. If a second magnetic object is placed in the field, the two objects experience ...
Physics 218 - Purdue Physics
... directed against its motion. Enter the proper sign (+, - or 0) for each quantity listed. Explain each answer. on way up Work done by weight Work done by friction ...
... directed against its motion. Enter the proper sign (+, - or 0) for each quantity listed. Explain each answer. on way up Work done by weight Work done by friction ...
Momentum and Impulse (Key)
... travelling at a constant velocity of 8.0 m/s [E]. It hits an immovable wall and comes to a complete stop in 0.25 s. i) Calculate the impulse provided to the car. [9.6 x 103 Ns [W]] ...
... travelling at a constant velocity of 8.0 m/s [E]. It hits an immovable wall and comes to a complete stop in 0.25 s. i) Calculate the impulse provided to the car. [9.6 x 103 Ns [W]] ...
relative - Purdue Physics
... • Applies to situations when the object or the observer is accelerated • Gravitational fields also are a form of acceleration (take g, for example) • GR is the world’s best classical theory of gravitation • GR tells us how clocks slow down in a gravitational potential well (Earth’s surface). Crucial ...
... • Applies to situations when the object or the observer is accelerated • Gravitational fields also are a form of acceleration (take g, for example) • GR is the world’s best classical theory of gravitation • GR tells us how clocks slow down in a gravitational potential well (Earth’s surface). Crucial ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... A specific type of interaction between 2 objects. The basic assumptions of a collision: 1. Interaction is short lived compared to the time of observation 2. A relatively large force acts on each colliding object 3. The motion of one or both objects changes abruptly following ...
... A specific type of interaction between 2 objects. The basic assumptions of a collision: 1. Interaction is short lived compared to the time of observation 2. A relatively large force acts on each colliding object 3. The motion of one or both objects changes abruptly following ...
lecture2.pdf
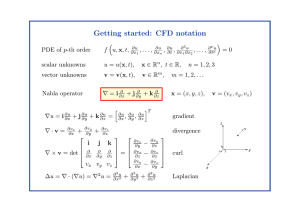
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
... It is important to understand the meaning and significance of each equation in order to develop a good numerical method and properly interpret the results ...
Forces PPT - Effingham County Schools
... another, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. • For every action, there is an equal, but opposite reaction (not balanced). A swimmer “acts” on the water, the “reaction” of the water pushes the swimmer forward. ...
... another, the second object exerts an equal and opposite force on the first object. • For every action, there is an equal, but opposite reaction (not balanced). A swimmer “acts” on the water, the “reaction” of the water pushes the swimmer forward. ...
Uniform Circular Motion
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
... around a circle with a fixed radius Can the velocity be accelerated even though it has constant speed? Yes, because the velocity may change due to direction. If direction changes and velocity changes then an object can accelerate. ...
Review of Physics 20
... A car is at rest on a horizontal road surface. The driver presses down on the gas pedal and the car accelerates forward for a few seconds until it reaches the speed limit. The driver eases off of the gas pedal and the car moves at constant speed. Describe and explain the car’s motion in terms of New ...
... A car is at rest on a horizontal road surface. The driver presses down on the gas pedal and the car accelerates forward for a few seconds until it reaches the speed limit. The driver eases off of the gas pedal and the car moves at constant speed. Describe and explain the car’s motion in terms of New ...
Document
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving • forces overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) change in velocity ...
... • Objects have a property called inertia which causes them to resist changes in their motion (Newton’s1st Law or Galileo’s law of inertia) if it is at rest, it stays at rest if it is moving, it keeps moving • forces overcome inertia to produce acceleration (2nd Law) change in velocity ...
Chapter4
... Fundamental (Field) Forces Types • Strong nuclear force • Electromagnetic force • Weak nuclear force • Gravity ...
... Fundamental (Field) Forces Types • Strong nuclear force • Electromagnetic force • Weak nuclear force • Gravity ...
Circular Motion and Gravitation
... Recall: Circumference= 2πr OR 2d d=diameter r=radius The Circumference Is your distance. ...
... Recall: Circumference= 2πr OR 2d d=diameter r=radius The Circumference Is your distance. ...