Motion, Forces, and Newton`s Laws
... C. Velocity 1. The speed and direction of an object’s motion is the velocity of the object. 2. Velocity is often represented by using a(n) arrow. a. The total length of the arrow shows speed. b. The direction of the arrow shows the direction the object moves. 3. When an object’s speed and direction ...
... C. Velocity 1. The speed and direction of an object’s motion is the velocity of the object. 2. Velocity is often represented by using a(n) arrow. a. The total length of the arrow shows speed. b. The direction of the arrow shows the direction the object moves. 3. When an object’s speed and direction ...
Lect-18
... done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational ...
... done by external forces in rotating a symmetrical rigid object about a fixed axis equals the change in the object’s rotational ...
Document
... As you drive past your friend standing at his/her house...they see this ball moving along with your car. So to them it appears the path the ball follows a ballistic path with both with vx = 20 m/s vy = 4 m/s. One interesting note. The y-component of the velocity did have a force upon it...GRAVITY! G ...
... As you drive past your friend standing at his/her house...they see this ball moving along with your car. So to them it appears the path the ball follows a ballistic path with both with vx = 20 m/s vy = 4 m/s. One interesting note. The y-component of the velocity did have a force upon it...GRAVITY! G ...
Assignment 8 Solutions
... b. [4 points] What is the pail’s minimum speed at the top of the circle if no water is to spill out? c. [3 points] If the pail with the speed found in part (b) were to suddenly disappear at the top of the circle, describe the subsequent motion of the water. Would it differ from the motion of a proje ...
... b. [4 points] What is the pail’s minimum speed at the top of the circle if no water is to spill out? c. [3 points] If the pail with the speed found in part (b) were to suddenly disappear at the top of the circle, describe the subsequent motion of the water. Would it differ from the motion of a proje ...
Principles and Problems Chapter 9 Linear
... momentum is conserved. Momentum is conserved during a collision. Kinetic energy is also conserved in an ...
... momentum is conserved. Momentum is conserved during a collision. Kinetic energy is also conserved in an ...
In what ways do forces affect an object`s motion?
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
... • Inertia is the tendency of an object to resist a change of motion Newton’s first law of motion states that an object will remain at rest or in constant straight-line motion unless unbalanced forces act on the object. • Newton’s second law of motion states that the acceleration of an object incre ...
Newtons Laws of Motion - Winston Churchill High School
... The act of moving or the ability to move from one place to another is called locomotion. Any animal or machine that moves depends on Newton’s third law to get around. When we walk, we push off the ground and move forward because of the ground pushing back on us in the opposite direction. ...
... The act of moving or the ability to move from one place to another is called locomotion. Any animal or machine that moves depends on Newton’s third law to get around. When we walk, we push off the ground and move forward because of the ground pushing back on us in the opposite direction. ...
Mechanics Notes II Forces, Inertia and Motion The mathematics of
... one would need three initial conditions to determine x(t) for times in the future. If one believes that only the initial position, x0 , and initial velocity, v0 , are necessary to determine x(t) for future times, then there can be at most second derivatives of x(t) in the equations of motion. Under ...
... one would need three initial conditions to determine x(t) for times in the future. If one believes that only the initial position, x0 , and initial velocity, v0 , are necessary to determine x(t) for future times, then there can be at most second derivatives of x(t) in the equations of motion. Under ...
e + + e
... 1) Ionization and excitation of atoms – Bethe-Bloch formula has within parenthesis different form than for ionization losses for heavy particles: a) electron can transfer during collision large part of energy b) exchange effects – impinging and impacted electrons can not be distinguished c) annihila ...
... 1) Ionization and excitation of atoms – Bethe-Bloch formula has within parenthesis different form than for ionization losses for heavy particles: a) electron can transfer during collision large part of energy b) exchange effects – impinging and impacted electrons can not be distinguished c) annihila ...
Part IV
... • STEP 2: Resolve the forces on each body into components – Use a convenient choice of x,y axes • Use the rules for finding vector components from Ch. 3. ...
... • STEP 2: Resolve the forces on each body into components – Use a convenient choice of x,y axes • Use the rules for finding vector components from Ch. 3. ...
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
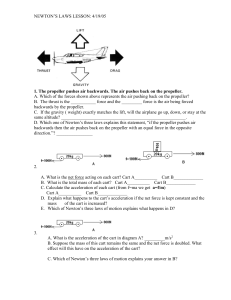
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...
... 4. Refer to the diagram labeled “A”. If the cart is moving to the right at 3.0m/s, what will happen to the 10kg weight sitting on the top of the cart if the cart stops abruptly? 5. Look up Bernoulli’s Principle in your text. What is the significance of Bernoulli’s Principle with respect to an airpla ...