Chapter 5: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... choose a coordinate system, (3) resolve each force into components, and (4) apply Newton’s second law to each coordinate direction separately. 24. The weight of an object with mass m is calculated from the equation W = mg. 25. If an object is at rest, and remains at rest, it is not accelerating, and ...
... choose a coordinate system, (3) resolve each force into components, and (4) apply Newton’s second law to each coordinate direction separately. 24. The weight of an object with mass m is calculated from the equation W = mg. 25. If an object is at rest, and remains at rest, it is not accelerating, and ...
Exam Review + Ch. 7: Momentum, Impulse, Center of Mass
... The total energy is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy of an object. The potential energy is the amount of work it took to put the object in its current position. It is normally written as U. For example, the potential energy of a book of mass m on top of a cabinet of height h is ...
... The total energy is the sum of the kinetic energy and the potential energy of an object. The potential energy is the amount of work it took to put the object in its current position. It is normally written as U. For example, the potential energy of a book of mass m on top of a cabinet of height h is ...
4 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
... Galileo tested his idea by rolling balls along plane surfaces tilted at different angles. • A ball rolling down an inclined plane speeds up. • A ball rolling up an inclined plane—in a direction opposed by gravity—slows down. • A ball rolling on a smooth horizontal plane has almost ...
preview as pdf - Pearson Higher Education
... alternative way of looking at single-particle dynamics. To discover the real power of momentum for problem solving, we need also to invoke Newton’s third law, which will lead us to one of the most important principles in physics: conservation of momentum. FIGURE 11.9 shows two objects with initial v ...
... alternative way of looking at single-particle dynamics. To discover the real power of momentum for problem solving, we need also to invoke Newton’s third law, which will lead us to one of the most important principles in physics: conservation of momentum. FIGURE 11.9 shows two objects with initial v ...
Notes on (calculus based) Physics
... Lecture-Example 1.4: (Weyl expansion) The list of overtones (frequencies of vibrations) of a drum is completely determined by the shape of the drumhead. Is the converse true? That is, what physical quantities regarding the shape of a drum can one infer, if the complete list of overtones is given. Th ...
... Lecture-Example 1.4: (Weyl expansion) The list of overtones (frequencies of vibrations) of a drum is completely determined by the shape of the drumhead. Is the converse true? That is, what physical quantities regarding the shape of a drum can one infer, if the complete list of overtones is given. Th ...
pdf file
... Apparently, the use of potentialities may lead to an infinitedimensional vector of higher-order potentialities. As this can be difficult to handle, it makes sense to look for ways to break off this chain of higher-order potentialities. One possible option is to consider only changes that involve a f ...
... Apparently, the use of potentialities may lead to an infinitedimensional vector of higher-order potentialities. As this can be difficult to handle, it makes sense to look for ways to break off this chain of higher-order potentialities. One possible option is to consider only changes that involve a f ...
Document
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
... Example : Two boxes and a pulley. Two boxes are connected by a cord running over a pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction between box A and the table is 0.20. We ignore the mass of the cord and pulley and any friction in the pulley, which means we can assume that a force applied to one end of ...
Grade 9 Physics - Hammonton Public Schools
... transferred from one object to another during collisions. ...
... transferred from one object to another during collisions. ...
- Lake Fenton Community School District
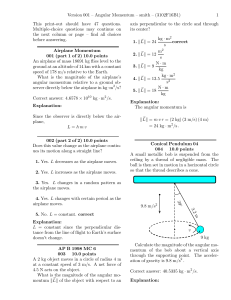
... Information: Scientific Notation “Scientific notation” is used to make very large or very small numbers easier to handle. For example the number 45,000,000,000,000,000 can be written as “4.5 x 1016 ”. The “16” tells you that there are sixteen decimal places between the right side of the four and the ...
... Information: Scientific Notation “Scientific notation” is used to make very large or very small numbers easier to handle. For example the number 45,000,000,000,000,000 can be written as “4.5 x 1016 ”. The “16” tells you that there are sixteen decimal places between the right side of the four and the ...
Slide 8
... • Newton’s Second Law – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. ...
... • Newton’s Second Law – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force acting on it and inversely proportional to its mass. ...
Introduction to Modern Physics PHYX 2710
... – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the imposed force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The acceleration is the same direction as that of the imposed force. F ma ...
... – The acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the magnitude of the imposed force and inversely proportional to the mass of the object. The acceleration is the same direction as that of the imposed force. F ma ...