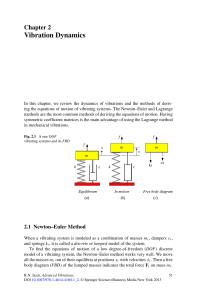
Working with moving pulleys
... to ground i.e. inertial frame of reference in order to apply Newton's second law of motion . We, therefore, need to rst determine acceleration with respect to ground using relation for relative ...
... to ground i.e. inertial frame of reference in order to apply Newton's second law of motion . We, therefore, need to rst determine acceleration with respect to ground using relation for relative ...
Knowledge Check (Answer Key)
... Mass: Mass is the amount of material present in an object. This dimension describes how much material makes up an object. Often, mass and weight are confused as being the same because the units used to describe them are similar. Weight is a derived unit, not a fundamental unit, and is a measurement ...
... Mass: Mass is the amount of material present in an object. This dimension describes how much material makes up an object. Often, mass and weight are confused as being the same because the units used to describe them are similar. Weight is a derived unit, not a fundamental unit, and is a measurement ...
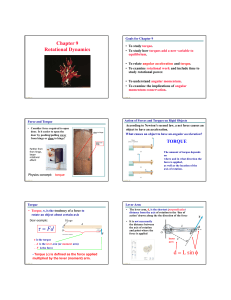
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... the law is valid are called inertial reference frames. Thus, the reference frame of the ground is an inertial reference frame, but that of the accelerating truck is not. Note that if some first reference frame is inertial, any other reference frame in uniform translational motion relative to the fir ...
... the law is valid are called inertial reference frames. Thus, the reference frame of the ground is an inertial reference frame, but that of the accelerating truck is not. Note that if some first reference frame is inertial, any other reference frame in uniform translational motion relative to the fir ...
Short Answers to Questions
... Q.2 An object is thrown vertically upward. Discuss the sign of acceleration due to gravity, relative to velocity, while the object is in air. Ans. Since direction of initial velocity is upward. So g will be negative, relative to velocity. For downward motion, g is positive with reference to the dire ...
... Q.2 An object is thrown vertically upward. Discuss the sign of acceleration due to gravity, relative to velocity, while the object is in air. Ans. Since direction of initial velocity is upward. So g will be negative, relative to velocity. For downward motion, g is positive with reference to the dire ...
Classical Mechanics: a Critical Introduction
... light. The description of atomic phenomena requires quantum mechanics, and the description of phenomena at very high velocities requires Einstein’s Theory of Relativity. Both quantum mechanics and relativity were invented in the twentieth century; the laws of classical mechanics were stated by Sir I ...
... light. The description of atomic phenomena requires quantum mechanics, and the description of phenomena at very high velocities requires Einstein’s Theory of Relativity. Both quantum mechanics and relativity were invented in the twentieth century; the laws of classical mechanics were stated by Sir I ...
Lecture 37 - USU Department of Physics
... For an electron all the electrostatic PE is converted to KE, eV 1/2 mv2 . First solve for p then for λ. Section 0 ...
... For an electron all the electrostatic PE is converted to KE, eV 1/2 mv2 . First solve for p then for λ. Section 0 ...
Objective Assignment - PRADEEP KSHETRAPAL PHYSICS
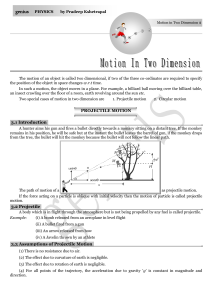
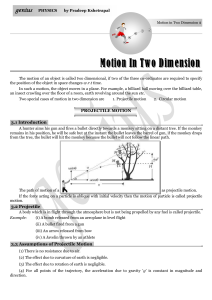
... 3.4 Principles of Physical Independence of Motions. (1) The motion of a projectile is a two-dimensional motion. So, it can be discussed in two parts. Horizontal motion and vertical motion. These two motions take place independent of each other. This is called the principle of physical independence o ...
... 3.4 Principles of Physical Independence of Motions. (1) The motion of a projectile is a two-dimensional motion. So, it can be discussed in two parts. Horizontal motion and vertical motion. These two motions take place independent of each other. This is called the principle of physical independence o ...
On a Report by the German Physical Society Concerning
... developed at MIT by diSessa (1980). In addition, within the Introductory University Physics Project (Di Stefano, 1996; Coleman, Holcomb & Rigden, 1998) the idea to base physics upon conservation laws, rather than Newton’s equations was put forward (Moore, 2003). The KPC uses the observation that the ...
... developed at MIT by diSessa (1980). In addition, within the Introductory University Physics Project (Di Stefano, 1996; Coleman, Holcomb & Rigden, 1998) the idea to base physics upon conservation laws, rather than Newton’s equations was put forward (Moore, 2003). The KPC uses the observation that the ...
Chapter 7 Kinetics and Structure of Colloidal Aggregates 7.1
... where Nk is the number concentration of aggregates of size k, and the first term on the r.h.s. represents all possible collisions leading to the formation of an aggregate of mass k, while the second is the rate of disappearance of the aggregates of mass k due to aggregation with aggregates of any ma ...
... where Nk is the number concentration of aggregates of size k, and the first term on the r.h.s. represents all possible collisions leading to the formation of an aggregate of mass k, while the second is the rate of disappearance of the aggregates of mass k due to aggregation with aggregates of any ma ...
Electrically driven flow near a colloidal particle close to an electrode
... The scaling analysis does confirm, however, that the direction of the EHD flow is independent of the applied polarity because the signs of the applied potential and current density are coupled. The experimental observations, however, demonstrate a polarity dependence. In the second part of the analy ...
... The scaling analysis does confirm, however, that the direction of the EHD flow is independent of the applied polarity because the signs of the applied potential and current density are coupled. The experimental observations, however, demonstrate a polarity dependence. In the second part of the analy ...