Lecture 7.1
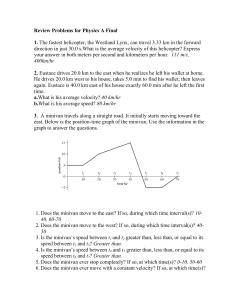
... Impulse demo • Cart equipped with force probe collides with rubber tube • Measure force vs. time and momentum ...
... Impulse demo • Cart equipped with force probe collides with rubber tube • Measure force vs. time and momentum ...
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... • Newton’s first law: If the net force on an object is zero, it will remain either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed. • Newton’s second law: • Newton’s third law: • Weight is the gravitational force on an object. • Free-body diagrams are essential for problemsolving. Do one obje ...
... • Newton’s first law: If the net force on an object is zero, it will remain either at rest or moving in a straight line at constant speed. • Newton’s second law: • Newton’s third law: • Weight is the gravitational force on an object. • Free-body diagrams are essential for problemsolving. Do one obje ...
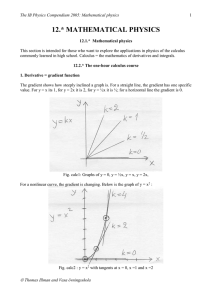
12. MATHEMATICAL PHYSICS
... true"!). In relativity we must change Newton's II law F = ma since m is not constant. We can use the momentum instead : F = ma = m(v-u) = mv - mu and then impulse = Ft = change in momentum = p = mv - mu which for an infinitely short time dt becomes: Fdt = dp and dividing with dt then: F = dp/dt (f ...
... true"!). In relativity we must change Newton's II law F = ma since m is not constant. We can use the momentum instead : F = ma = m(v-u) = mv - mu and then impulse = Ft = change in momentum = p = mv - mu which for an infinitely short time dt becomes: Fdt = dp and dividing with dt then: F = dp/dt (f ...
Regular Note
... The normal force is the support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object Ex. If a book is resting upon a surface, then the surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the book Special case: horizontal normal force when a perso ...
... The normal force is the support force exerted upon an object that is in contact with another stable object Ex. If a book is resting upon a surface, then the surface is exerting an upward force upon the book in order to support the weight of the book Special case: horizontal normal force when a perso ...
Angular Momentum (AIS)
... If both of these wheels accelerate from rest to the same angular velocity ω in the same time t. • The angular acceleration, α, must be the same for both wheels. Also, the total angle turned through must be the same. • But, when moving with angular velocity ω, the particles of wheel B are moving fast ...
... If both of these wheels accelerate from rest to the same angular velocity ω in the same time t. • The angular acceleration, α, must be the same for both wheels. Also, the total angle turned through must be the same. • But, when moving with angular velocity ω, the particles of wheel B are moving fast ...
Special Rotational Dynamics Outline
... equation, r sin θ is the perpendicular distance between a line along the direction of motion and the reference point/axis of rotation. For an object moving in a circular path of radius r, its angular momentum is simply L = mvr. For rigid objects rotating about a fixed axis (with no translation of th ...
... equation, r sin θ is the perpendicular distance between a line along the direction of motion and the reference point/axis of rotation. For an object moving in a circular path of radius r, its angular momentum is simply L = mvr. For rigid objects rotating about a fixed axis (with no translation of th ...
Motion Notes
... This law is sometimes called the Law of Inertia. This means if the net force acting on an object is zero, the object remains at rest, or if the object is already moving, continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. ...
... This law is sometimes called the Law of Inertia. This means if the net force acting on an object is zero, the object remains at rest, or if the object is already moving, continues to move in a straight line with constant speed. ...
2004_11_03ImpulseMomentum
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
... Hailstones Versus Raindrops Unlike rain, hail usually does not come to rest after striking a surface. Instead, the hailstones bounce off the roof of the car. If hail fell instead of rain, would the force on the roof be smaller than, equal to, or greater? ...
Rotational Kinetic Energy
... bodies rotating about one of their symmetry axes. For these cases, the direction of the angular momentum is given by the right hand rule. Curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction that the rigid body is rotating. Your thumb will point in the direction of the angular momentum. The angular ...
... bodies rotating about one of their symmetry axes. For these cases, the direction of the angular momentum is given by the right hand rule. Curl the fingers of your right hand in the direction that the rigid body is rotating. Your thumb will point in the direction of the angular momentum. The angular ...
Plan for March 2010
... motion of an object), the absence of a net force is necessary to maintain a constant speed, and deviance from these rules may be accounted for if we consider friction as a somewhat hidden force. The next topic we will deal with, the role of inertia, is at first glance, on the surface not tremendousl ...
... motion of an object), the absence of a net force is necessary to maintain a constant speed, and deviance from these rules may be accounted for if we consider friction as a somewhat hidden force. The next topic we will deal with, the role of inertia, is at first glance, on the surface not tremendousl ...
F - Madison Public Schools
... ALL objects attract each other with a force of gravitational attraction. Gravitational forces are universal. This force of gravitational attraction is directly dependent upon the masses of both objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance that separates their centers. ...
... ALL objects attract each other with a force of gravitational attraction. Gravitational forces are universal. This force of gravitational attraction is directly dependent upon the masses of both objects and inversely proportional to the square of the distance that separates their centers. ...
Lecture Notes
... 2. The static frictional force can point towards the center of the circle, but the kinetic frictional force opposes the direction of motion, making it very difficult to regain control of the car and continue around the curve. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... 2. The static frictional force can point towards the center of the circle, but the kinetic frictional force opposes the direction of motion, making it very difficult to regain control of the car and continue around the curve. © 2014 Pearson Education, Inc. ...