Chapter 11 - UCF Physics
... defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
... defined as the cross product of the particle’s instantaneous position vector r and its instantaneous linear momentum p ...
(a) (b)
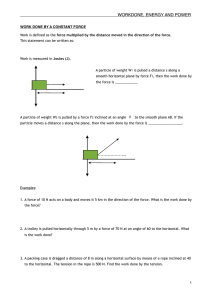
... Chapter 3 Work and Mechanical Energy Work Done by Force. Power Kinetic Energy and the Work. Potential Energy of a System Conservative and Non-conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Changes in Mechanical Energy for Non-conservative Forces Relationship Between Conservative Forces and Po ...
... Chapter 3 Work and Mechanical Energy Work Done by Force. Power Kinetic Energy and the Work. Potential Energy of a System Conservative and Non-conservative Forces Conservation of Mechanical Energy Changes in Mechanical Energy for Non-conservative Forces Relationship Between Conservative Forces and Po ...
4-6 - mrhsluniewskiscience
... vertical direction). ∑Fy = may Or: (down, of course) • SI Units: Newtons (just like any force!). g = 9.8 m/s2 If m = 1 kg, W = 9.8 N ...
... vertical direction). ∑Fy = may Or: (down, of course) • SI Units: Newtons (just like any force!). g = 9.8 m/s2 If m = 1 kg, W = 9.8 N ...
Physics 130 - University of North Dakota
... Hooke’s Law = Simple Harmonic Motion Force always points toward the equilibrium position. ...
... Hooke’s Law = Simple Harmonic Motion Force always points toward the equilibrium position. ...
1. Consider n identical point masses on a straight line connected by
... where ϕi , i = 1, . . . , n, is the displacement from equilibrium of the i th point mass of mass m, and where ϕ̇i = dϕi /dt , find the equations of motion of the system [ 4 marks ] . (b) Keeping the linear mass density constant as the mass m of each point mass tends to zero, in concert with the dist ...
... where ϕi , i = 1, . . . , n, is the displacement from equilibrium of the i th point mass of mass m, and where ϕ̇i = dϕi /dt , find the equations of motion of the system [ 4 marks ] . (b) Keeping the linear mass density constant as the mass m of each point mass tends to zero, in concert with the dist ...
Physics 9 - Sports: Chapter 2
... the left, will it speed up, slow down, or stay at the same speed if the man pushes with a force of... ...
... the left, will it speed up, slow down, or stay at the same speed if the man pushes with a force of... ...
P. LeClair - The University of Alabama
... This impulse force is independent of how much rope is already off of the table, which makes sense: it only involves changing the momentum of an infinitesimal bit of rope at one instant, and does not depend on what the rest of the rope is doing. Since the bit of rope changes its velocity from zero to ...
... This impulse force is independent of how much rope is already off of the table, which makes sense: it only involves changing the momentum of an infinitesimal bit of rope at one instant, and does not depend on what the rest of the rope is doing. Since the bit of rope changes its velocity from zero to ...
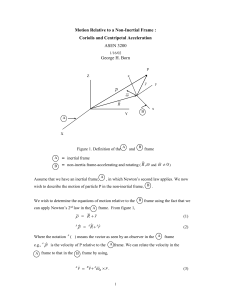
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT applied forces and should not appear on a free body diagram. These apparent forces arise only because we are describing the motion relative to a rotating coordinate frame. In other words, if we cho ...
... opposite to those of the accelerations. They are referred to as “apparent” forces because they ARE NOT applied forces and should not appear on a free body diagram. These apparent forces arise only because we are describing the motion relative to a rotating coordinate frame. In other words, if we cho ...
Mechanics and Properties of Matter Revision Questions Multiple
... Assuming that he was travelling horizontally when he left the edge and that air resistance can be ignored, at what speed did he approach the jump? A B C D E ...
... Assuming that he was travelling horizontally when he left the edge and that air resistance can be ignored, at what speed did he approach the jump? A B C D E ...