Force and acceleration Chapter_3_Lesson_1
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...
... Mass and Acceleration • If you throw a softball and a baseball as hard as you can, why don’t they have the same speed? • The difference is due to their masses. • If it takes the same amount of time to throw both balls, the softball would have less. • Force, mass, acceleration and acceleration are r ...
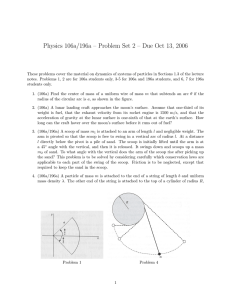
Physics 106a/196a – Problem Set 2 – Due Oct 13,...
... The system is in a uniform gravitational field, pointing downward. Find the total kinetic and potential energy of the system as a function of θ and θ̇. 5. (106a/196a) A proton of mass m1 collides elastically with an unknown nucleus in a bubble chamber and is scattered through an angle ψ1 . The ratio ...
... The system is in a uniform gravitational field, pointing downward. Find the total kinetic and potential energy of the system as a function of θ and θ̇. 5. (106a/196a) A proton of mass m1 collides elastically with an unknown nucleus in a bubble chamber and is scattered through an angle ψ1 . The ratio ...
Practice test 2, hints Question 1: Magnetic field lines always form
... Question 9: The proton and the positron have the same charge and they are in the same field, so they experience the same force, F = qE. The acceleration is a = F/m, so the lighter particle (the positron) has the greater acceleration. When the particles reach the other plate, the potential energy U ...
... Question 9: The proton and the positron have the same charge and they are in the same field, so they experience the same force, F = qE. The acceleration is a = F/m, so the lighter particle (the positron) has the greater acceleration. When the particles reach the other plate, the potential energy U ...
Newton`s Laws
... the moving object is transferred to the stationary object which causes the moving object to stop and the stationary object to start moving, but the total momentum stays the same. Collisions with connected objects – when two objects collide and become connected as a result of that collision, ½ of the ...
... the moving object is transferred to the stationary object which causes the moving object to stop and the stationary object to start moving, but the total momentum stays the same. Collisions with connected objects – when two objects collide and become connected as a result of that collision, ½ of the ...
II. Describing Motion
... direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram is shows the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow reveals the direction in which the force acts. ...
... direction of all forces acting upon an object in a given situation. The size of the arrow in a free-body diagram is shows the magnitude of the force. The direction of the arrow reveals the direction in which the force acts. ...
Chap #3
... Begin by choosing the positive direction as down. That seems reasonable since the fire fighter will slide down the pole and not up the pole. The two forces on the fire fighter are his weight, W=mg, which acts downward, the force of sliding friction, f, which acts upward ( ie the friction force oppos ...
... Begin by choosing the positive direction as down. That seems reasonable since the fire fighter will slide down the pole and not up the pole. The two forces on the fire fighter are his weight, W=mg, which acts downward, the force of sliding friction, f, which acts upward ( ie the friction force oppos ...
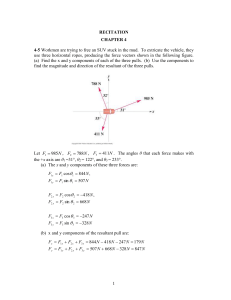
Recitation Ch 4-1
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...
... 4-34 A factory worker pushes horizontally on a 250 N crate with a force of 75 N on a horizontal rough floor. A 135 N crate rests on top of the one being pushed and moves along with it. Make a free-body diagram of each crate if the friction force is less than the worker’s push. There is a friction fo ...