AP-1 Cutnell 06-10 1st Sem Rev Key Points
... is carrying a 120 kg crate. The crate does not slip as the truck moves s = 65 m. What is the total work done on the crate by all the forces acting on it? ...
... is carrying a 120 kg crate. The crate does not slip as the truck moves s = 65 m. What is the total work done on the crate by all the forces acting on it? ...
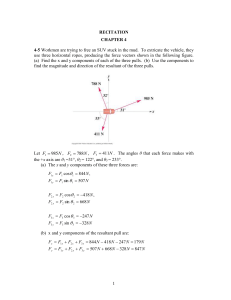
Recitation Ch 4-1
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
NEWTON`S THREE LAWS OF MOTION
... NEWTON’S THREE LAWS OF MOTION I. An object will remain at rest or will continue to move uniformly in a straight line at a constant velocity (speed and direction) unless acted upon by a force. Inertia example pushing a stationary object on a table 2. The rate of change of velocity of an object is pro ...
... NEWTON’S THREE LAWS OF MOTION I. An object will remain at rest or will continue to move uniformly in a straight line at a constant velocity (speed and direction) unless acted upon by a force. Inertia example pushing a stationary object on a table 2. The rate of change of velocity of an object is pro ...
Le mouvement et les types de forces
... ________________________ the object, thus decreasing its velocity. In this case, the object is undergoing ________________________ (or “negative acceleration”). A force can also modify the trajectory of a moving object. This change in direction is considered another form of ________________________. ...
... ________________________ the object, thus decreasing its velocity. In this case, the object is undergoing ________________________ (or “negative acceleration”). A force can also modify the trajectory of a moving object. This change in direction is considered another form of ________________________. ...
Newton*s Laws of Motion
... by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the fish ...
... by pushing the fish forwards, propelling the fish through the water. The size of the force on the water equals the size of the force on the fish; the direction of the force on the water (backwards) is opposite the direction of the force on the fish ...
What is Force
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
... Newton’s First Law: Objects in motion tend to stay in motion and objects at rest tend to stay at rest unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. Newton’s Second Law: Force equals mass times acceleration (F = ma). Newton’s Third Law: For every action there is an equal and opposite reaction. ...
Law of Inertia
... “The acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body” * “in the same direction as the net force” ◦ a in the same direction of body’s motion speed up ◦ a in opposite directi ...
... “The acceleration of a body is directly proportional to the magnitude of the net force, in the same direction as the net force, and inversely proportional to the mass of the body” * “in the same direction as the net force” ◦ a in the same direction of body’s motion speed up ◦ a in opposite directi ...
Newton`s Laws Study Guide
... “An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line, unless acted on by an unbalanced force.” In other words, if an object is still (not moving), an unbalanced force is necessary to make it move. Once an object is moving, it will go ...
... “An object at rest remains at rest and an object in motion remains in motion at a constant speed and in a straight line, unless acted on by an unbalanced force.” In other words, if an object is still (not moving), an unbalanced force is necessary to make it move. Once an object is moving, it will go ...
Newton on K’s 3 Law, To Frame the World—30 Sept • Announcements
... • The force of the gravity of the sun is causing the direction of the motion to change. ...
... • The force of the gravity of the sun is causing the direction of the motion to change. ...
physics midterm review
... 6. A car accelerates from rest at a rate of 5 m/s/s for a period of 4.2 seconds and then moves at a constant speed for 8 seconds more. How far did it travel? ...
... 6. A car accelerates from rest at a rate of 5 m/s/s for a period of 4.2 seconds and then moves at a constant speed for 8 seconds more. How far did it travel? ...
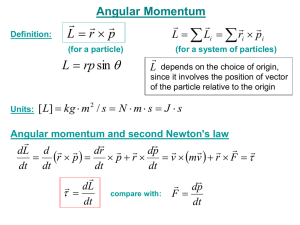
lecture23
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...
... speed is v2. What is the angular speed ω of the stick after the collision? External forces: weight of the stick and force on the stick by the pivoting axle produce no torque. Weight of the bullet is negligible. ...
Lecture 8, PPT version
... A: There are no accelerations (no gravity) All reference frames in Special Relativity are “inertial reference frames”; the observers are not accelerating and Newton’s first law (N1) is observed N1: an object will remain in a state of uniform motion in a straight line or in a state of rest until acte ...
... A: There are no accelerations (no gravity) All reference frames in Special Relativity are “inertial reference frames”; the observers are not accelerating and Newton’s first law (N1) is observed N1: an object will remain in a state of uniform motion in a straight line or in a state of rest until acte ...
OWL Ch02 Review Game
... The relationship among force, mass, and acceleration is stated in ____. a. the law of conservation of momentum b. Newton's first law of motion c. Newton's second law of motion d. Newton's third law of motion ...
... The relationship among force, mass, and acceleration is stated in ____. a. the law of conservation of momentum b. Newton's first law of motion c. Newton's second law of motion d. Newton's third law of motion ...