Lab 5 – Circular Motion and Forces
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...
... Once you have become proficient at whirling the stopper so that the mark on the string stays even with the bottom of the tube, you’re ready to take data. 3. In the data table on the workshe ...
Momentum
... Impulse and Collision • In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time, which results in a change in momentum. The mass either speeds up or slows down. • This means that during a collision an object experiences IMPULSE! ...
... Impulse and Collision • In a collision, an object experiences a force for a specific amount of time, which results in a change in momentum. The mass either speeds up or slows down. • This means that during a collision an object experiences IMPULSE! ...
Getting Ready SPH4U Significant figures 1. Indicate the number of
... 16. A 20-g mass and a 50-g mass are dropped from rest from the same height above the floor. (a) Will the masses land simultaneously? If not, which will land first? Explain your choice. (b) Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on the 50-g mass as it is falling. (c) What is the weigh ...
... 16. A 20-g mass and a 50-g mass are dropped from rest from the same height above the floor. (a) Will the masses land simultaneously? If not, which will land first? Explain your choice. (b) Draw a free-body diagram showing all the forces acting on the 50-g mass as it is falling. (c) What is the weigh ...
Ch 7 Kinetic Energy and Work
... K = Wa + Wg If the initial and final velocities of the object being moved are equal then: Wa = -Wg It does not matter if the Kf and Ki are zero or not, as long as they are equal. You can lift something at constant velocity, or you can pick up a stationary object and then hold it still. ...
... K = Wa + Wg If the initial and final velocities of the object being moved are equal then: Wa = -Wg It does not matter if the Kf and Ki are zero or not, as long as they are equal. You can lift something at constant velocity, or you can pick up a stationary object and then hold it still. ...
Document
... Example: A man of mass m runs around the edge of a horizontal turntable that is mounted on a frictionless vertical axis through its center. The velocity of the man, relative to the disk, is v. The turntable is rotating in the opposite direction with an angular velocity of , relative to the earth. ...
... Example: A man of mass m runs around the edge of a horizontal turntable that is mounted on a frictionless vertical axis through its center. The velocity of the man, relative to the disk, is v. The turntable is rotating in the opposite direction with an angular velocity of , relative to the earth. ...
Question Identical constant forces push two identical objects A
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
... What is the minimum total mechanical energy that the particle can have if you know that it has traveled over the entire region of X shown? ...
force
... Regarding Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The acceleration of an object is always in the same direction as the net force. • In using Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent • Newton’s second law also applies when a net force acts in the direction opposi ...
... Regarding Newton’s 2nd Law of Motion • The acceleration of an object is always in the same direction as the net force. • In using Newton’s second law, it is helpful to realize that the units N/kg and m/s2 are equivalent • Newton’s second law also applies when a net force acts in the direction opposi ...
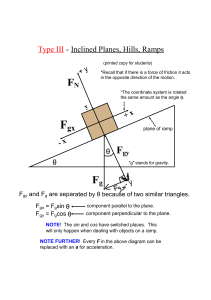
Type III Inclined Planes, Hills, Ramps
... makes a 40o angle with the horizontal. The counterweight has a mass of 35 kg and is suspended with a massless string and a friction less pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction on the plane is 0.23. a) For the acceleration of the object not to exceed 0.42 m/s2 up the ramp, what must be the ...
... makes a 40o angle with the horizontal. The counterweight has a mass of 35 kg and is suspended with a massless string and a friction less pulley. The coefficient of kinetic friction on the plane is 0.23. a) For the acceleration of the object not to exceed 0.42 m/s2 up the ramp, what must be the ...
File
... by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the average velocity of the car for the time interval t=0 to t=10 s. b) Calculate the instantaneous velocity of the car at i) t=0; ii) t=5 s; iii) t=10 s. c) How long after starting from rest is the car again rest? Ans: a)12 m ...
... by x(t ) bt 2 ct 3 , where b=2.40 m/s2 and c=0.120 m/s3. a) Calculate the average velocity of the car for the time interval t=0 to t=10 s. b) Calculate the instantaneous velocity of the car at i) t=0; ii) t=5 s; iii) t=10 s. c) How long after starting from rest is the car again rest? Ans: a)12 m ...
No Slide Title
... A force is called “conservative” if W does not depend on the path but only on the coordinates of the start and finish points. In this case: W1 = W2 = W3 A force is called “non-conservative” if W depends not only on the coordinates of the start and finish points but on the path as well. In this case ...
... A force is called “conservative” if W does not depend on the path but only on the coordinates of the start and finish points. In this case: W1 = W2 = W3 A force is called “non-conservative” if W depends not only on the coordinates of the start and finish points but on the path as well. In this case ...