Summary Notes - Cathkin High School
... Graphs are an excellent way of giving information, especially to show relationships between quantities. In this section we will be examining three types of motion-time graphs. Displacement-time graphs Velocity-time graphs Acceleration-time graphs If you have an example of one of these types of graph ...
... Graphs are an excellent way of giving information, especially to show relationships between quantities. In this section we will be examining three types of motion-time graphs. Displacement-time graphs Velocity-time graphs Acceleration-time graphs If you have an example of one of these types of graph ...
4.1 The Concepts of Force and Mass
... 6.3.5. Consider the box in the drawing. We can slide the box up the frictionless incline from point A and to point C or we can slide it along the frictionless horizontal surface from point A to point B and then lift it to point C. How does the work done on the box along path A-C,WAC, compare to the ...
... 6.3.5. Consider the box in the drawing. We can slide the box up the frictionless incline from point A and to point C or we can slide it along the frictionless horizontal surface from point A to point B and then lift it to point C. How does the work done on the box along path A-C,WAC, compare to the ...
Course Outline Course title: Physics
... This is designed to introduce the principles of newtonian mechanics at the freshmen level of the undergraduate study for engineering majors or equivalent. The key concepts to be developed throughout the semester are: vectors, equations of motions, Newton’s laws, conservation laws of energy, momentum ...
... This is designed to introduce the principles of newtonian mechanics at the freshmen level of the undergraduate study for engineering majors or equivalent. The key concepts to be developed throughout the semester are: vectors, equations of motions, Newton’s laws, conservation laws of energy, momentum ...
Document
... figures (the most used being the dot, the triangle, the circle and the square). The drawing has spiritual and ritual meaning in both Buddhism and Hinduism. ...
... figures (the most used being the dot, the triangle, the circle and the square). The drawing has spiritual and ritual meaning in both Buddhism and Hinduism. ...
Rigid Body Simulation (1)
... τ(t ) τi (t ) (ri (t ) x(t )) Fi (t ) Tells us about the force distribution over the object ...
... τ(t ) τi (t ) (ri (t ) x(t )) Fi (t ) Tells us about the force distribution over the object ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion
... A 2.0 kg mass sliding on a table with an initial velocity of +1.0 m/s, slows to +0.5 m/s, in 2.0 seconds. A force acting on the mass causes it to lose speed. What is the magnitude and direction of this force? a) F = −0.5N b) F = +0.5N c) F = −1.0 N d) F = +1.0 N e) F = −2.0 N ...
... A 2.0 kg mass sliding on a table with an initial velocity of +1.0 m/s, slows to +0.5 m/s, in 2.0 seconds. A force acting on the mass causes it to lose speed. What is the magnitude and direction of this force? a) F = −0.5N b) F = +0.5N c) F = −1.0 N d) F = +1.0 N e) F = −2.0 N ...
Conceptual Physics
... Read all key terms. Underline all words you are unfamiliar with. Then go back and create a flash card for each term. Use the term in a sentence, define it, or draw a picture for the term. ...
... Read all key terms. Underline all words you are unfamiliar with. Then go back and create a flash card for each term. Use the term in a sentence, define it, or draw a picture for the term. ...
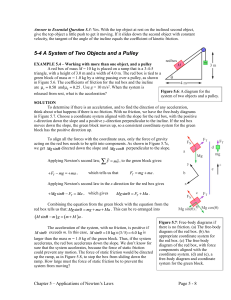
5-4 A System of Two Objects and a Pulley
... To determine if there is an acceleration, and to find the direction of any acceleration, think about what happens if there is no friction. With no friction, we have the free-body diagrams in Figure 5.7. Choose a coordinate system aligned with the slope for the red box, with the positive x-direction ...
... To determine if there is an acceleration, and to find the direction of any acceleration, think about what happens if there is no friction. With no friction, we have the free-body diagrams in Figure 5.7. Choose a coordinate system aligned with the slope for the red box, with the positive x-direction ...
motion in two dimension
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
... put one on another and each moved in slightly different directions . The platform on top will experience simultaneous motion in four directions. For a well leveled platform though, the motion will only be in two dimensions. Do not confuse direction with dimension . There is indefinite number of dire ...
Wednesday, Oct. 11, 2006
... – But due to the small mass, electron’s energy loss gets complicated • Relativistic corrections take large effect even down to a few keV level • Electron projectiles can transfer large fractions of energies to the atomic electrons they collide – Produce d-rays or knock-on electrons Which have the ...
... – But due to the small mass, electron’s energy loss gets complicated • Relativistic corrections take large effect even down to a few keV level • Electron projectiles can transfer large fractions of energies to the atomic electrons they collide – Produce d-rays or knock-on electrons Which have the ...
Magnetism
... Below I have drawn the trajectory for two charged particles traveling through a magnetic field. Is particle 1 positive or negatively charged? ...
... Below I have drawn the trajectory for two charged particles traveling through a magnetic field. Is particle 1 positive or negatively charged? ...
Chapter 9- Static Equilibrium
... The Conditions for Equilibrium Recalling an important note: We consider that the mass of an object with uniform mass distribution (or uniform object for short) is such that it can be assumed to be located at the centre of the object. This point is know as either centre of mass or centre of gravity ...
... The Conditions for Equilibrium Recalling an important note: We consider that the mass of an object with uniform mass distribution (or uniform object for short) is such that it can be assumed to be located at the centre of the object. This point is know as either centre of mass or centre of gravity ...
Force-Mass-Acceleration method
... - Potential Energy approach can be used to specifically treat the work done by gravity forces and spring forces Simplify analysis of many problems. Gravitational Potential Energy • Motion in close proximity to earth’s surface g constant • The gravitational potential energy of a particle Vg = wor ...
... - Potential Energy approach can be used to specifically treat the work done by gravity forces and spring forces Simplify analysis of many problems. Gravitational Potential Energy • Motion in close proximity to earth’s surface g constant • The gravitational potential energy of a particle Vg = wor ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...