Newton`s Laws II - Rutgers Physics
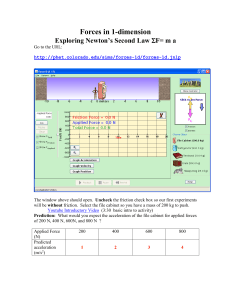
... A) Measure acceleration and tension simultaneously using a force and a motion sensor. 0. First, test the four wheels on the Pasco cart by spinning each one by hand to see if it spins for at least 3 seconds before stopping. If it stops quickly, try pushing the wheels (along their axes) away from the ...
... A) Measure acceleration and tension simultaneously using a force and a motion sensor. 0. First, test the four wheels on the Pasco cart by spinning each one by hand to see if it spins for at least 3 seconds before stopping. If it stops quickly, try pushing the wheels (along their axes) away from the ...
SHM - Red Hook Central School District
... w = 2pf. = 0.4 p Hz =1.26 rad/s. • t = 10.66 s • x = 0.03 cos (1.26 x 10.66) = 0.019 m • You must use radians on calculator. ...
... w = 2pf. = 0.4 p Hz =1.26 rad/s. • t = 10.66 s • x = 0.03 cos (1.26 x 10.66) = 0.019 m • You must use radians on calculator. ...
Jeopardy
... at 65mph. One is leaving the east coast going west and the other is leaving the west coast going east, on the same highway. At what time ...
... at 65mph. One is leaving the east coast going west and the other is leaving the west coast going east, on the same highway. At what time ...
Question #3, p
... As with the previous question, we are assuming that air resistance will not be a significant factor in the calculation. This leaves only the gravitational interaction between Mars and the rock. The (magnitude of the) acceleration due to gravity (a) on Mars is 3.71m/s2 will also apply to the falling ...
... As with the previous question, we are assuming that air resistance will not be a significant factor in the calculation. This leaves only the gravitational interaction between Mars and the rock. The (magnitude of the) acceleration due to gravity (a) on Mars is 3.71m/s2 will also apply to the falling ...
Chapter 10 Forces
... What information are you given? Mass of smaller sledgehammer = 3.0 kg Velocity of smaller sledgehammer = 1.5 m/s Mass of larger sledgehammer = 4.0 kg Velocity of larger sledgehammer = 0.9 m/s ...
... What information are you given? Mass of smaller sledgehammer = 3.0 kg Velocity of smaller sledgehammer = 1.5 m/s Mass of larger sledgehammer = 4.0 kg Velocity of larger sledgehammer = 0.9 m/s ...
Adiabatic Charged Particle Motion in Rapidly Rotating
... drifts. If one has presentin addition the other five drifts, the proofcannotbe carriedthrough.The samedifficultyappearsin The theory of adiabatic particle motion in electromagnetic differentguiseif onetriesto carry out thoseproofsthat employ fieldsis well developedthrough first order in gyroradius[e ...
... drifts. If one has presentin addition the other five drifts, the proofcannotbe carriedthrough.The samedifficultyappearsin The theory of adiabatic particle motion in electromagnetic differentguiseif onetriesto carry out thoseproofsthat employ fieldsis well developedthrough first order in gyroradius[e ...
Grade 11: Physical Sciences Outline
... Conservation of energy with non-conservative forces present Define a conservative force as a force for which the work done in moving an object between two points is independent of the path taken. Examples are gravitational force, the elastic force in a spring and electrostatic forces (coulomb forces ...
... Conservation of energy with non-conservative forces present Define a conservative force as a force for which the work done in moving an object between two points is independent of the path taken. Examples are gravitational force, the elastic force in a spring and electrostatic forces (coulomb forces ...
Lecture-15-10
... for a certain period of time, first as in (a) and then as in (b). In which case does the dumbbell acquire the greater center-of-mass speed ? ...
... for a certain period of time, first as in (a) and then as in (b). In which case does the dumbbell acquire the greater center-of-mass speed ? ...
- Philsci
... away. Moreover, this approach resulted in principal elimination of the gravitational divergence problem. Another new result concerned the speed of light. The conclusion was that the speed of light is not a fundamental physical constant: it is a physical quantity determined by a gravitational potenti ...
... away. Moreover, this approach resulted in principal elimination of the gravitational divergence problem. Another new result concerned the speed of light. The conclusion was that the speed of light is not a fundamental physical constant: it is a physical quantity determined by a gravitational potenti ...
Unit 2 Motion and Force
... • A change in velocity can be: either a change in how fast something is moving, or a change in the direction it is moving. • Acceleration occurs when: an object changes its speed, it's direction, or both. ...
... • A change in velocity can be: either a change in how fast something is moving, or a change in the direction it is moving. • Acceleration occurs when: an object changes its speed, it's direction, or both. ...











![06 Momentum WS 08 [v6.0]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017198328_1-636fbdb6d6c62db5233df770cc2cf61d-300x300.png)